
How to use AI to analyze and visualize CAN data with Grafana Assistant
Note: A version of this post originally appeared on the CSS Electronics blog.
Martin Falch, co-owner and head of sales and marketing at CSS Electronics, is an expert on CAN bus data. Martin works closely with end users, typically OEM engineers, across diverse industries, including automotive, maritime, and industrial. He is passionate about data visualization and AI—and he's been working extensively with Grafana Assistant.
At CSS Electronics, we build pro specs and simple-to-use CAN bus data loggers including optional WiFi/LTE/GPS. In short, CAN bus is a protocol used for communicating sensor data within vehicles and machinery, including trucks, cars, ships, and robots.
Our end users include engineers at automotive and industrial manufacturers (OEMs) who need to monitor assets in the field for R&D, diagnostics, or predictive maintenance. A large share of our users also visualize their data via Grafana dashboards using Amazon Athena or Google BigQuery data sources (see our previous blog post for details).
In this blog, we show how Grafana Assistant can be used to easily unleash the power of AI for data analysis and dashboard visualization—directly within Grafana!
Why use Grafana Assistant for CAN data analyses?
Our users face a challenge: They can collect tons of CAN/LIN data using the CANedge, but they have to then explore or visualize data across several devices, thousands of log files, and months (or even years) of data.
Most of our users are engineers, but they're not data scientists. And even if they are, statistical data analysis/visualization can be extremely time consuming.
Why not use ChatGPT?
One solution to this challenge is to use ChatGPT to help analyze the data, which we wrote about in a 2023 article. However, ChatGPT has some practical limitations:
- Limited to manually uploading small files (e.g. 100 MB CSV)
- Analysis results are not easy to share
- Outputs are "static" (e.g., Python-generated plots)
Key features of Grafana Assistant

In practice, our end users typically upload gigabytes (or terabytes) of data to their own AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure cloud servers using our devices. Here, the data is auto-processed into Parquet data lakes, which can be queried via Grafana’s Athena/BigQuery data sources. In other words, the complete data lake is easily accessible within Grafana.
With the new assistant, Grafana Cloud now enables seamless LLM access to existing data sources that are already in place. This introduces multiple powerful features:
- Zero set up: If you have already deployed a Grafana integration, you can start prompting your data immediately—no set up required.
- Analyze terabytes of data: Unlike ChatGPT, you don't have to limit your analysis to 100 MB of data. The assistant can query your entire data lake out-the-box.
- Data exploration: Simply chat your way to powerful data insights and through complex diagnostic analyses—no query language or coding knowledge required.
- Dashboard creation: The assistant can create fully customized Grafana dashboards in seconds based on high level prompts, drastically reducing time spent.
- Retain and share insights: Any data insights can be easily summarized into Grafana dashboards, enabling you to navigate the data temporally and share it with your team.
It's basically Cursor/Windsurf for your dashboards and data lake.
How to start analyzing CAN data with Grafana Assistant
If you have already connected your data source in Grafana Cloud, no further set up is necessary.
To start chatting with the assistant, you can open the chat window via the left-menu Assistant tab. Alternatively, you can open the chat panel within a dashboard via the sparkle icon in the upper right corner.
However, to get the best experience, we recommend following these steps:
- Use a dashboard template: At CSS we provide various dashboard templates customized for our end users, which include relevant Grafana variable dropdowns. Using templates as the basis for LLM-based dashboard development is highly recommended as it allows dashboard users to subsequently interact with the generated dashboards (e.g. switching between different devices)
- Select data source as context: Make sure to select the relevant data source in the Grafana Assistant chat window to explicitly tell it what data to work with.
- Use a system prompt: In our documentation we provide a "system prompt" that our users can add as a "rule" within the Grafana Assistant settings. This provides context about the data lake structure, query syntax and more—and significantly improves the results.
Example use cases
To showcase how Grafana Assistant can help with data analyses, we'll use our public data pack, which consists of 1GB of data from a Kia EV6 electric vehicle. Below we highlight example use cases for the LLM:
Example 1: See what data is available
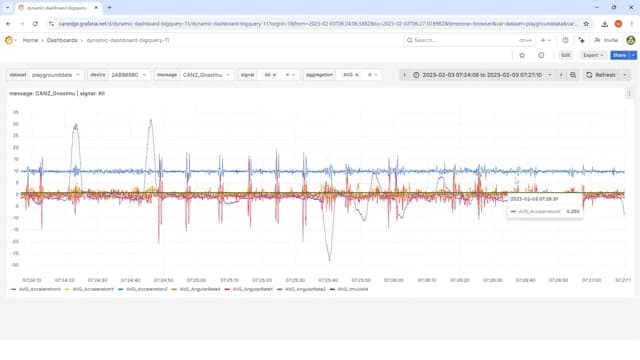
First, we use the LLM to get an overview of our data lake.
This is a useful starting point for exploring a CAN bus data lake as you do not necessarily have a clear overview of what devices, CAN messages, and CAN signals are available. Further, constructing the SQL queries to extract this information is quite complex.
Prompt:
My data source contains data from a Kia EV6 electric car, recorded with a CANedge CAN bus data logger with device ID 2A896980. The data includes battery data from the EV and GPS/IMU data from a sensor module. I want to know the following:
1: What tables and columns are available for this device?
2: What time period does the data span?
Grafana Assistant starts analyzing the data via multiple queries, summarizing the results in a tabular form, and in the chat. Notice how the LLM iterates through multiple queries to understand the data structure. You can of course inspect what queries are used to generate each result, ensuring full transparency. The summary provides us with a good starting point for further investigation.
Example 2: Explore data ad hoc
In many cases you'll want to explore the data directly in the chat window prior to creating actual panels.
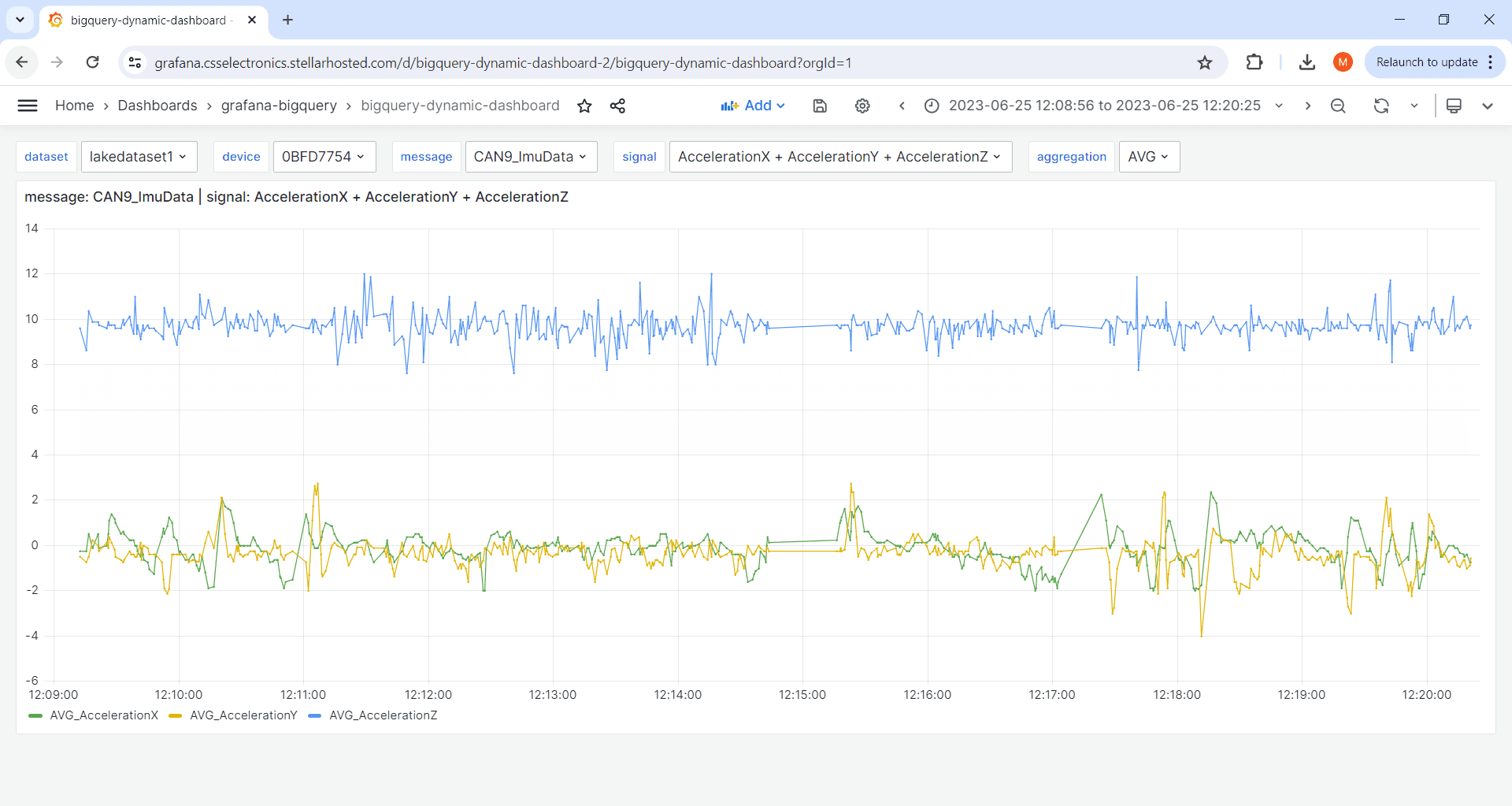
Here, Grafana Assistant runs the relevant queries and produces the output in-chat as text or as plots. We can also prompt the LLM to create a panel that displays speed over time within our dashboard, which Grafana does successfully as shown below.
Prompt:
What is the average speed from the CAN2_GnssSpeed message in July 2023? It's in m/s. Please create a panel in this dashboard to visualize the average speed over time
Example 3: Create dashboard via a high-level prompt
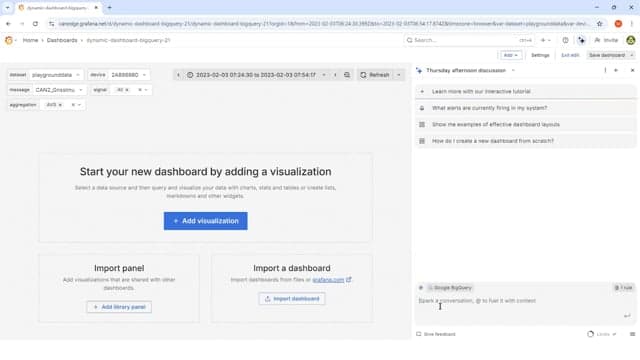
An obvious use case for Grafana Assistant is to create a new dashboard from scratch. In this example we try a minimal-effort prompt—leaving a lot up to the imagination of the LLM.
The result is a functional 12-panel dashboard where all SQL queries are as expected (i.e., as per our system prompt guidance). Notice in particular that the LLM proactively identifies available (and relevant) messages/signals. Pretty cool! It's worth reflecting on how commoditized LLMs + tools have already become. If this was 2022 we'd have been blown away.
However, the dashboard we get is highly inconsistent between re-runs of the same prompt. This is of course to be expected given the open-ended nature of our request. In our view, there's not much practical value to providing prompts that are this high level if the goal is to create real Grafana dashboards.
Prompt:
My data source contains data from a Kia EV6 electric car, recorded with a CANedge CAN bus data logger with device ID 2A896980. The data includes battery data from the EV and GPS/IMU data from a sensor module.
Update my dashboard to include panels showing my Kia EV6 battery data and GPS/IMU data.
Example 4: Create a dashboard via a detailed prompt
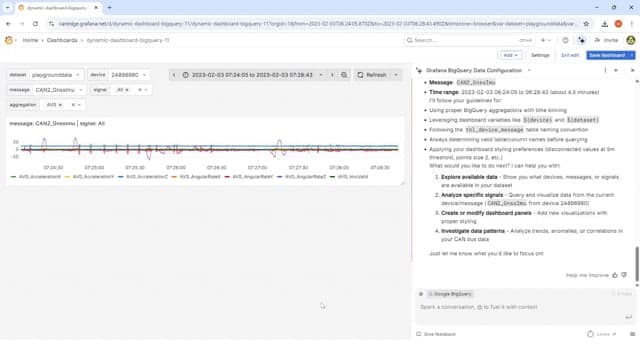
Instead of using a fairly vague prompt, a much better approach is of course to provide highly detailed guidance, similar to what you would provide a human assistant if they were to design your dashboard. You can find the full detailed prompt here.
As you can see, the result looks as intended. And more importantly, when we run this 10x (in new conversations each time), we get a 90%+ consistent dashboard each time.
You might argue that writing a prompt like this is also time consuming, but in our experience it is still five to 10 times faster than if we were to construct this dashboard from scratch. For example, notice that many of our message/signal names are approximate, leaving Grafana Assistant to figure out what the exact table and column names are. Further, some of the panels involve semi-complex queries (e.g., the consumed State of Charge and the delta distance traveled), which would require significant SQL expertise to create.
Most importantly, the prompt specifies no SQL syntax, which is important as 99%+ of our end users have zero SQL experience.
Check out the generated dashboard in our public playground.
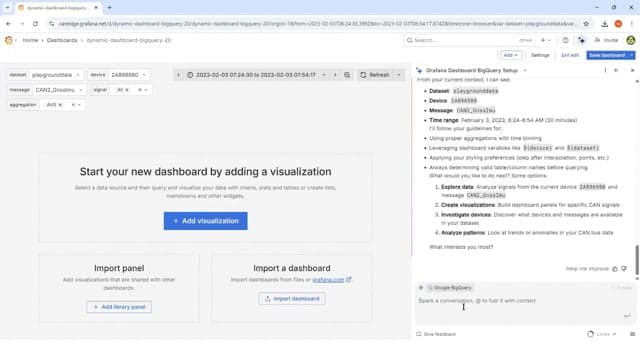
Our summary thoughts
We spent 20+ hours with Grafana Assistant. Here are our overarching thoughts.
1: Excellent concept. For users that have already hooked up Grafana to their data, it is extremely simple to start working with the data through the LLM. This ease-of-access is a critical advantage—and the Grafana Assistant UI is great.
2: A drunk genius. Grafana Assistant can give you that "magical experience" where you sit back and watch it produce an entire Grafana dashboard in one shot according to your specifications. However, in some cases it will produce invalid queries, get stuck or hallucinate—just like all LLMs. Make sure to always review the output.
3: Visualization vs. analysis. The LLM is able to modify dashboards and execute SQL queries, making it an excellent tool for data visualization and light exploration. However, it is not able to run scripts (in contrast to ChatGPT, for example), making it less suitable for highly complex, multi-step data analysis—at least for now. Such functionality could be a powerful future mode/variation of the assistant.
4: Huge potential. While the current version has limitations in terms of performance and data source support, we are confident that Grafana Assistant will become an extremely handy tool for data visualization and exploration. In just our one month of testing, Grafana added a ton of improvements to the LLM, so we are excited to see how this tool develops!
To learn more and see additional showcases, check out our full Grafana Assistant article!
Grafana Cloud is the easiest way to get started with metrics, logs, traces, dashboards, and more. We have a generous forever-free tier and plans for every use case. Sign up for free now!


