This is documentation for the next version of Grafana Tempo documentation. For the latest stable release, go to the latest version.
Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server
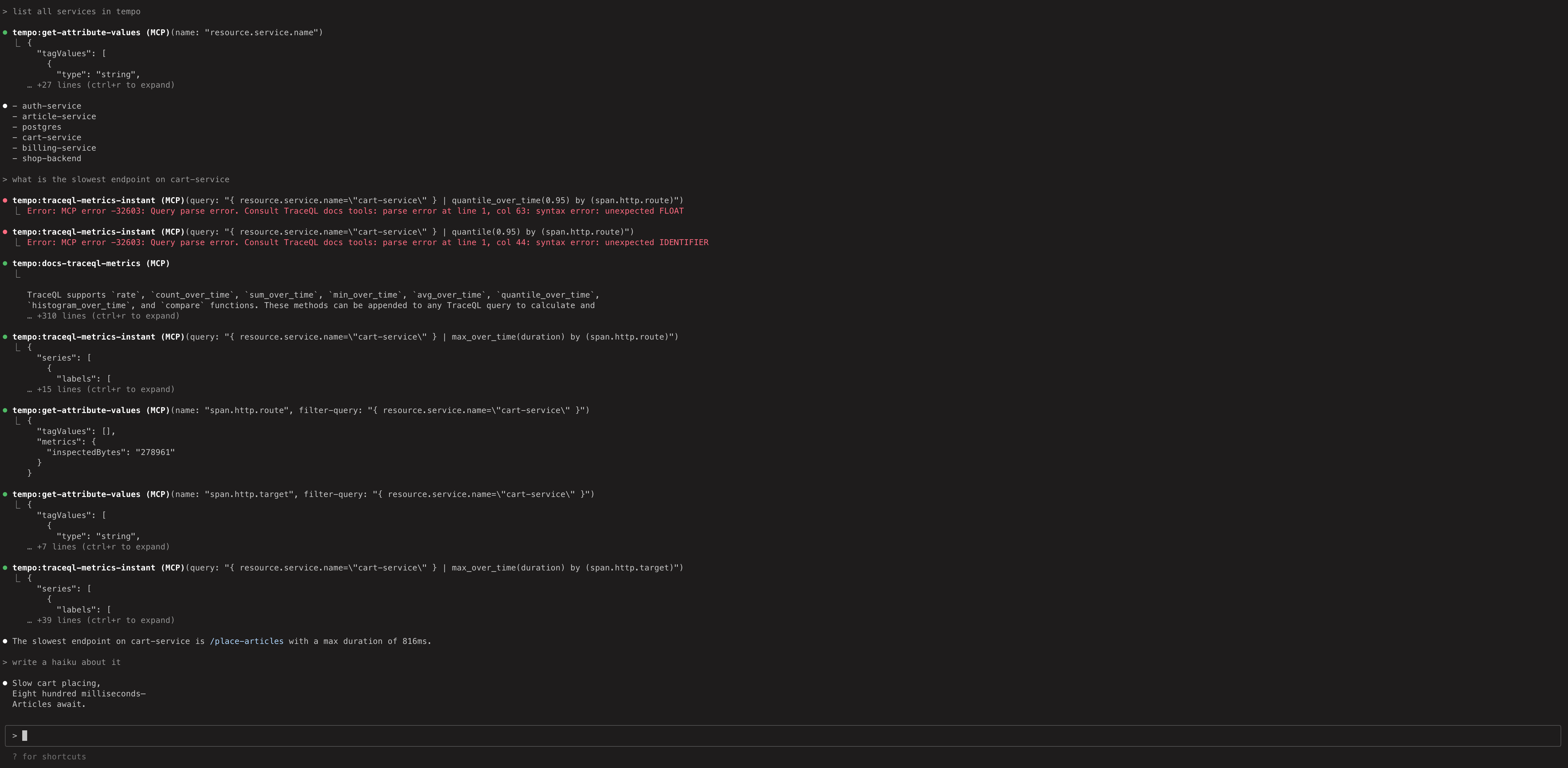
Tempo includes an MCP (Model Context Protocol) server that provides AI assistants and Large Language Models (LLMs) with direct access to distributed tracing data through TraceQL queries and other endpoints.
For examples on how you can use the MCP server, refer to LLM-powered insights into your tracing data: introducing MCP support in Grafana Cloud Traces.
For more information on MCP, refer to the MCP documentation.
Configuration
Enable the MCP server in your Tempo configuration:
query_frontend:
mcp_server:
enabled: trueWarning
Be aware that using this feature will likely cause tracing data to be passed to an LLM or LLM provider. Consider the content of your tracing data and organizational policies when enabling this.
Quick start
To experiment with the MCP server using dummy data and Claude Code:
- Run the local docker-compose example in
/example/docker-compose/single-binary. This exposes the MCP server athttp://localhost:3200/api/mcp - Run
claude mcp add --transport=http tempo http://localhost:3200/api/mcpto add a reference to Claude Code. - Run
claudeand ask some questions.
This MCP server has also been tested successfully in cursor using the mcp-remote package.