This is documentation for the next version of Grafana documentation. For the latest stable release, go to the latest version.
Graphite query editor
Grafana includes a Graphite-specific query editor to help you build queries. The query editor helps you quickly navigate the metric space, add functions, and change function parameters. It supports a variety of Graphite queries, including complex nested queries, through the use of query references.
For general documentation on querying data sources in Grafana, see Query and transform data.
Query editor elements
The query editor consists of the following elements:
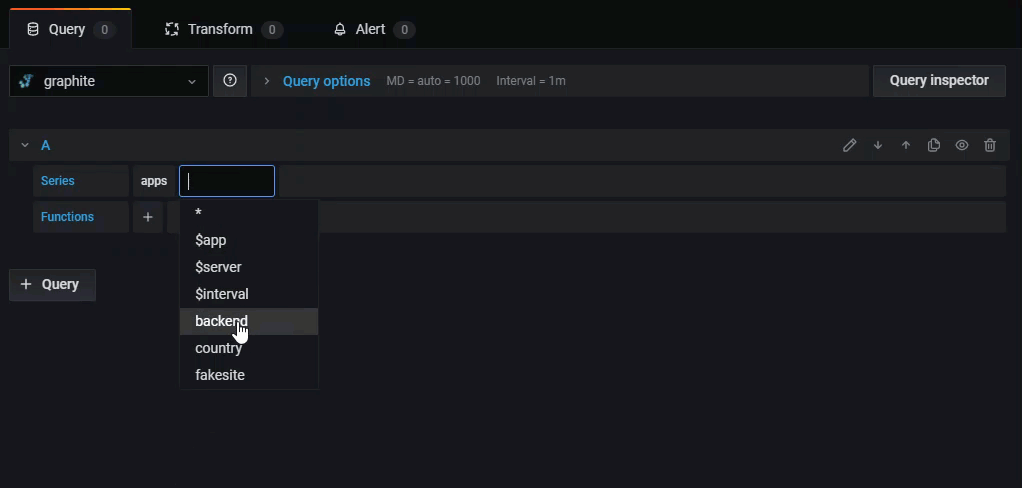
Series - A series in Graphite is a unique time-series dataset, represented by a specific metric name and timestamped values. Click select metric to select a metric from the drop-down.
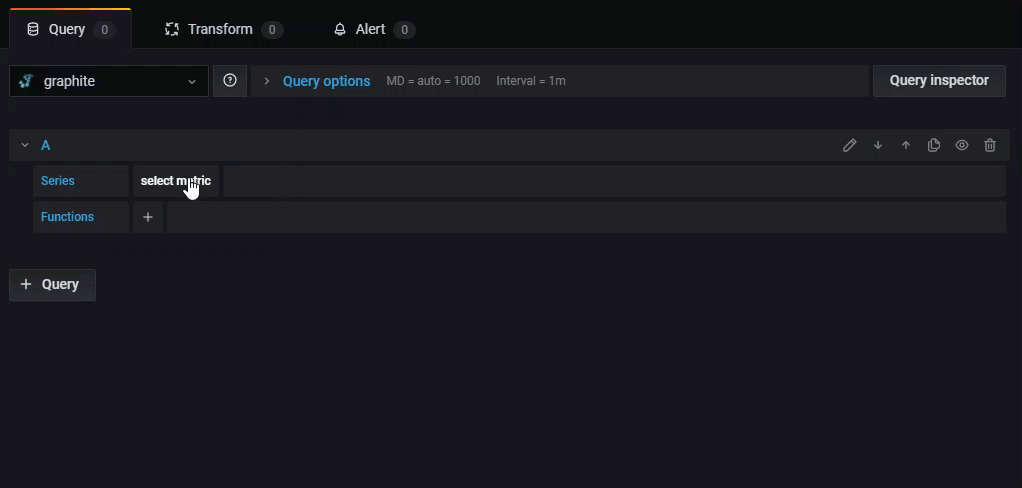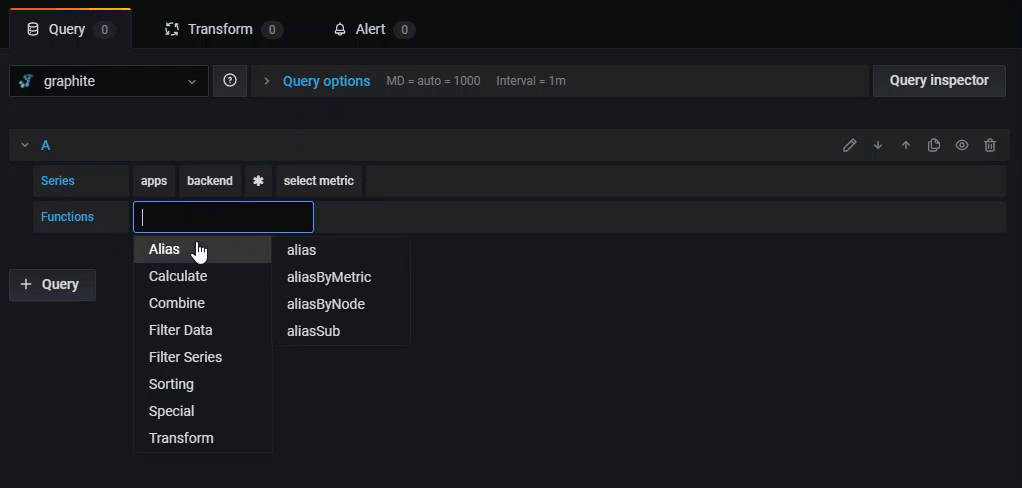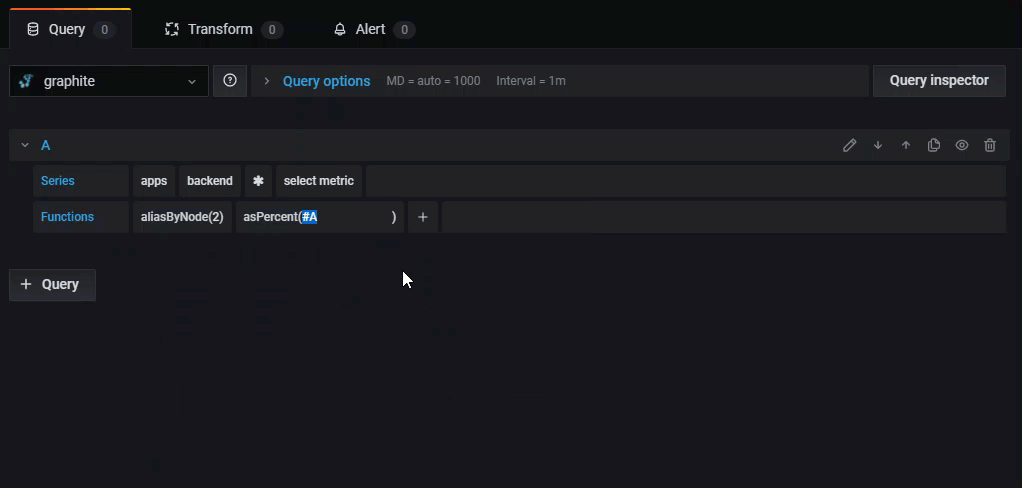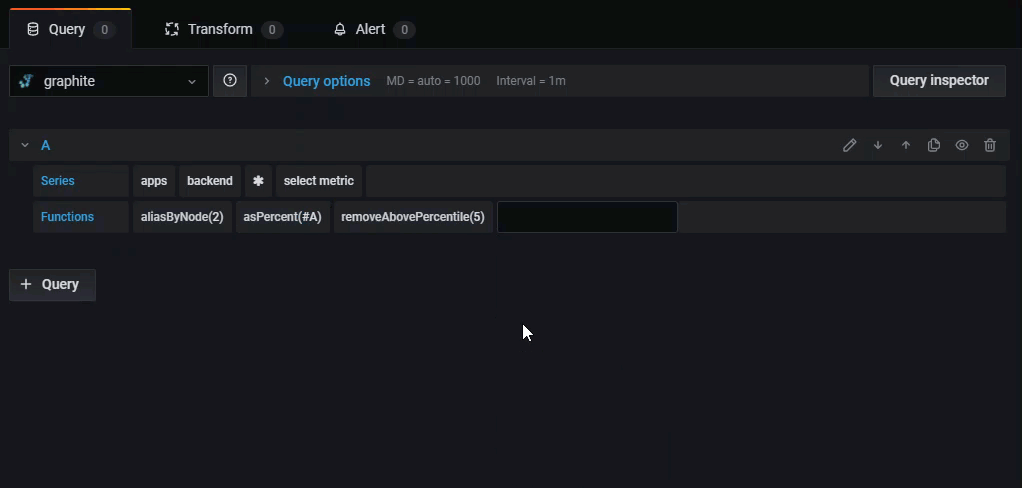
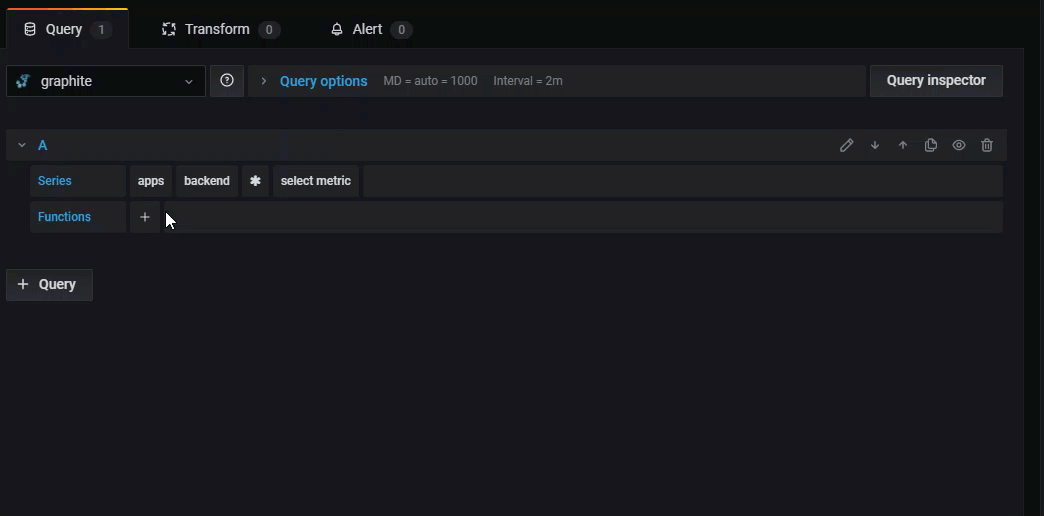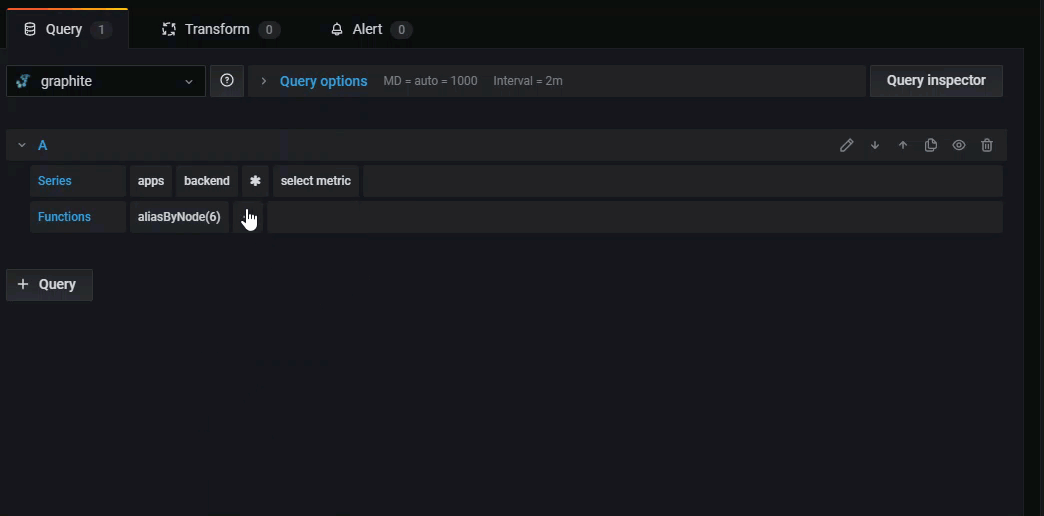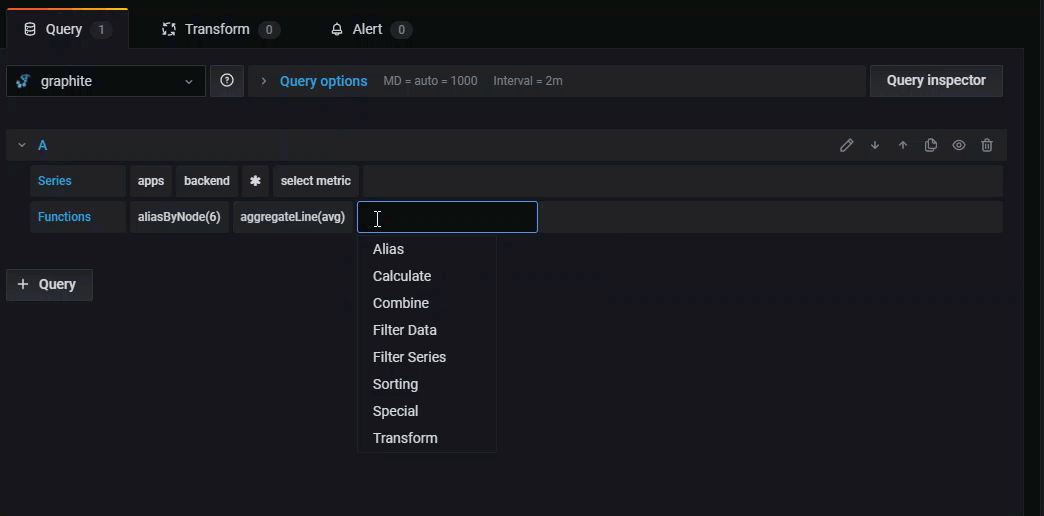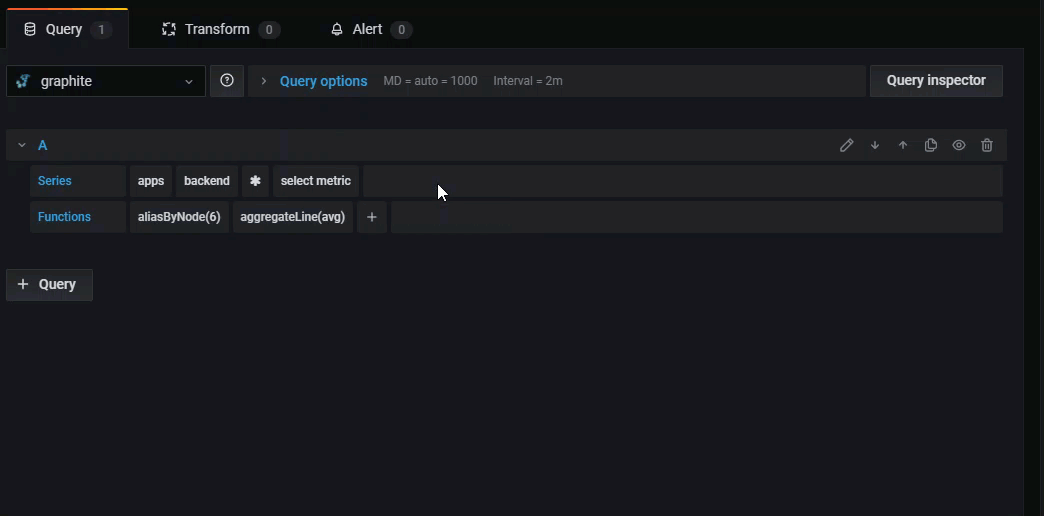
Functions - Graphite uses functions to manipulate data. Click the + sign to view a list of functions in the drop-down. You can create a query with multiple functions.
To view the raw query, click the Pencil icon in the upper right. Click the Pencil icon again to continue adding series and functions.
Choose metrics to query
Click Select metric to browse the available metrics. You can navigate using your mouse or arrow keys. You can also select a wildcard.
Functions
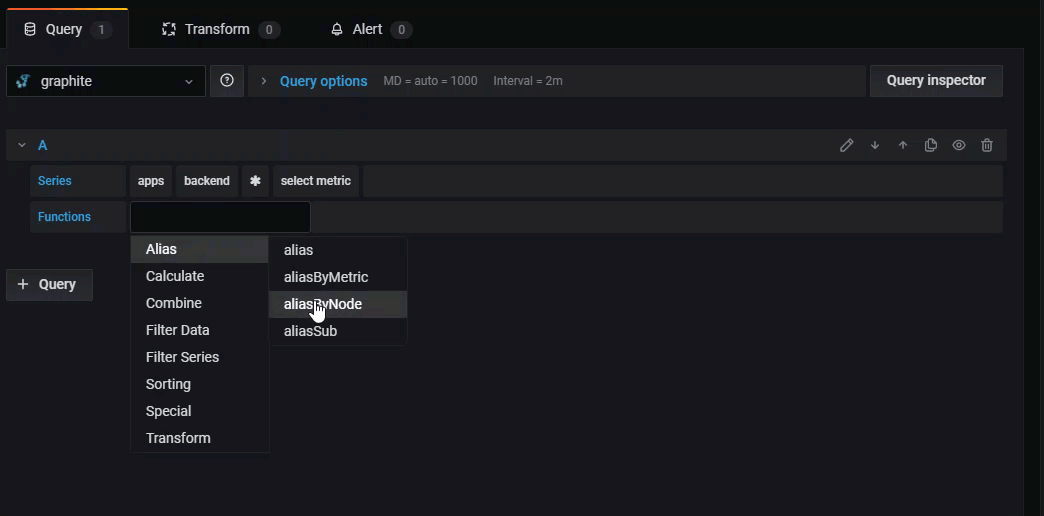
Click the + sign next to Function to add a function from the drop-down. You can also search by typing the first few letters of the function name.
After selecting a function, Grafana adds it to your query and automatically places your cursor in the first parameter field.
To edit a parameter, click it to open an editable text box.
To remove a function simply click on it, then click the X icon that appears above it.
Some functions like aliasByNode support an optional second argument. To add this argument, hover your mouse over the argument and a dialog box appears. To remove the second optional parameter, click on it to delete it.
Refer to Functions in the Graphite documentation for more information.
Warning
Some functions accept a second argument, which can itself be another function that returns a series. If you need to add a second argument that is a function, Grafana recommends using a series reference from a second query instead of embedding the function directly.
Currently, the query editor does not support parsing a second function argument when switching between the query builder and the code editor.
Sort labels
If the same labels appear on multiple graphs, they may be sorted differently and assigned different colors.
To ensure consistent sorting and coloring, use the sortByName() function to order labels alphabetically.
Modify the metric name in my tables or charts
Use alias functions, such as aliasByNode() or aliasSub(), to change metric names on Grafana tables or graphs.
Consolidate data points
Grafana consolidates all Graphite metrics so that Graphite doesn’t return more data points than there are pixels in the graph.
By default, Grafana consolidates data points using the avg function.
To control how Graphite consolidates metrics, use the Graphite consolidateBy() function.
Note
Grafana calculates legend summary values like
max,min, andtotalon the client side, after data has been calculated. Depending on the consolidation function used, only one or two of these values may be accurate at the same time.
Combine time series
To combine time series, click Combine in the Functions list.
Select and explore data with tags
In Graphite, everything is a tag.
When exploring data, previously selected tags filter the remaining result set.
To select data, use the seriesByTag function, which takes tag expressions (=, !=, =~, !=~) to filter timeseries.
The Grafana query builder does this for you automatically when you select a tag.
Note
Regular expression searches can be slow on high-cardinality tags, so try to use other tags to reduce the scope first. To help reduce the results, start by filtering on a particular name or namespace.
Nested queries
Grafana lets you reference one query from another using its query letter, similar to how cell references work in a spreadsheet.
For example, if you add a second query and want to build on the results of query A, you can reference it using #A.
This approach allows you to build compound or nested queries, making your panels more flexible and easier to manage.
Use wildcards to make fewer queries
To display multiple time series on the same graph, use wildcards in your query to return all matching series at once.
For example, to monitor CPU utilization across a variety of metrics, you can use a single query like cpu.percent.*.g to retrieve all matching time series.
This approach is more efficient than writing separate queries for each series, such as cpu.percent.user.g, cpu.percent.system.g, and others, which would result in multiple queries to the data source.
Apply annotations
Annotations overlay rich event information on top of graphs. You can add annotation queries in the dashboard menu’s Annotations view.
Graphite supports two ways to query annotations:
- A regular metric query, using the
Graphite querytextbox. - A Graphite events query, using the
Graphite event tagstextbox with a tag, wildcard, or empty value
Integration with Loki
When you change the data source to Loki in Explore, your Graphite queries are automatically converted to Loki queries. Loki label names and values are extracted based on the mapping information defined in your Graphite data source configuration. Grafana automatically transforms queries that use tags with seriesByTags() without requiring additional setup.