This is documentation for the next version of Grafana Tempo documentation. For the latest stable release, go to the latest version.
Quick start for Tempo
Using this quickstart, you can set up a Tempo instance using Docker Compose so you can play and understand how Tempo works. If you want to use Tempo in production, refer to the Set up for tracing documentation.
The Tempo repository provides multiple examples to help you quickly get started using Tempo and distributed tracing data.
Every example has a docker-compose.yaml manifest that includes all of the options needed to explore trace data in Grafana, including resource configuration and trace data generation.
The Tempo examples running with Docker using docker-compose include a version of Tempo and a storage configuration suitable for testing or development.
Before you begin
To follow this guide, you need:
- Git
- Docker
- The Docker Compose plugin (included with Docker Desktop)
Tip
Alternatively, you can try out this example in our interactive learning environment: Quick start for Tempo.
It’s a fully configured environment with all the dependencies installed.
Provide feedback, report bugs, and raise issues in the Grafana Killercoda repository.
Clone the Tempo repository and start Docker
This quick start guide uses the single-binary docker-compose example. Check out our collection of examples to explore various
operating modes and configurations.
Clone the Tempo repository:
git clone https://github.com/grafana/tempo.gitGo into the examples directory:
cd tempo/example/docker-compose/single-binaryStart the services defined in the docker-compose file:
docker compose up -dVerify that the services are running:
docker compose psYou should see something like:
docker compose ps NAME COMMAND SERVICE STATUS PORTS local-grafana-1 "/run.sh" grafana running 0.0.0.0:3000->3000/tcp local-k6-tracing-1 "/k6-tracing run /ex…" k6-tracing running local-prometheus-1 "/bin/prometheus --c…" prometheus running 0.0.0.0:9090->9090/tcp local-tempo-1 "/tempo -config.file…" tempo running 0.0.0.0:3200->3200/tcp, 0.0.0.0:4317-4318->4317-4318/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9411->9411/tcp, 0.0.0.0:14268->14268/tcp
Explore the traces in Grafana
As part of the Docker Compose manifest, Grafana is now accessible on port 3000. You can use Grafana to explore the traces generated by the k6-tracing service.
Open a browser and navigate to http://localhost:3000.
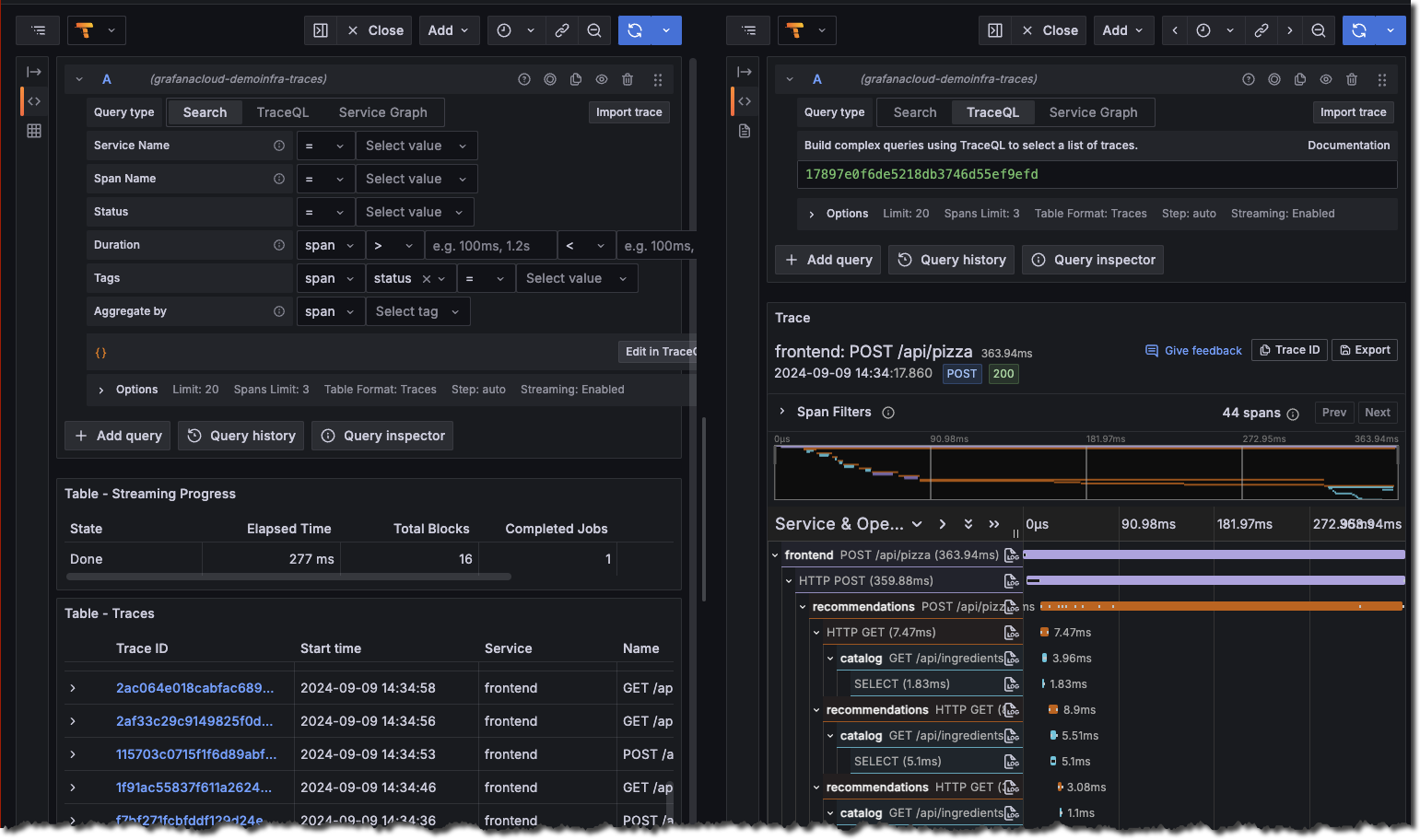
Once logged in, navigate to the Explore page, select the Tempo data source and select the Search tab. Select Run query to list the recent traces stored in Tempo. Select one to view the trace diagram:
![Use the query builder to explore tracing data in Grafana]()
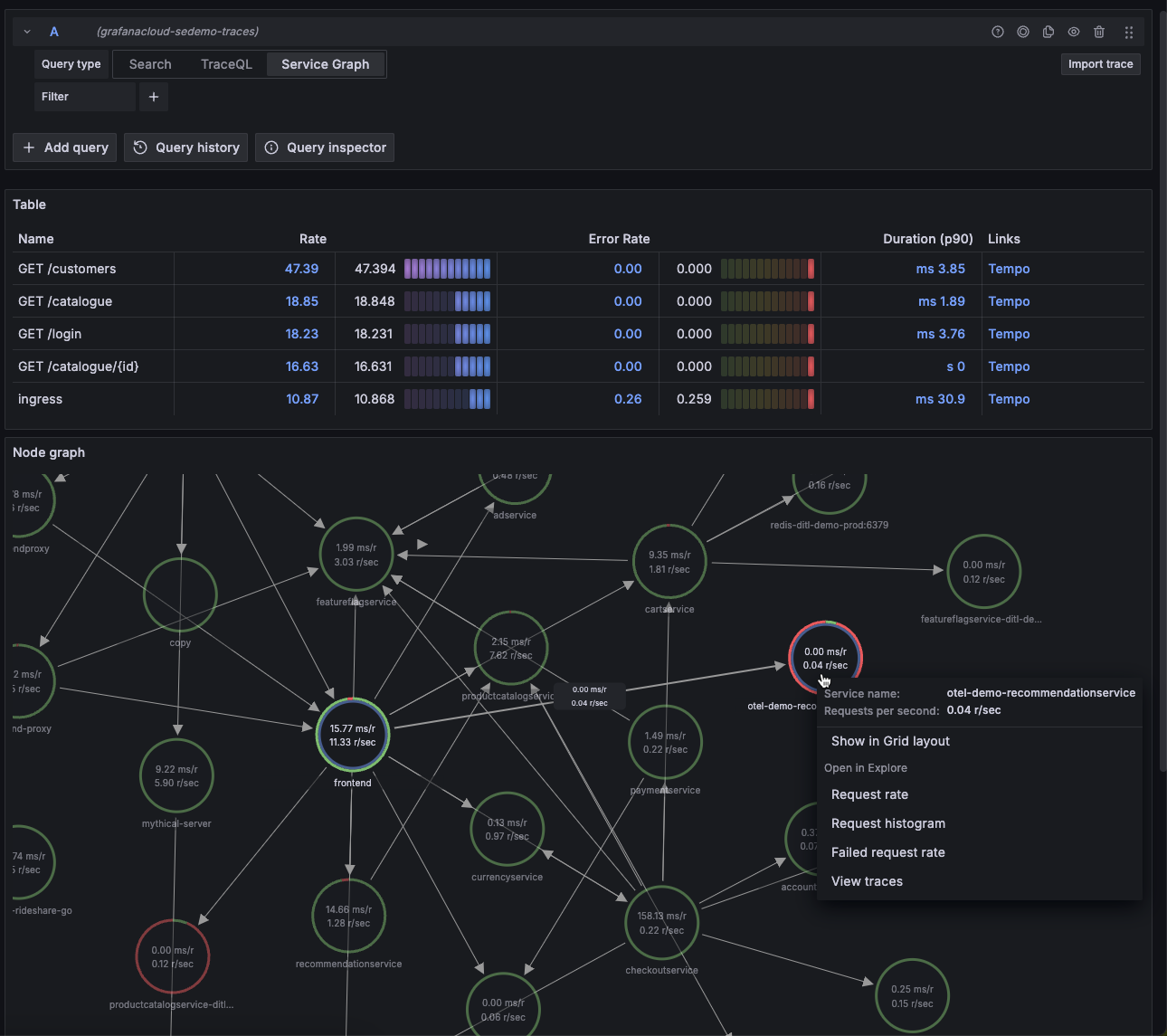
A couple of minutes after Tempo starts, select the Service graph tab for the Tempo data source in the Explore page. Select Run query to view a service graph, generated by Tempo’s metrics-generator.
![Service graph sample]()
To stop the services:
docker compose down -v
Traces Drilldown plugin
The Traces Drilldown plugin offers an opinionated non query-based approach to exploring traces. Let’s take a look at some of its key features and panels.
- Open a browser and navigate to http://localhost:3000/a/grafana-exploretraces-app.
- Within the filter bar, there is a dropdown menu set to Rate of Full traces. Change this to Duration and All spans.
This updated panel view looks like this:

Breakdown of the view:
- The histogram at the top shows the distribution of span durations. The lighter the color, the more spans in that duration bucket. In this example, most spans fall within
537ms, which is considered the average duration for the system. - The high peaks in the histogram indicate spans that are taking longer than the average (As high as
2.15s). These are likely to be the spans that are causing performance issues. You can investigate further to identify the root cause.
Select Slow traces tab in the navigation bar to view the slowest traces in the system.

shop-backend appears to be the primary culprit for the slow traces. This happens when a user initiates the article-to-cart operation. From here, you can select the Trace Name to open the Trace View panel.

The Trace View panel provides a detailed view of the trace. The panel is divided into three sections:
- The top section shows the trace ID, duration, and the service that generated the trace.
- The middle section shows the trace timeline. Each span is represented as a horizontal bar. The color of the bar represents the span’s status. The width of the bar represents the duration of the span.
- The bottom section shows the details of the selected span. This includes the span name, duration, and tags.
Drilling into the shop-backend span, you can see that the place-articles operation has an exception event tied to it. This is likely the root cause of the slow trace.

If you would like to dive deeper into the Traces Drilldown plugin and its panel concepts, refer to the Traces Drilldown Concepts.
Next steps
You have successfully set up Tempo and Grafana to explore traces generated by the k6-tracing service.
Now that you’ve explored the basics of Tempo, you can:
- Set up Tempo by following the Set up for tracing documentation.
- Learn how to instrument your application to emit traces.
Alternative: Complete MLTP example
If you would like to use a demo with multiple telemetry signals, then try the Introduction to Metrics, Logs, Traces, and Profiling in Grafana.
Intro-to-mltp provides a self-contained environment for learning about Mimir, Loki, Tempo, Pyroscope, and Grafana.
The project includes detailed explanations of each component and annotated configurations for a single-instance deployment.
Data from intro-to-mltp can also be pushed to Grafana Cloud.
Further reading
Here are some resources to help you learn more about Tempo: