Important: This documentation is about an older version. It's relevant only to the release noted, many of the features and functions have been updated or replaced. Please view the current version.
Using MySQL in Grafana
Only available in Grafana v4.3+.
Grafana ships with a built-in MySQL data source plugin that allow you to query any visualize data from a MySQL compatible database.
Adding the data source
- Open the side menu by clicking the Grafana icon in the top header.
- In the side menu under the
Dashboardslink you should find a link namedData Sources. - Click the
+ Add data sourcebutton in the top header. - Select MySQL from the Type dropdown.
Database User Permissions (Important!)
The database user you specify when you add the data source should only be granted SELECT permissions on
the specified database & tables you want to query. Grafana does not validate that the query is safe. The query
could include any SQL statement. For example, statements like USE otherdb; and DROP TABLE user; would be
executed. To protect against this we Highly recommmend you create a specific mysql user with restricted permissions.
Example:
CREATE USER 'grafanaReader' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
GRANT SELECT ON mydatabase.mytable TO 'grafanaReader';You can use wildcards (*) in place of database or table if you want to grant access to more databases and tables.
Macros
To simplify syntax and to allow for dynamic parts, like date range filters, the query can contain macros.
We plan to add many more macros. If you have suggestions for what macros you would like to see, please open an issue in our GitHub repo.
The query editor has a link named Generated SQL that show up after a query as been executed, while in panel edit mode. Click on it and it will expand and show the raw interpolated SQL string that was executed.
Table queries
If the Format as query option is set to Table then you can basically do any type of SQL query. The table panel will automatically show the results of whatever columns & rows your query returns.
Query editor with example query:
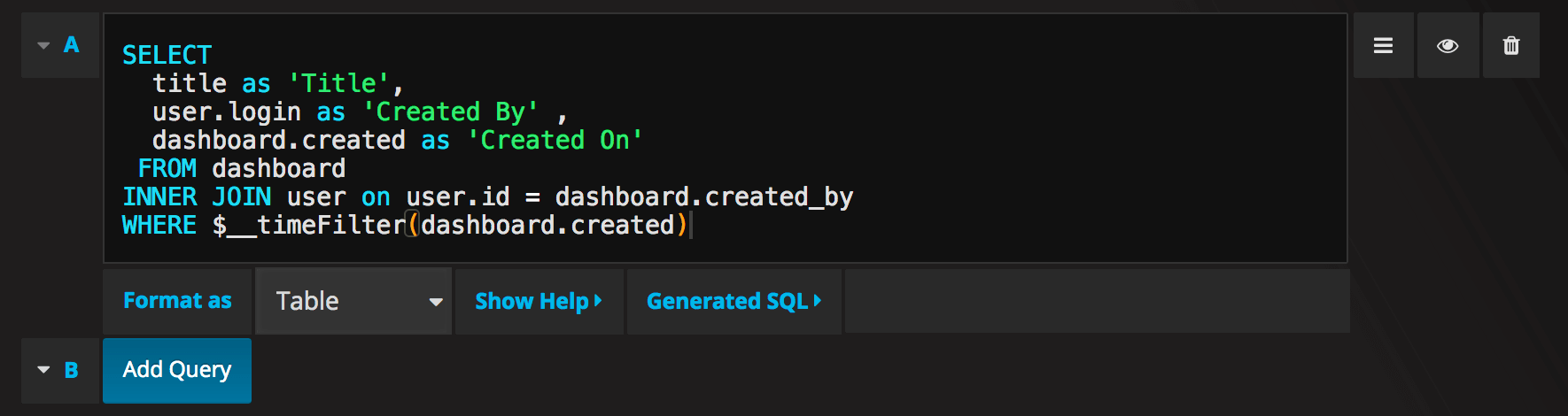
The query:
SELECT
title as 'Title',
user.login as 'Created By' ,
dashboard.created as 'Created On'
FROM dashboard
INNER JOIN user on user.id = dashboard.created_by
WHERE $__timeFilter(dashboard.created)You can control the name of the Table panel columns by using regular as SQL column selection syntax.
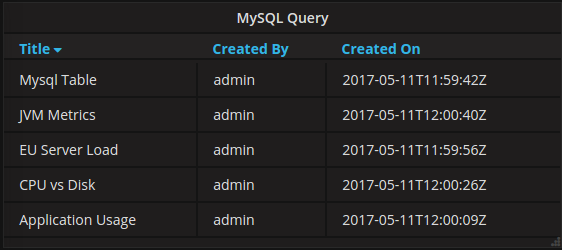
The resulting table panel:
Time series queries
If you set Format as to Time series, for use in Graph panel for example, then there are some requirements for
what your query returns.
- Must be a column named
time_secrepresenting a unix epoch in seconds. - Must be a column named
valuerepresenting the time series value. - Must be a column named
metricrepresenting the time series name.
Example:
SELECT
min(UNIX_TIMESTAMP(time_date_time)) as time_sec,
max(value_double) as value,
metric1 as metric
FROM test_data
WHERE $__timeFilter(time_date_time)
GROUP BY metric1, UNIX_TIMESTAMP(time_date_time) DIV 300
ORDER BY time_sec ascCurrently, there is no support for a dynamic group by time based on time range & panel width. This is something we plan to add.
Templating
This feature is currently available in the nightly builds and will be included in the 5.0.0 release.
Instead of hard-coding things like server, application and sensor name in you metric queries you can use variables in their place. Variables are shown as dropdown select boxes at the top of the dashboard. These dropdowns makes it easy to change the data being displayed in your dashboard.
Checkout the Templating documentation for an introduction to the templating feature and the different types of template variables.
Query Variable
If you add a template variable of the type Query, you can write a MySQL query that can
return things like measurement names, key names or key values that are shown as a dropdown select box.
For example, you can have a variable that contains all values for the hostname column in a table if you specify a query like this in the templating variable Query setting.
SELECT hostname FROM my_hostA query can returns multiple columns and Grafana will automatically create a list from them. For example, the query below will return a list with values from hostname and hostname2.
SELECT my_host.hostname, my_other_host.hostname2 FROM my_host JOIN my_other_host ON my_host.city = my_other_host.cityAnother option is a query that can create a key/value variable. The query should return two columns that are named __text and __value. The __text column value should be unique (if it is not unique then the first value is used). The options in the dropdown will have a text and value that allows you to have a friendly name as text and an id as the value. An example query with hostname as the text and id as the value:
SELECT hostname AS __text, id AS __value FROM my_hostYou can also create nested variables. For example if you had another variable named region. Then you could have
the hosts variable only show hosts from the current selected region with a query like this (if region is a multi-value variable then use the IN comparison operator rather than = to match against multiple values):
SELECT hostname FROM my_host WHERE region IN($region)Using Variables in Queries
Template variables are quoted automatically so if it is a string value do not wrap them in quotes in where clauses. If the variable is a multi-value variable then use the IN comparison operator rather than = to match against multiple values.
There are two syntaxes:
$<varname> Example with a template variable named hostname:
SELECT
UNIX_TIMESTAMP(atimestamp) as time_sec,
aint as value,
avarchar as metric
FROM my_table
WHERE $__timeFilter(atimestamp) and hostname in($hostname)
ORDER BY atimestamp ASC[[varname]] Example with a template variable named hostname:
SELECT
UNIX_TIMESTAMP(atimestamp) as time_sec,
aint as value,
avarchar as metric
FROM my_table
WHERE $__timeFilter(atimestamp) and hostname in([[hostname]])
ORDER BY atimestamp ASCAlerting
Time series queries should work in alerting conditions. Table formatted queries is not yet supported in alert rule conditions.



