What's new from Grafana Labs
Grafana Labs products, projects, and features can go through multiple release stages before becoming generally available. These stages in the release life cycle can present varying degrees of stability and support. For more information, refer to release life cycle for Grafana Labs.
Loading...
Area of interest:
Cloud availability:
Cloud editions:
Self-managed availability:
Self-managed editions:
No results found. Please adjust your filters or search criteria.
There was an error with your request.
The table visualization for logs, announced in public preview for Grafana 10.3, is generally available in Cloud (all editions) and with Grafana 10.4.
New to the table visualization with 10.4:
Grafana can now be used to manage both Prometheus and Mimir Alertmanagers with UTF-8 configurations. For more information, please see the release notes for Alertmanager 0.27.0.
AngularJS support in Grafana was deprecated in v9 and will be turned off by default in Grafana v11. When this happens, any plugin which depended on AngularJS will not load, and dashboard panels will be unable to show data.
This update to the Filter data by values transformation simplifies data filtering by enabling partial string matching on field values thanks to two new matchers: Contains substring and Does not contain substring. With the substring matcher built into the Filter data by values transformation, you can efficiently filter large datasets, displaying relevant information with speed and precision. Whether you’re searching for keywords, product names, or user IDs, this feature streamlines the process, saving time and effort while ensuring accurate data output.
The Log Volume Explorer has been promoted to General Availability! First announced at ObsCon London in Nov 2023, the Log Volume Explorer adds to our set of features that help you manage your observability spend. Identify the source of logs ingested into Grafana Cloud and answer questions like “Which of my teams, environments, Kubernetes clusters, and/or applications are generating the most logs?” Find the Log Volume Explorer under Administration > Cost Management > Logs.
Are you a k8s user? Do your requirements involve testing internal services or generating load from inside your network? Private Load Zones are a new feature of Grafana Cloud k6 that allow you to run k6 load generators from your k8s cluster and push metrics to Grafana Cloud and visualize them in the Grafana Cloud k6 app plugin.
Save money and apply an extra layer of network security by using Azure Private Link to send metrics, logs, traces, and profiles to Grafana Cloud.
Subfolders are here at last!
Some of you want subfolders in order to keep things tidier. It’s easy for dashboard sprawl to get out of control, and setting up folders in a nested hierarchy helps with that.
If you’ve wanted to visualize your Grafana Cloud k6 test results in a dashboard you’ve been limited to displaying data as a time series. But sometimes a single number is more digestible and can help you make an assessment of your test results quicker.
Configuring OAuth providers was a bit cumbersome in Grafana: Grafana Cloud users had to reach out to Grafana Support, self-hosted users had to manually edit the configuration file, set up environment variables, and then they had to restart Grafana. On Cloud, the Advanced Auth page is there to configure some of the providers, but configuring Generic OAuth hasn’t been available until now and there was no way to manage the settings through the Grafana UI, nor was there a way to manage the settings through Terraform or the Grafana API.
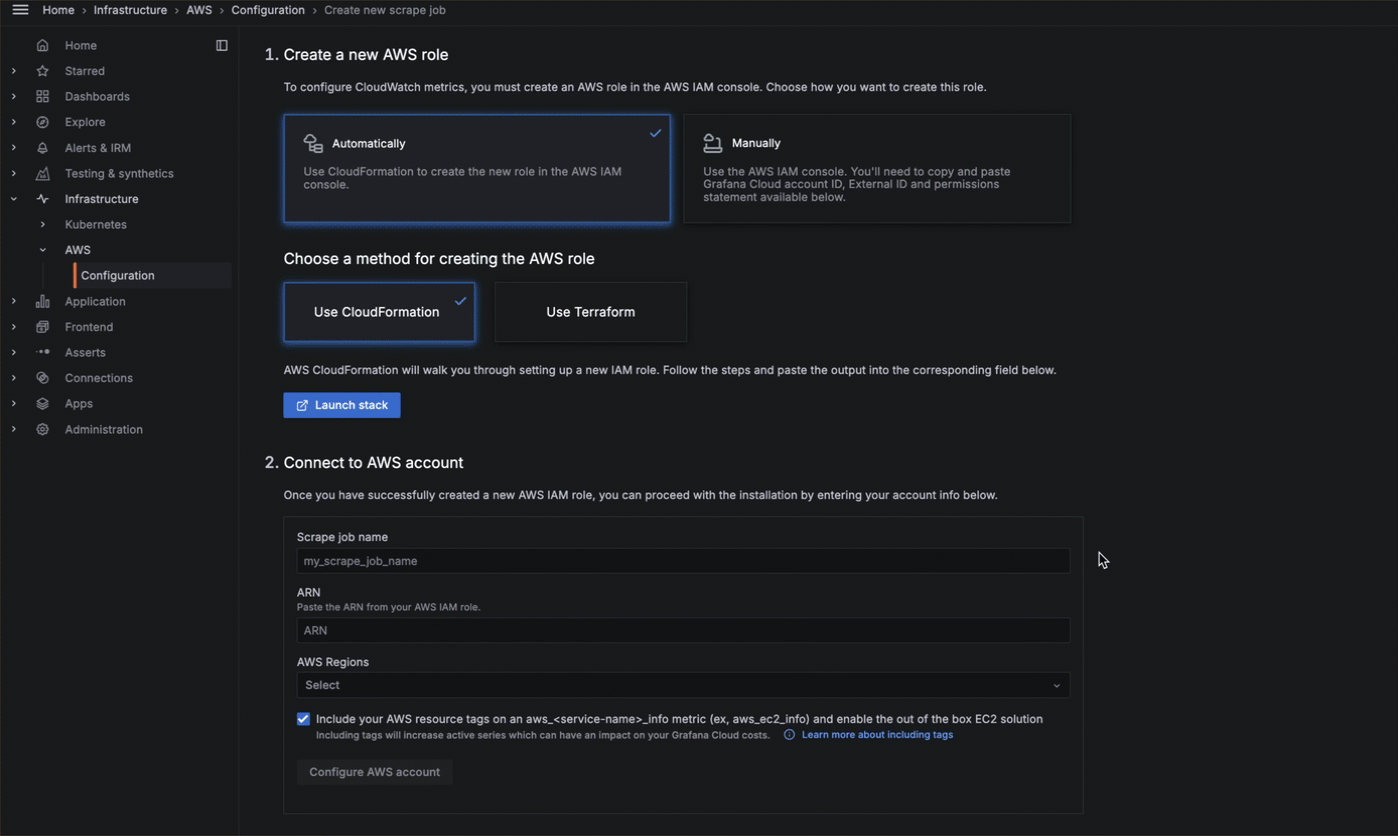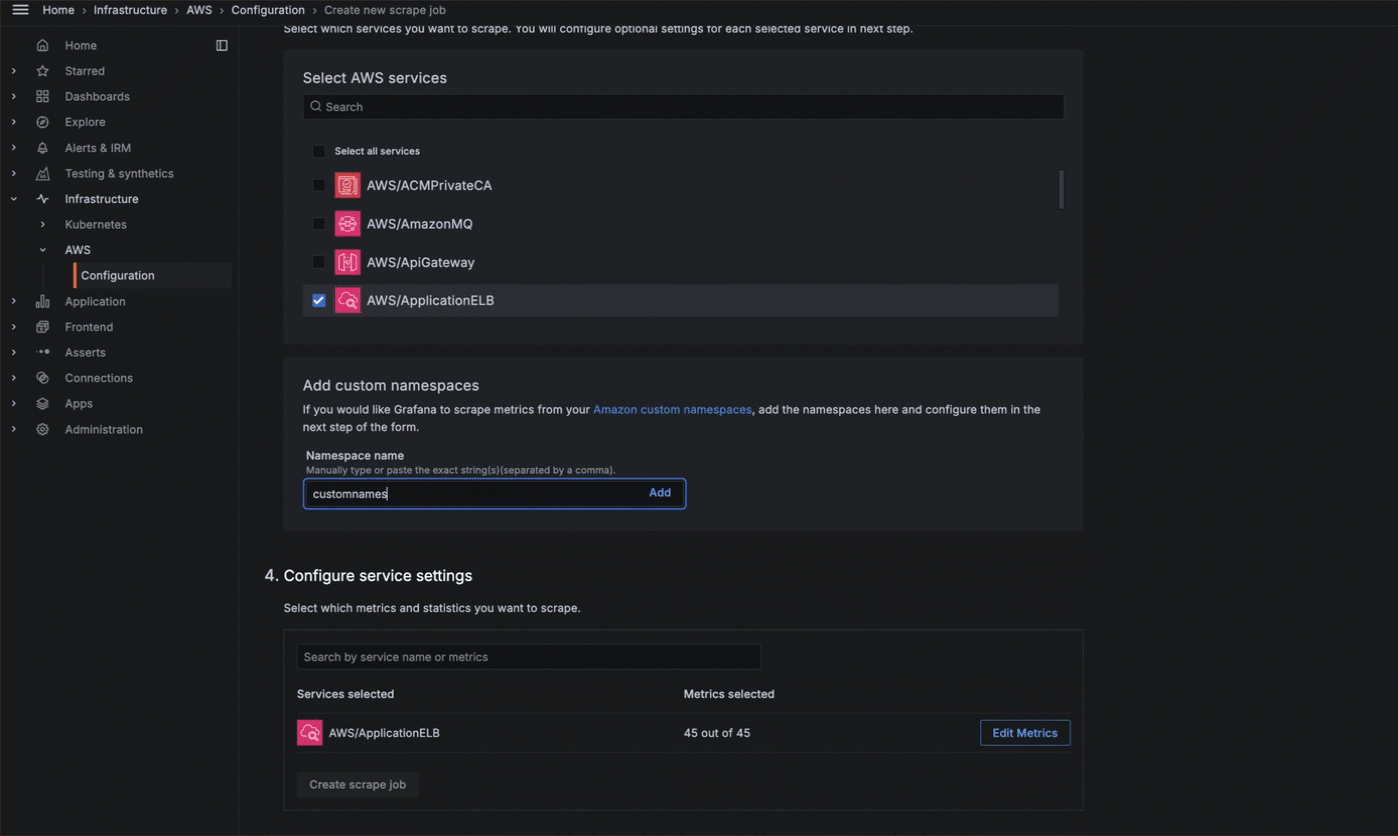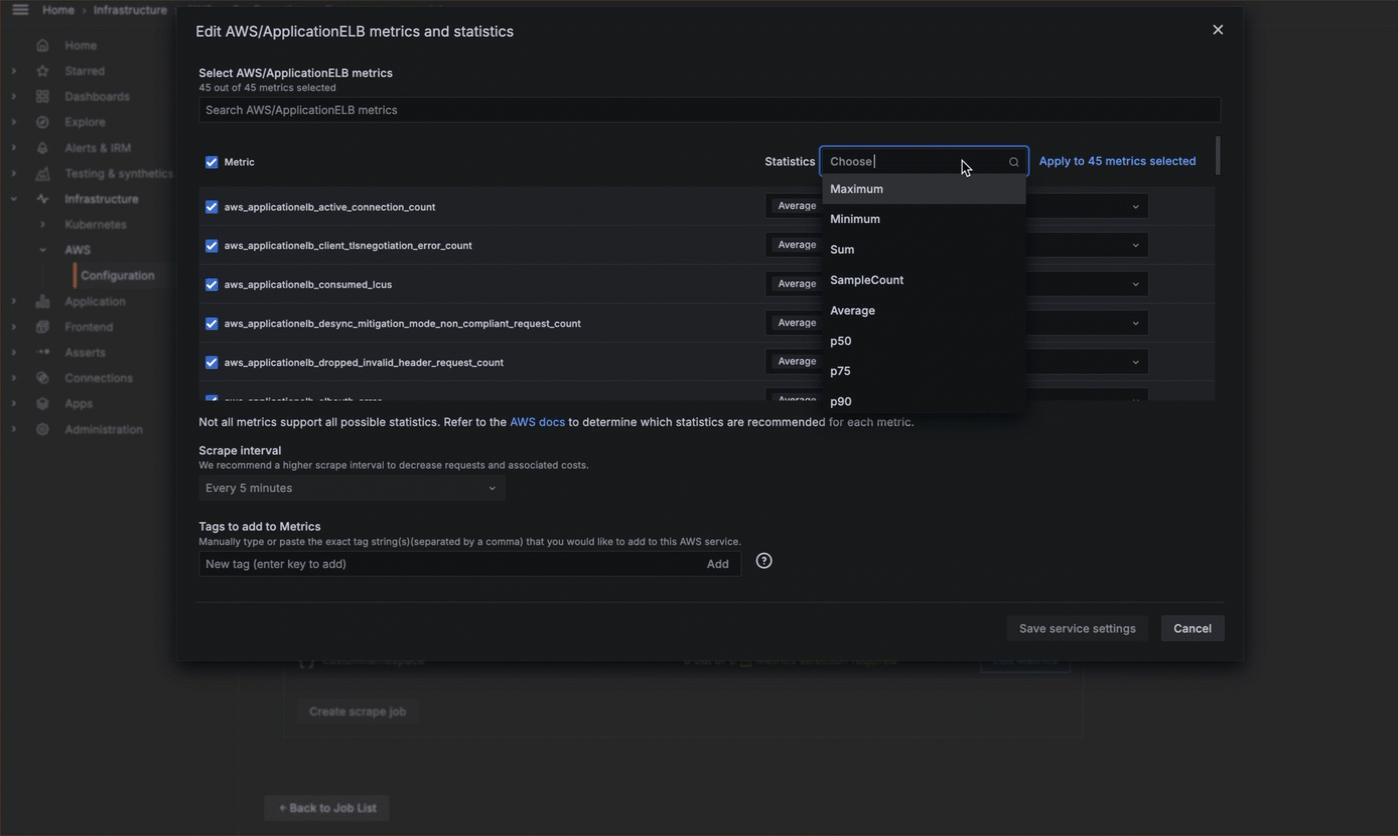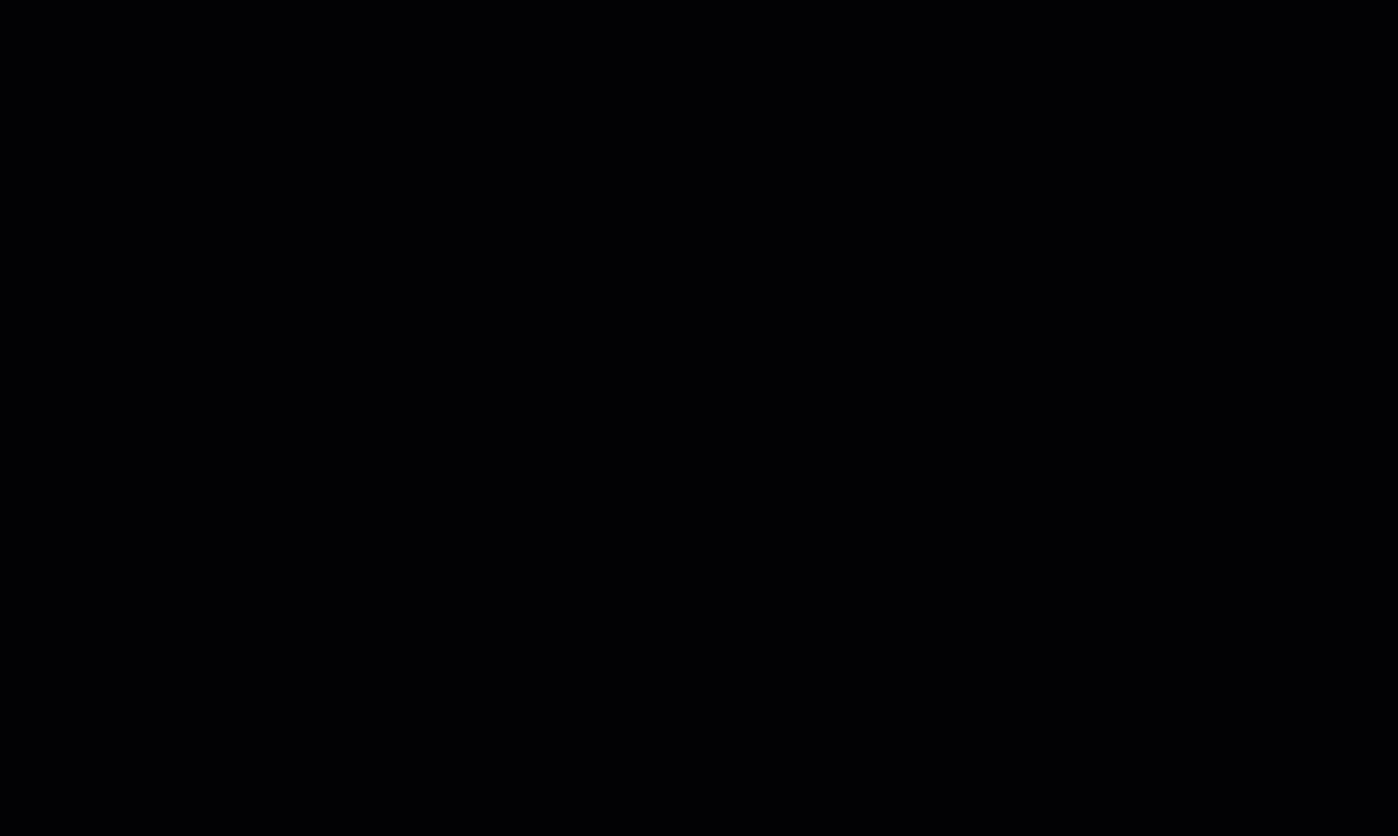
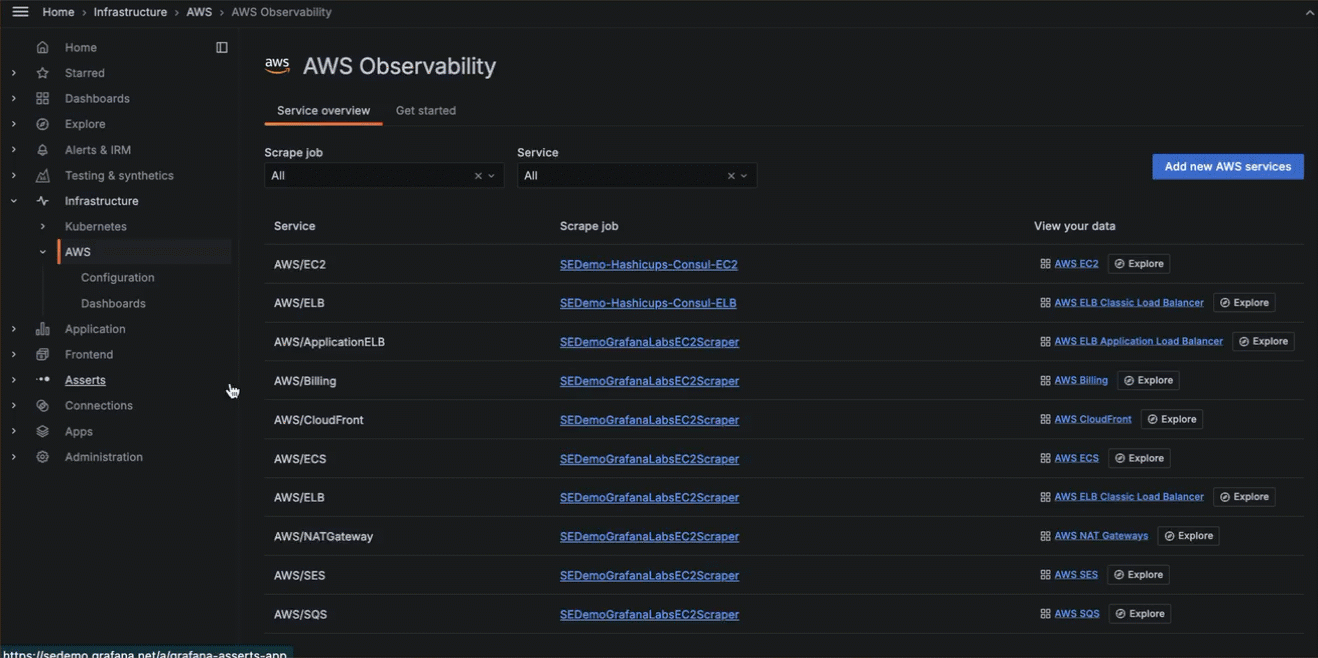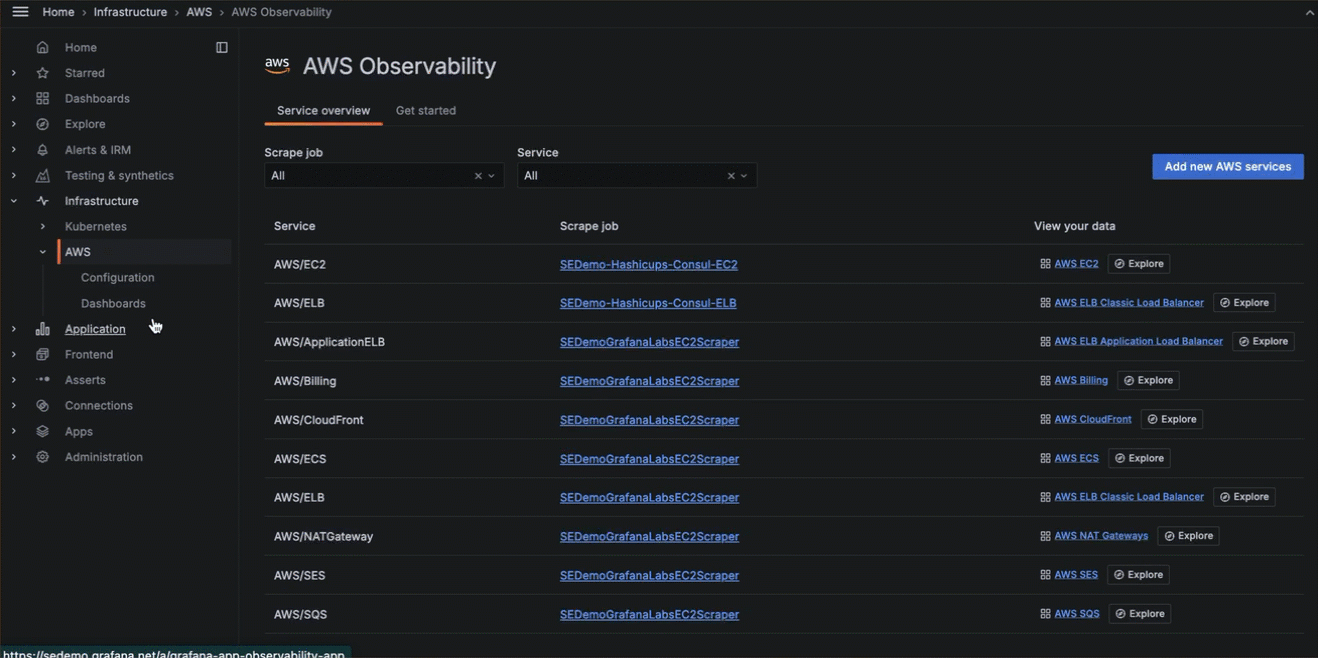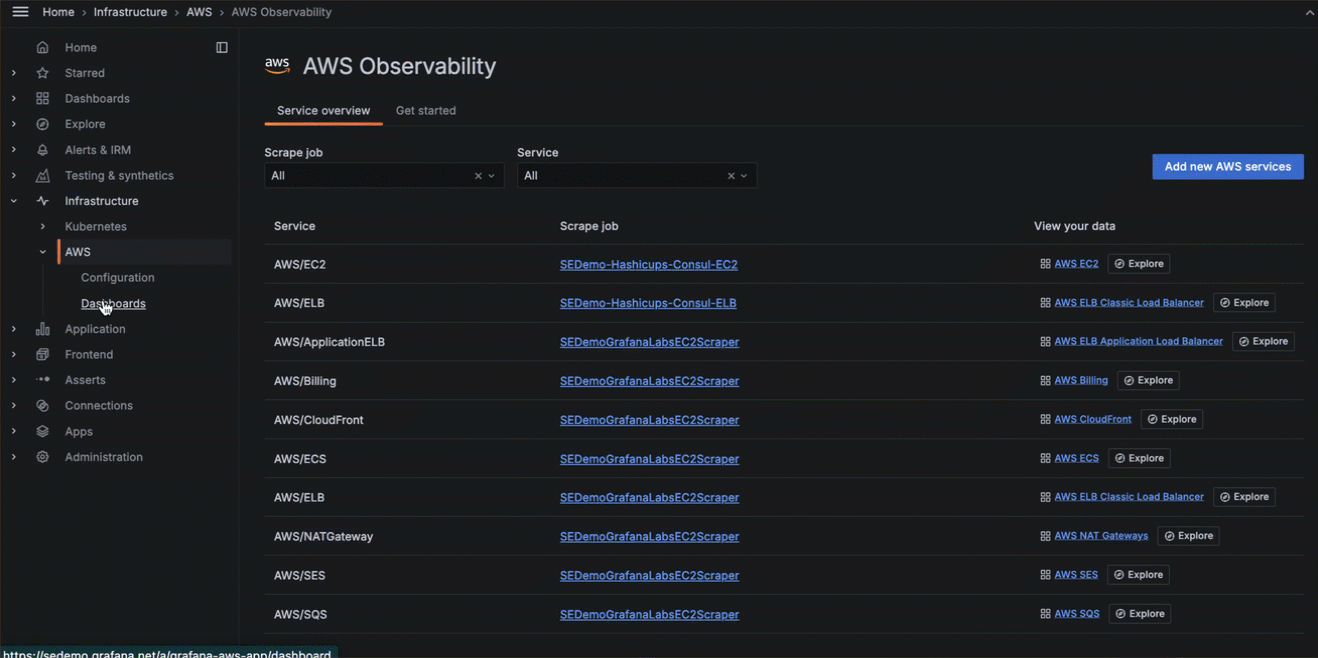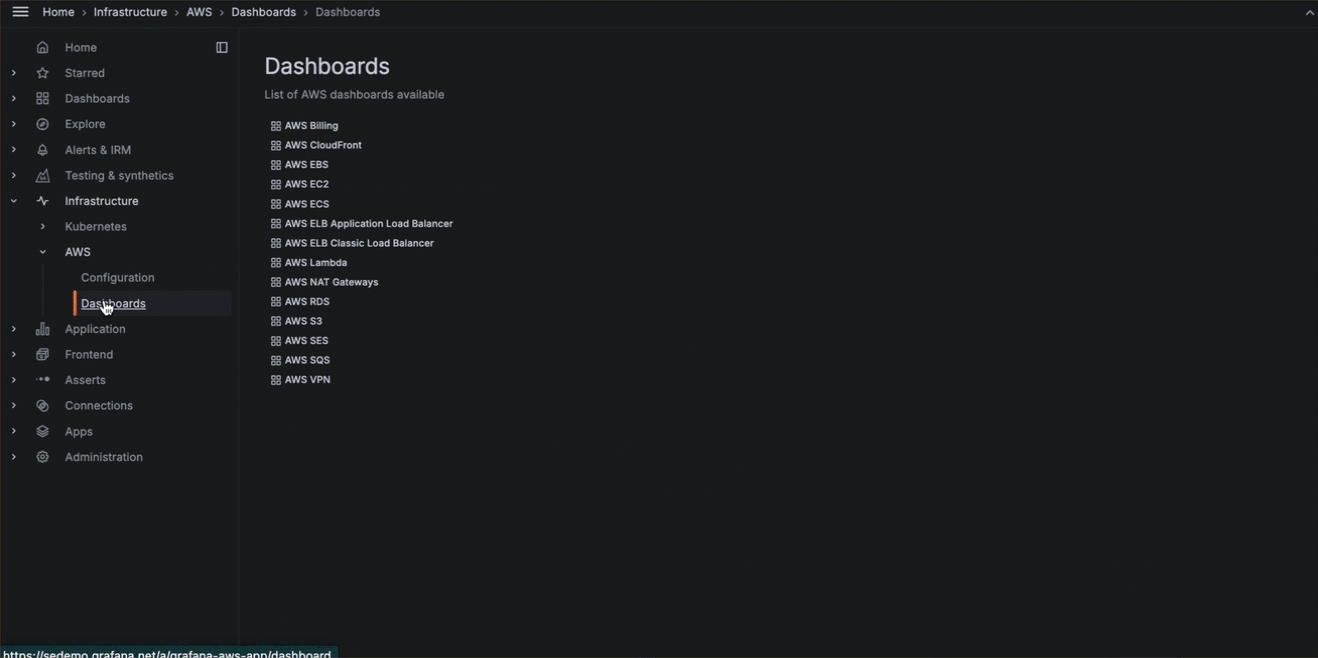
It’s hard to diagnose and resolve issues when your observability data is dispersed across many systems, which can lead to longer times to troubleshoot. Grafana’s AWS Observability provides a centralized location to work with critical observability data so you can fully understand the state of your systems. You can:
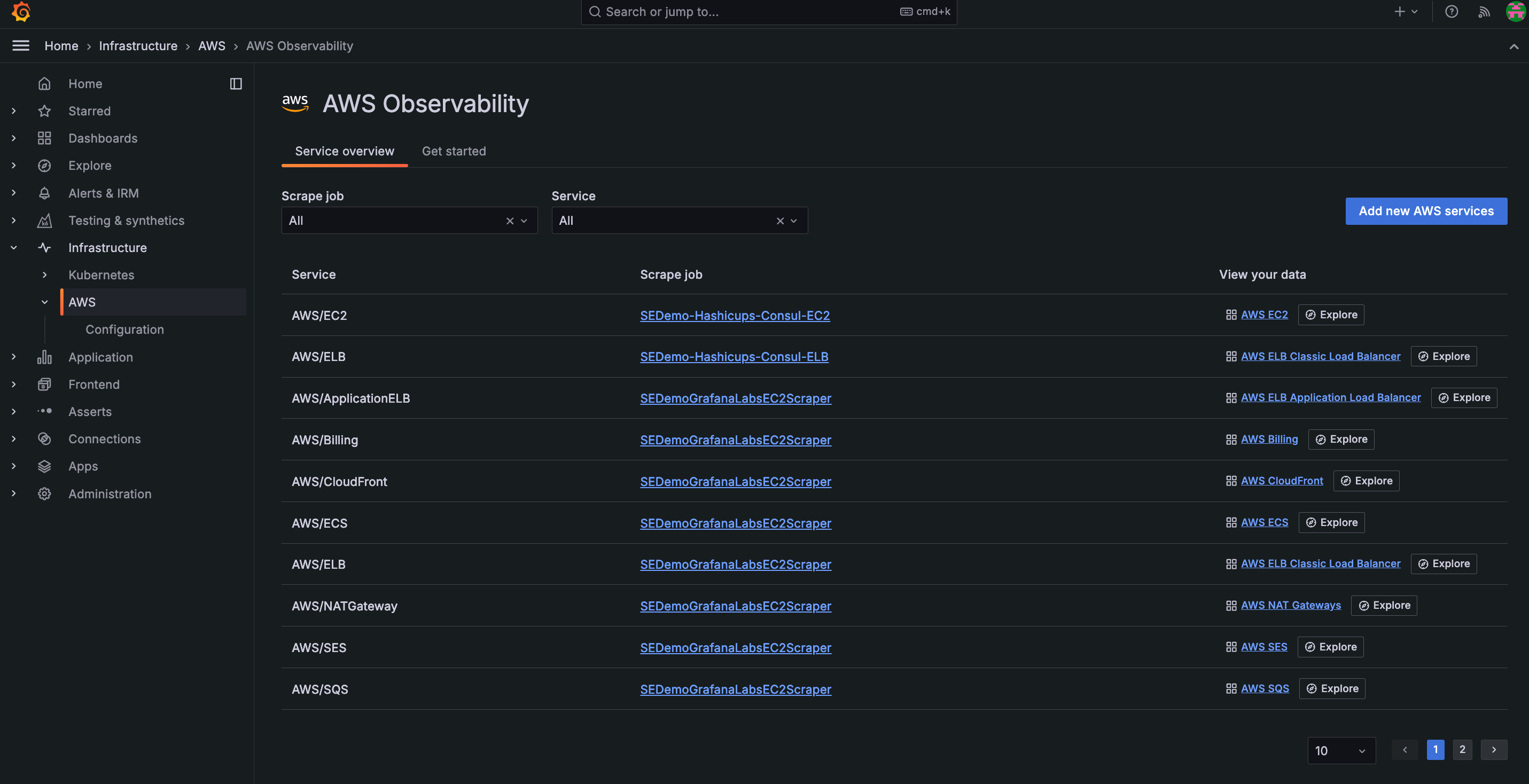
You can choose to configure manually, or use a more streamlined configuration process with CloudFormation or Terraform. To send CloudWatch metrics to Grafana Cloud, you:
- Connect to your AWS account.
- Configure the connection between Grafana Cloud and your AWS account.
- Continue configuration with either CloudFormation or Terraform.
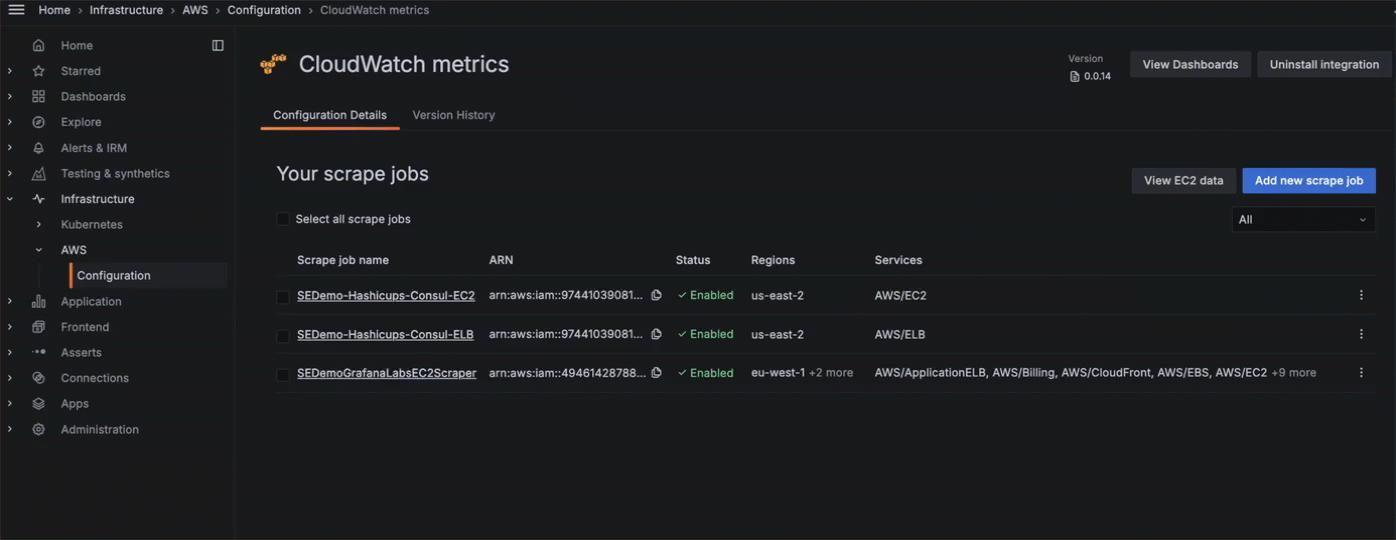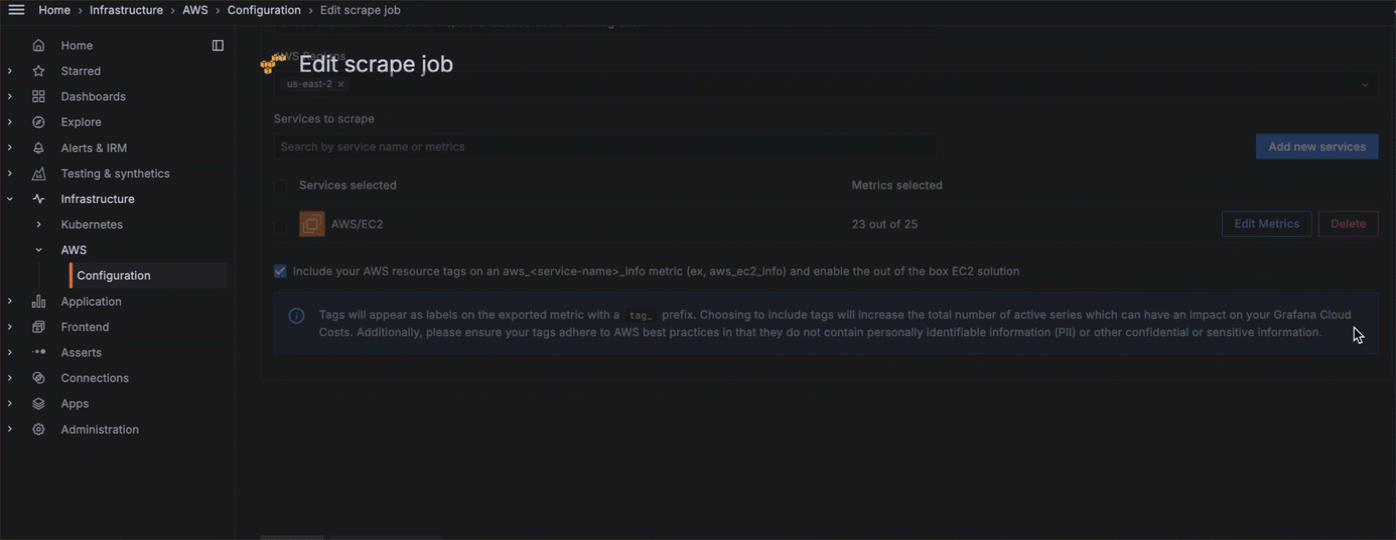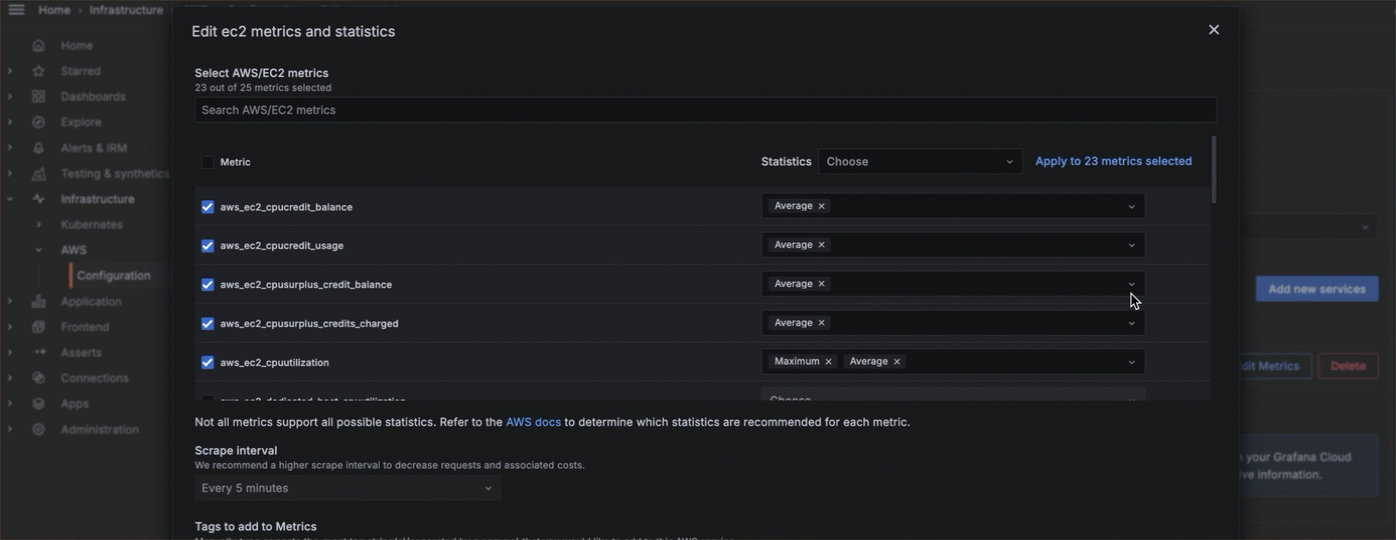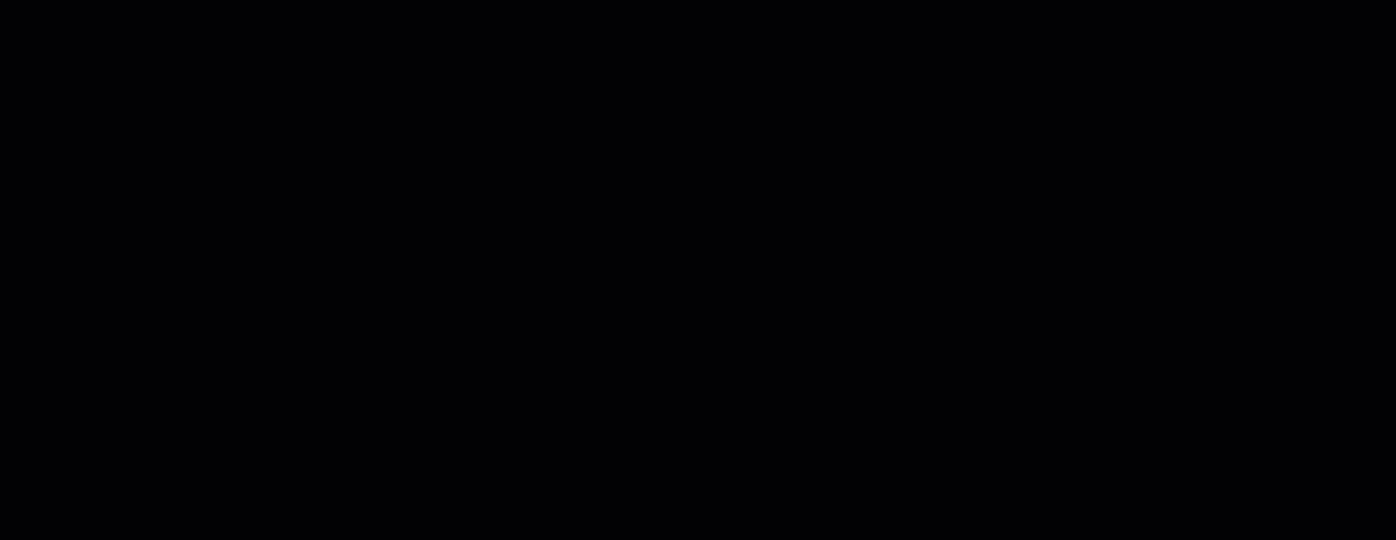
- Choose what service to monitor, what metrics to gather, the scrape interval, and what statistics to gather.
- Add any custom namespaces you want to monitor.
![Metrics configuration]()
You can also edit or delete scrape jobs.
AWS Observability provides preconfigured dashboards embedded within the app.
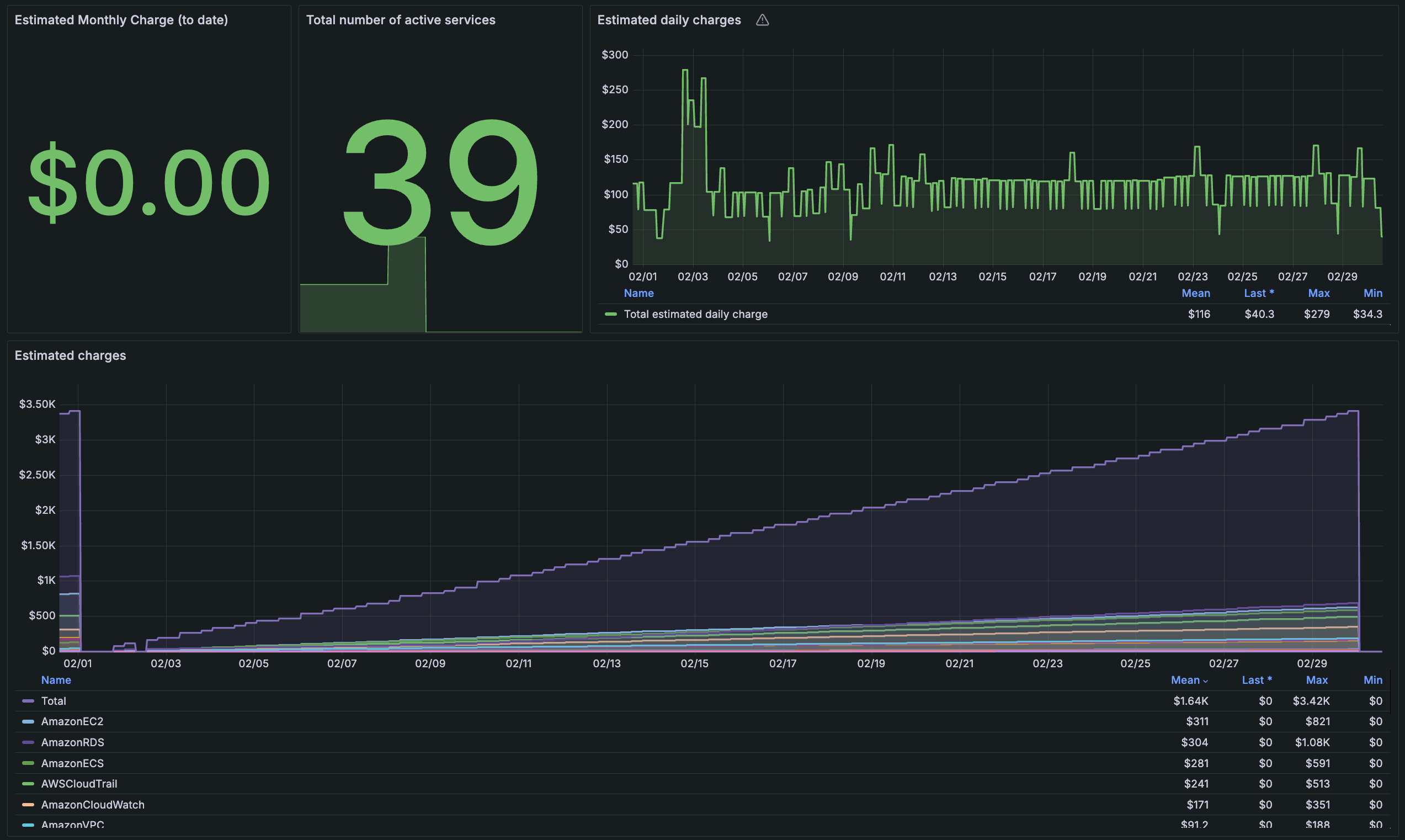
You can easily access dashboards to monitor AWS costs and cloud services. For example, the following shows the billing dashboard.
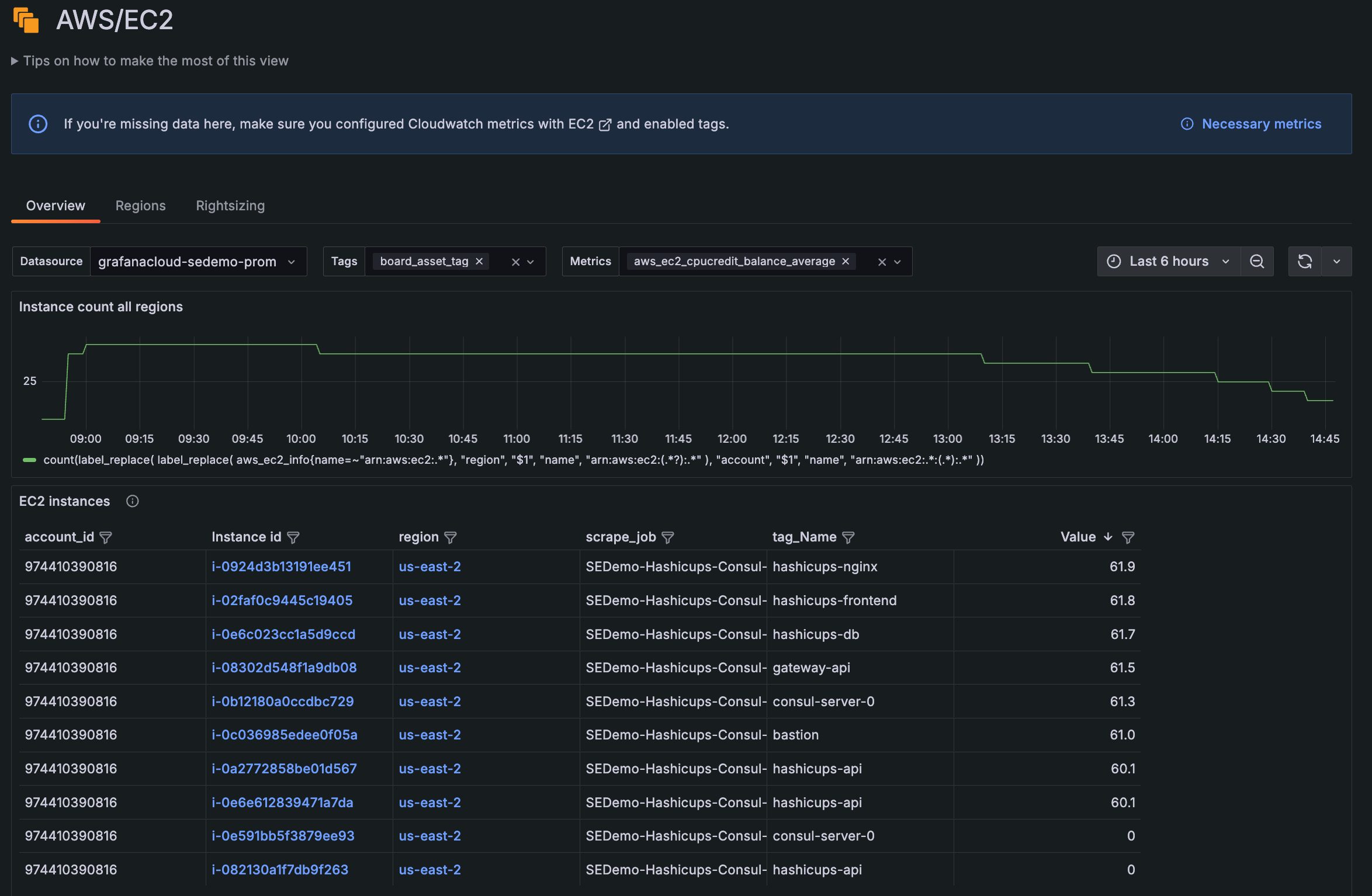
Grafana AWS Observability offers an out-of-the-box, embedded experience for you to efficiently explore and analyze your Amazon EC2 data.
The list of EC2 instances is available from the Overview tab.
You can now create subtables out of your data using the new Group to nested tables transformation. To use this feature, enable the groupToNestedTableTransformation
feature toggle.