Important: This documentation is about an older version. It's relevant only to the release noted, many of the features and functions have been updated or replaced. Please view the current version.
Geomap
The Geomap panel visualization allows you to view and customize the world map using geospatial data. You can configure various overlay styles and map view settings to easily focus on the important location-based characteristics of the data.
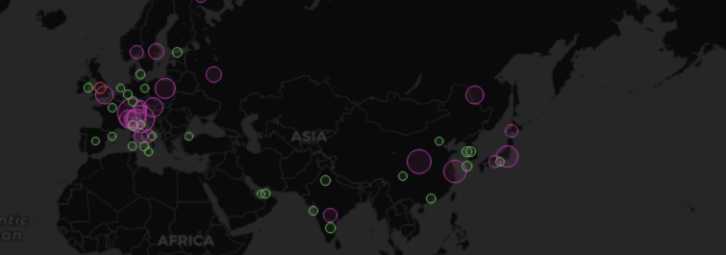
Map View
The map view controls the initial view of the map when the dashboard loads.
Initial View
The initial view configures how the GeoMap panel renders when the panel is first loaded.
- View sets the center for the map when the panel first loads.
- Latitude (available when the View mode is Coordinates)
- Longitude (available when the View mode is Coordinates)
- Zoom sets the initial zoom level for the GeoMap panel, or the initial maximum zoom level in case the Fit data layers view is selected.
Map layers
The Geomap visualization supports showing multiple layers. Each layer determines how you visualize geospatial data on top of the base map.
Types
There are three map layer types to choose from in the Geomap visualization.
- Markers renders a marker at each data point.
- Heatmap visualizes a heatmap of the data.
- GeoJSON renders static data from a GeoJSON file.
There are also four alpha layer types.
- Night / Day (alpha) renders a night / day region.
- Icon at last point (alpha) renders an icon at the last data point.
- Dynamic GeoJSON (alpha) styles a GeoJSON file based on query results.
- Route (alpha) render data points as a route.
Note: Basemap layer types can also be added as layers. You can specify an opacity.
Layer Controls
The layer controls allow you to create layers, change their name, reorder and delete layers.
- Add layer creates an additional, configurable data layer for the Geomap visualization. When you add a layer, you are prompted to select a layer type. You can change the layer type at any point during panel configuration. See the Layer Types section above for details on each layer type.
- The layer controls allow you to rename, delete, and reorder the layers of the panel.
- Edit layer name (pencil icon) renames the layer.
- Trash Bin deletes the layer.
- Reorder (six dots/grab handle) allows you to change the layer order. Data on higher layers will appear above data on lower layers. The panel will update the layer order as you drag and drop to help simplify choosing a layer order.
You can add multiple layers of data to a single Geomap panel in order to create rich, detailed visualizations.
Location
The Geomap panel needs a source of geographical data. This data comes from a database query, and there are four mapping options for your data.
- Auto automatically searches for location data. Use this option when your query is based on one of the following names for data fields.
- geohash: “geohash”
- latitude: “latitude”, “lat”
- longitude: “longitude”, “lng”, “lon”
- lookup: “lookup”
- Coords specifies that your query holds coordinate data. You will get prompted to select numeric data fields for latitude and longitude from your database query.
- Geohash specifies that your query holds geohash data. You will be prompted to select a string data field for the geohash from your database query.
- Lookup specifies that your query holds location name data that needs to be mapped to a value. You will be prompted to select the lookup field from your database query and a gazetteer. The gazetteer is the directory that is used to map your queried data to a geographical point.
Basemap layer
A basemap layer provides the visual foundation for a mapping application. It typically contains data with global coverage. Several base layer options are available each with specific configuration options to style the base map.
Types
There are four basemap layer types to choose from in the Geomap visualization.
- Open Street Map adds a map from a collaborative free geographic world database.
- CARTO adds a layer from CARTO Raster basemaps.
- ArcGIS adds a layer from an ESRI ArcGIS MapServer.
- XYZ adds a map from a generic tile layer.
Default
The default base layer uses the CARTO map. You can define custom default base layers in the .ini configuration file.
Configure the default base layer with provisioning
You can configure the default base map using config files with Grafana’s provisioning system. For more information on all the settings, refer to the provisioning docs page.
Use the JSON configuration option default_baselayer_config to define the default base map. There are currently four base map options to choose from: carto, esri-xyz, osm-standard, xyz. Here are some provisioning examples for each base map option.
- carto loads the CartoDB tile server. You can choose from
auto,dark, andlighttheme for the base map and can be set as shown below. TheshowLabelstag determines whether or not Grafana shows the Country details on top of the map. Here is an example:
geomap_default_baselayer = `{
"type": "carto",
"config": {
"theme": "auto",
"showLabels": true
}
}`- esri-xyz loads the ESRI tile server. There are already multiple server instances implemented to show the various map styles:
world-imagery,world-physical,topo,usa-topo, andocean. Thecustomserver option allows you to configure your own ArcGIS map server. Here are some examples:
geomap_default_baselayer = `{
"type": "esri-xyz",
"config": {
"server": "world-imagery"
}
}`geomap_default_baselayer = `{
"type": "esri-xyz",
"config": {
"server": "custom",
"url": "[tile server url]",
"attribution": "[tile server attribution]"
}
}`- osm-standard loads the OpenStreetMap tile server. There are no additional configurations needed and the
configfields can be left blank. Here is an example:
default_baselayer_config = `{
"type": "osm-standard",
"config": {}
}`- xyz loads a custom tile server defined by the user. Set a valid tile server
url, with {z}/{x}/{y} for this option in order to properly load a default base map. Here is an example:
default_baselayer_config = `{
"type": "xyz",
"config": {
"attribution": "Open street map",
"url": "https://tile.openstreetmap.org/{z}/{x}/{y}.png"
}
}`enable_custom_baselayers allows you to enable or disable custom open source base maps that are already implemented. The default is true.



