Grafana Cloud in 2024: Year in review
Throughout 2024, we made a ton of updates to Grafana Cloud, our fully managed, cloud-hosted observability platform powered by the Grafana LGTM (Loki for logs,Grafana for visualization,Tempo for traces,Mimir for metrics) Stack. And, looking back, most of those updates were made with the same three goals in mind: to make Grafana Cloud more efficient, more intelligent, and easier to use, including for those just starting out on their observability journey.
“Grafana Cloud and the LGTM Stack have really appealed to the early adopters — to the kinds of people who want to get their hands dirty, learn the query languages, and build their own dashboards,” said Tom Wilkie, CTO of Grafana Labs, at ObservabilityCON 2024. “We grew with the rise of observability and with all of these practitioners learning how to build things and get value out of these tools. But what we found over the past few years is that we’ve been appealing more to a broader, more mainstream audience.”
In this post, we recap some of the big updates we’ve made to Grafana Cloud this year, and how they can help advance, or kickstart, your team’s observability strategy.
Extending adaptive telemetry to logs — and beyond
In 2023, we introduced Adaptive Metrics, a Grafana Cloud feature that enables teams to aggregate unused and partially used metrics into lower cardinality versions of themselves to reduce observability costs.
Since then, Adaptive Metrics has delivered a 35% reduction in metrics costs, on average, for more than 1,200 organizations — a figure that speaks to how impactful the feature can be, in terms of benefitting an organization’s bottom line.
Building on that momentum this year, we introduced Adaptive Logs. Now generally available in all Grafana Cloud tiers, Adaptive Logs identifies commonly ingested log patterns and creates a set of customized sampling recommendations based on how frequently those patterns are queried. The end result? You can reduce the volume of unnecessary logs to lower your observability costs.

Through our acquisition of TailCtrl, an early-stage company specializing in adaptive trace sampling, we’ve also started to accelerate our development of Adaptive Traces. The move represents our continued efforts to extend the adaptive telemetry concept across the LGTM Stack, so you can more easily and cost-effectively analyze observability data at scale.
Simplified data analysis with the Explore apps suite
Update: As of Feb. 20, 2025, the Explore apps (Explore Metrics, Explore Logs, Explore Traces, Explore Profiles) are now the Drilldown apps (Metrics Drilldown, Logs Drilldown, Traces Drilldown, Profiles Drilldown).
In September, we announced public previews of Explore Traces and Explore Profiles, which joined Explore Metrics and Explore Logs — now generally available — to create a full suite of Explore apps for Grafana and Grafana Cloud.
These apps streamline data exploration and analysis through intuitive, point-and-click UIs, enabling you to drill down and visualize data without having to know query languages like PromQL, LogQL, or TraceQL. Together, the Explore apps ensure that everyone — from beginners to experts — can get value out of their telemetry data and realize the full potential of observability.
With the release of our Explore apps for all four pillars of observability, users can now choose from three different options in Grafana Cloud to help them get insights from telemetry stored in Prometheus (or Mimir), Loki, Tempo, or Pyroscope:
- Code: Use query languages like PromQL, LogQL, and TraceQL.
- Low code: Use builder mode, which provides more of a visual programming experience.
- No code: Use the Explore apps suite to access screens that are already pre-populated with graphs.

Enhancements to Synthetic Monitoring and Application Observability
Synthetic Monitoring
In 2024, we rolled out a revamped version of Grafana Cloud Synthetic Monitoring to help you simulate even the most complex transactions and ensure the best possible end-user experience.

Powered by Grafana k6, Synthetic Monitoring now includes two new check types — multiHTTP and k6 scripted checks — to support more complex testing scenarios. We also introduced k6 browser checks, now in public preview, which let you collect frontend Web Vitals metrics, capture custom performance metrics, and perform user actions like clicking buttons or completing forms.
Application Observability
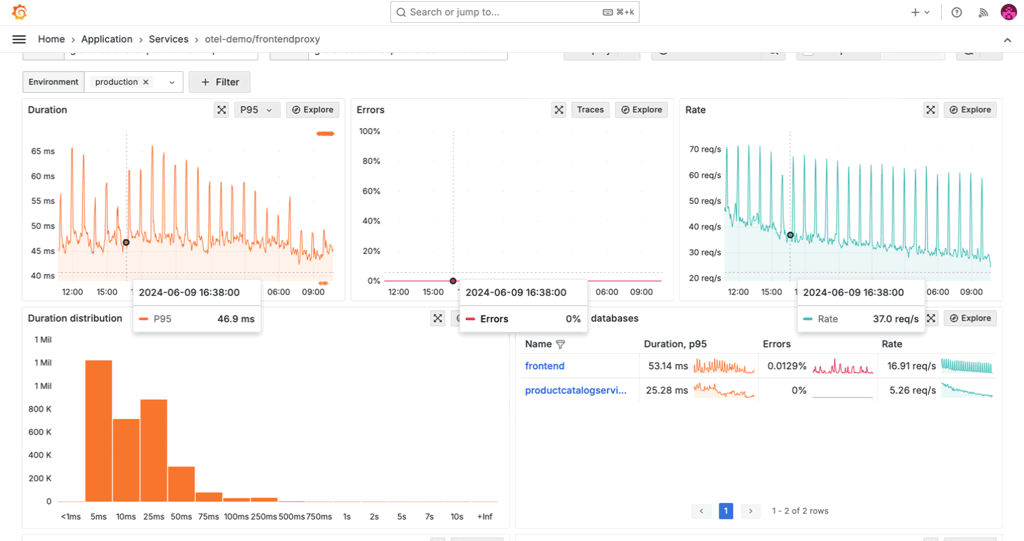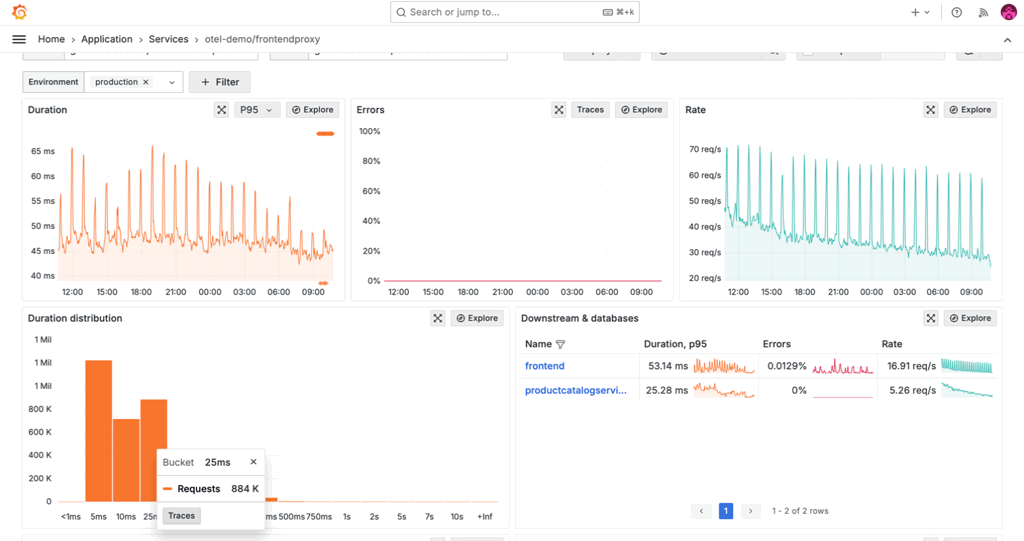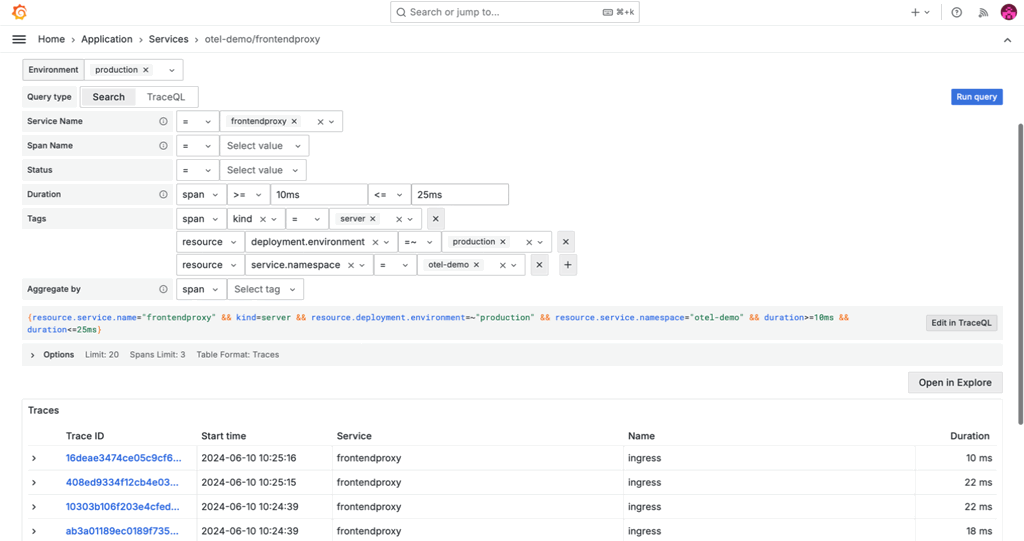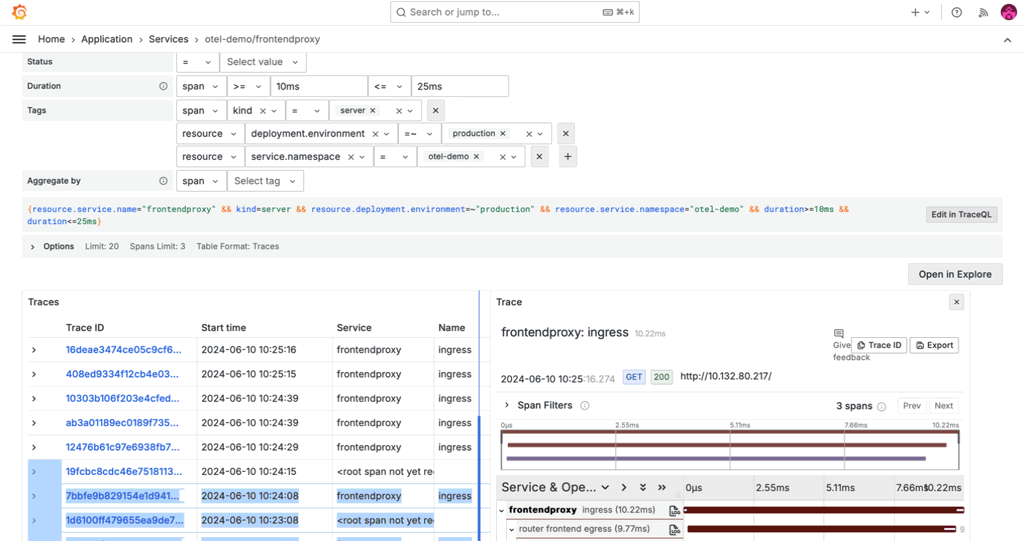
We also continued to evolve Grafana Cloud Application Observability, our opinionated, out-of-the-box solution designed to improve the reliability of modern applications. Featuring native support for both OpenTelemetry and Prometheus, Application Observability helps developers and SREs seamlessly unify application and infrastructure insights for faster root cause analysis.
Some of the key additions we made to Application Observability this year include:
- Time frame comparison to analyze service performance over time
- Automatic baseline to compare RED metrics for services and operations against historic upper and lower thresholds.
- The filter-by feature to manage which data is visible based on attribute values
- In-context navigation for faster root cause analysis
You can learn more in our technical docs for Synthetic Monitoring and Application Observability.
Control collectors at scale with Fleet Management
Managing observability workloads can quickly overwhelm even the most experienced admins — especially if they’re responsible for tracking hundreds of collectors across different environments. That’s why, last month, we announced Fleet Management in Grafana Cloud, a powerful new way to monitor and manage observability collectors efficiently, regardless of scale.
Fleet Management, in public preview, helps you manage hundreds or thousands of collectors efficiently. It enables you to roll out configurations remotely, monitor collector health across all deployments, and control cost simply by activating or deactivating pipelines as needed.

Currently, Fleet Management supports Grafana Alloy, our open source distribution of the OpenTelemetry Collector, fully compatible with the OTLP protocol and featuring native pipelines for OTel and Prometheus. As leading contributors to the Open Agent Management Protocol (OpAMP) project, we hope to extend support to traditional OTel Collectors in the future.
You can learn more about Fleet Management in our technical docs.
AI/ML advancements
AI/ML continued to reshape the observability space throughout 2024 — and Grafana Cloud was no exception. In case you missed them, here are some of the major AI/ML announcements we made this year.
Contextualized root cause analysis workflows
At ObservabilityCON 2024, we introduced a suite of unified workflows connecting Asserts and Grafana Cloud solutions that helps automate the correlation of anomalies across infrastructure and application layers to provide a more cohesive troubleshooting experience. The workflows cover a wide range of monitoring needs, including application performance, Kubernetes workload monitoring, infrastructure monitoring, real user monitoring, and simplified SLO management. These AI-driven inferences enable even junior engineers to more effectively understand and diagnose issues in complex systems.

Observability for your generative AI apps
While generative AI has emerged as a powerful force for synthesizing new content, monitoring these complex AI systems can be a challenge. This is why we rolled out our AI Observability solution, a Grafana Cloud integration designed to provide insights into gen AI use cases.
AI Observability leverages OpenLIT, the open source SDK that has been engineered to monitor, diagnose, and optimize generative AI systems. This means you can now observe every nuance of your AI models, from performance bottlenecks to anomaly detection, all within the unified Grafana interface. Key features include performance monitoring, cost optimization, end-to-end tracing, and prompt and response tracking.

More flexible and powerful diagnostics with Sift
Sift is a machine-learning-powered diagnostic feature in Grafana Cloud that automates routine parts of incident investigation. Since we launched Sift into public preview last year, we’ve been working to expand its capabilities, including:
- A new homepage and Configuration tab that allows you to customize the way Sift runs
- An HTTP Error Series check that helps detect an increase in HTTP errors within the investigation’s cluster and namespace
- An investigation timeline to help correlate events.
Infrastructure observability improvements
Kubernetes Monitoring
We made a series of improvements to Kubernetes Monitoring in Grafana Cloud in 2024, including new visualizations to help you monitor costs and new tools to streamline troubleshooting.
For example, we introduced the Cost Overview tab, where you can quickly see a 90-day view of your total compute costs, average cost per pod, and average pod count.
For faster and easier troubleshooting in Kubernetes Monitoring, it’s also now possible to:
- Find deleted objects, such as clusters, nodes, pods, containers, workloads, and namespaces.
- Zoom into a specific area on a graph to narrow a time range.
- Jump directly to the list of clusters, nodes, workloads, and alerts from the home page.
You can check out our Kubernetes Monitoring docs to learn more.
Multi-cloud monitoring
Managing multi-cloud environments often means juggling different monitoring tools for each provider, leading to increased complexity. Cloud Provider Observability — an application for monitoring AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud services, all in Grafana Cloud — helps address this very challenge. Now generally available, Cloud Provider Observability provides comprehensive insights across cloud services with a single, out-of-the-box solution that is easy to set up and scale. Learn more in our documentation.

But wait… there’s more!
Here are a couple other Grafana Cloud features and milestones we wanted to share before we wrap up 2024.
ML-enhanced guidance in Grafana SLO
Grafana SLO makes it easy to create, manage, and scale service level objectives, SLO dashboards, and error budget alerts in Grafana Cloud.
That said, we’ve noticed teams struggle to set their initial Service Level Indicators (SLI) target percentage, or modify an existing target percentage on their SLOs. If you assume, for example, that you want to create an SLO to ensure 99.5% of HTTP requests return successfully in under 500 ms, how do you know that 99.5% is a realistic target for your service?
To solve for this, we’ve made a major update to our guided wizard in Grafana SLO: the use of machine learning to predict the risk of hitting an SLI target percentage.
After defining an SLO, the target selection page now offers ML-based guidance to select a target percentage that you’ll have confidence in your ability to meet. We query 90 days of history from the metrics used in the SLO definition, and run simulations to predict the likelihood of meeting a given target. You can also slide the target percentage to see an updated prediction of the likelihood of meeting that target.
To learn more about Grafana SLO, please refer to our technical docs.
New Enterprise data sources to tap into
Throughout the year, we’ve been steadily building out our line-up of Enterprise data sources for Grafana Cloud. Today, we offer more than 30 Enterprise data sources that help you query and visualize data from external systems using your existing Grafana Cloud dashboards. Atlassian Statuspage, PagerDuty, and Catchpoint are just a few of the many new data sources we rolled out this year.
We also introduced a new public roadmap for data source plugins being built by Grafana, our partners, and our community. You can use it to track our plans for plugin development, as well as request new ones.
Grafana Cloud is the easiest way to get started with metrics, logs, traces, and dashboards. We have a generous free forever tier and plans for every use case.Sign up for free now!


