Important: This documentation is about an older version. It's relevant only to the release noted, many of the features and functions have been updated or replaced. Please view the current version.
Using InfluxDB in Grafana
Grafana ships with very feature rich data source plugin for InfluxDB. Supporting a feature rich query editor, annotation and templating queries.
Adding the data source
- Open the side menu by clicking the Grafana icon in the top header.
- In the side menu under the
Dashboardslink you should find a link namedData Sources. - Click the
+ Add data sourcebutton in the top header. - Select InfluxDB from the Type dropdown.
NOTE: If you’re not seeing the
Data Sourceslink in your side menu it means that your current user does not have theAdminrole for the current organization.
Proxy vs Direct access
Proxy access means that the Grafana backend will proxy all requests from the browser. So requests to InfluxDB will be channeled through
grafana-server. This means that the URL you specify needs to be accessible from the server you are running Grafana on. Proxy access
mode is also more secure as the username & password will never reach the browser.
Min time interval
A lower limit for the auto group by time interval. Recommended to be set to write frequency, for example 1m if your data is written every minute.
This option can also be overridden/configured in a dashboard panel under data source options. It’s important to note that this value needs to be formatted as a
number followed by a valid time identifier, e.g. 1m (1 minute) or 30s (30 seconds). The following time identifiers are supported:
Query Editor
You find the InfluxDB editor in the metrics tab in Graph or Singlestat panel’s edit mode. You enter edit mode by clicking the panel title, then edit. The editor allows you to select metrics and tags.
Filter data (WHERE)
To add a tag filter click the plus icon to the right of the WHERE condition. You can remove tag filters by clicking on
the tag key and select --remove tag filter--.
Regex matching
You can type in regex patterns for metric names or tag filter values, be sure to wrap the regex pattern in forward slashes (/). Grafana
will automatically adjust the filter tag condition to use the InfluxDB regex match condition operator (=~).
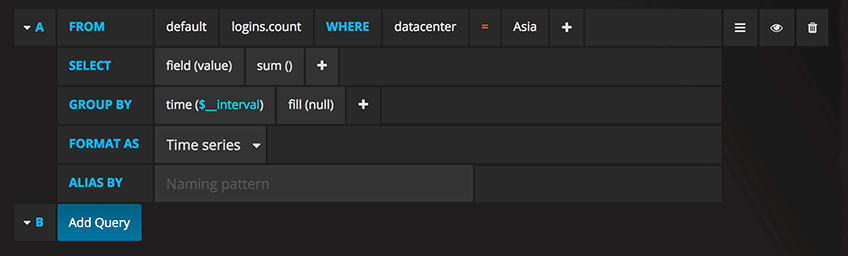
Field & Aggregation functions
In the SELECT row you can specify what fields and functions you want to use. If you have a
group by time you need an aggregation function. Some functions like derivative require an aggregation function. The editor tries simplify and unify this part of the query. For example:![]()
The above will generate the following InfluxDB SELECT clause:
SELECT derivative(mean("value"), 10s) /10 AS "REQ/s" FROM ....Select multiple fields
Use the plus button and select Field > field to add another SELECT clause. You can also
specify an asterix * to select all fields.
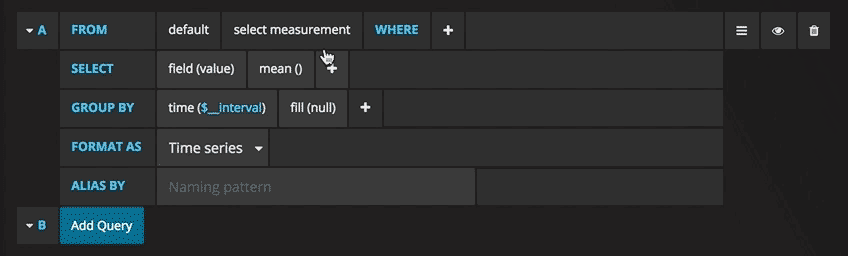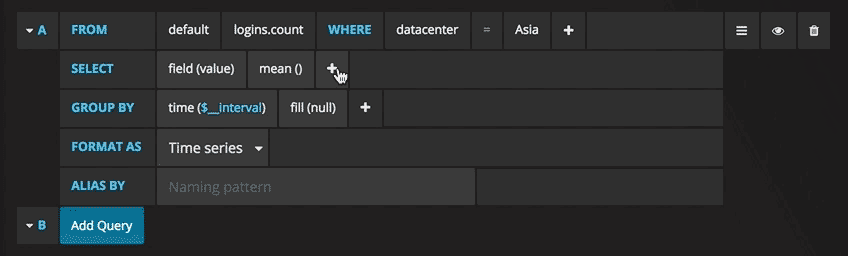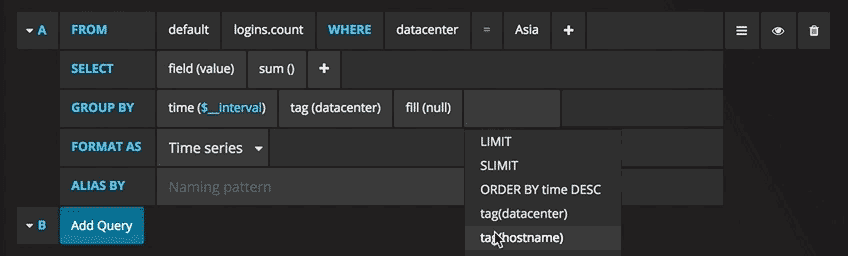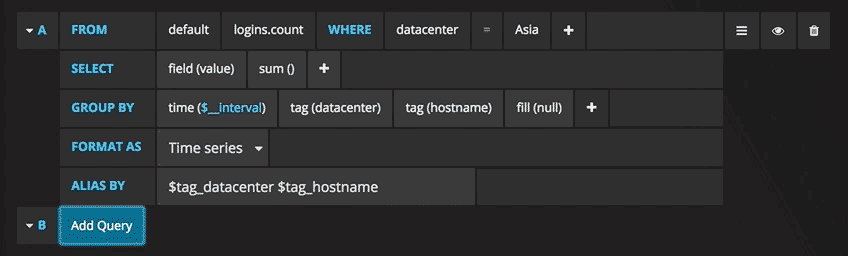
Group By
To group by a tag click the plus icon at the end of the GROUP BY row. Pick a tag from the dropdown that appears.
You can remove the group by by clicking on the tag and then click on the x icon.
Text Editor Mode (RAW)
You can switch to raw query mode by clicking hamburger icon and then Switch editor mode.
If you use Raw Query be sure your query at minimum have
WHERE $timeFilterAlso please always have a group by time and an aggregation function, otherwise InfluxDB can easily return hundreds of thousands of data points that will hang the browser.
Alias patterns
- $m = replaced with measurement name
- $measurement = replaced with measurement name
- $col = replaced with column name
- $tag_exampletag = replaced with the value of the
exampletagtag. The syntax is$tag_yourTagName(must start with$tag_). To use your tag as an alias in the ALIAS BY field then the tag must be used to group by in the query. - You can also use [[tag_hostname]] pattern replacement syntax. For example, in the ALIAS BY field using this text
Host: [[tag_hostname]]would substitute in thehostnametag value for each legend value and an example legend value would be:Host: server1.
Table query / raw data

You can remove the group by time by clicking on the time part and then the x icon. You can
change the option Format As to Table if you want to show raw data in the Table panel.
Templating
Instead of hard-coding things like server, application and sensor name in you metric queries you can use variables in their place. Variables are shown as dropdown select boxes at the top of the dashboard. These dropdowns makes it easy to change the data being displayed in your dashboard.
Checkout the Templating documentation for an introduction to the templating feature and the different types of template variables.
Query variable
If you add a template variable of the type Query you can write a InfluxDB exploration (meta data) query. These queries can
return things like measurement names, key names or key values.
For example you can have a variable that contains all values for tag hostname if you specify a query like this in the templating variable Query setting.
SHOW TAG VALUES WITH KEY = "hostname"You can also create nested variables. For example if you had another variable, for example region. Then you could have
the hosts variable only show hosts from the current selected region with a query like this:
SHOW TAG VALUES WITH KEY = "hostname" WHERE region =~ /$region/You can fetch key names for a given measurement.
SHOW TAG KEYS [FROM <measurement_name>]If you have a variable with key names you can use this variable in a group by clause. This will allow you to change group by using the variable dropdown at the top of the dashboard.
Using variables in queries
There are two syntaxes:
$<varname> Example:
SELECT mean("value") FROM "logins" WHERE "hostname" =~ /^$host$/ AND $timeFilter GROUP BY time($__interval), "hostname"[[varname]] Example:
SELECT mean("value") FROM "logins" WHERE "hostname" =~ /^[[host]]$/ AND $timeFilter GROUP BY time($__interval), "hostname"Why two ways? The first syntax is easier to read and write but does not allow you to use a variable in the middle of a word. When the Multi-value or Include all value
options are enabled, Grafana converts the labels from plain text to a regex compatible string. Which means you have to use =~ instead of =.
Example Dashboard: InfluxDB Templated Dashboard
Ad hoc filters variable
InfluxDB supports the special Ad hoc filters variable type. This variable allows you to specify any number of key/value filters on the fly. These filters will automatically
be applied to all your InfluxDB queries.
Annotations
Annotations allows you to overlay rich event information on top of graphs. You add annotation queries via the Dashboard menu / Annotations view.
An example query:
SELECT title, description from events WHERE $timeFilter order ascFor InfluxDB you need to enter a query like in the above example. You need to have the where $timeFilter
part. If you only select one column you will not need to enter anything in the column mapping fields. The
Tags field can be a comma separated string.
Configure datasource with provisioning
It’s now possible to configure datasources using config files with Grafanas provisioning system. You can read more about how it works and all the settings you can set for datasources on the provisioning docs page
Here are some provisioning examples for this datasource.
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: InfluxDB
type: influxdb
access: proxy
database: site
user: grafana
password: grafana
url: http://localhost:8086