Important: This documentation is about an older version. It's relevant only to the release noted, many of the features and functions have been updated or replaced. Please view the current version.
Prometheus data source
Grafana includes built-in support for Prometheus. This topic explains options, variables, querying, and other options specific to the Prometheus data source. Refer to Add a data source for instructions on how to add a data source to Grafana. Only users with the organization admin role can add data sources.
Note: You can use Grafana Cloud to avoid the overhead of installing, maintaining, and scaling your observability stack. The free forever plan includes Grafana, 10K Prometheus series, 50 GB logs, and more.Create a free account to get started.
Prometheus settings
To access Prometheus settings, hover your mouse over the Configuration (gear) icon, then click Data Sources, and then click the Prometheus data source.
Prometheus query editor
Below you can find information and options for Prometheus query editor in dashboard and in Explore.
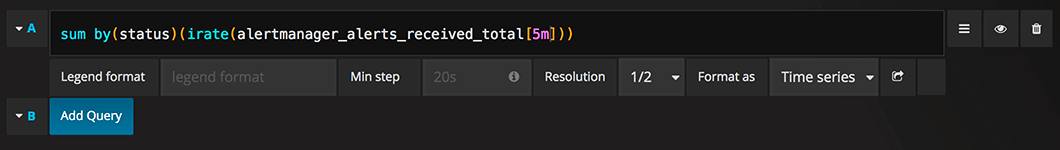
Query editor in dashboards
Open a graph in edit mode by clicking the title > Edit (or by pressing e key while hovering over panel).
Note: Grafana modifies the request dates for queries to align them with the dynamically calculated step. This ensures consistent display of metrics data, but it can result in a small gap of data at the right edge of a graph.
Instant queries in dashboards
The Prometheus data source allows you to run “instant” queries, which query only the latest value. You can visualize the results in a table panel to see all available labels of a timeseries.
Instant query results are made up only of one data point per series but can be shown in the graph panel with the help of series overrides.
To show them in the graph as a latest value point, add a series override and select Points > true.
To show a horizontal line across the whole graph, add a series override and select Transform > constant.
Support for constant series overrides is available from Grafana v6.4
Query editor in Explore
Metrics browser
The metrics browser allows you to quickly find metrics and select relevant labels to build basic queries. When you open the browser you will see all available metrics and labels. If supported by your Prometheus instance, each metric will show its HELP and TYPE as a tooltip.

When you select a metric, the browser narrows down the available labels to show only the ones applicable to the metric. You can then select one or more labels for which the available label values are shown in lists in the bottom section. Select one or more values for each label to tighten your query scope.
Note: If you do not remember a metric name to start with, you can also select a few labels first, to narrow down the list and then find relevant label values.
All lists in the metrics browser have a search field above them to quickly filter for metrics or labels that match a certain string. The values section only has one search field. Its filtering applies to all labels to help you find values across labels once they have been selected, for example, among your labels app, job, job_name only one might with the value you are looking for.
Once you are satisfied with your query, click “Use query” to run the query. The button “Use as rate query” adds a rate(...)[$__interval] around your query to help write queries for counter metrics.
The “Validate selector” button will check with Prometheus how many time series are available for that selector.
Limitations
The metrics browser has a hard limit of 10,000 labels (keys) and 50,000 label values (including metric names). If your Prometheus instance returns more results, the browser will continue functioning. However, the result sets will be cut off above those maximum limits.
Templating
Instead of hard-coding things like server, application and sensor name in your metric queries, you can use variables in their place. Variables are shown as dropdown select boxes at the top of the dashboard. These dropdowns make it easy to change the data being displayed in your dashboard.
Check out the Templating documentation for an introduction to the templating feature and the different types of template variables.
Query variable
Variable of the type Query allows you to query Prometheus for a list of metrics, labels or label values. The Prometheus data source plugin
provides the following functions you can use in the Query input field.
For details of what metric names, label names and label values are please refer to the Prometheus documentation.
Using interval and range variables
Support for
$__range,$__range_sand$__range_msonly available from Grafana v5.3
You can use some global built-in variables in query variables, for example, $__interval, $__interval_ms, $__range, $__range_s and $__range_ms. See Global built-in variables for more information. They are convenient to use in conjunction with the query_result function when you need to filter variable queries since the label_values function doesn’t support queries.
Make sure to set the variable’s refresh trigger to be On Time Range Change to get the correct instances when changing the time range on the dashboard.
Example usage:
Populate a variable with the busiest 5 request instances based on average QPS over the time range shown in the dashboard:
Query: query_result(topk(5, sum(rate(http_requests_total[$__range])) by (instance)))
Regex: /"([^"]+)"/Populate a variable with the instances having a certain state over the time range shown in the dashboard, using $__range_s:
Query: query_result(max_over_time(<metric>[${__range_s}s]) != <state>)
Regex:Using $__rate_interval
Note: Available in Grafana 7.2 and above
$__rate_interval is the recommended interval to use in the rate and increase functions. It will “just work” in most cases, avoiding most of the pitfalls that can occur when using a fixed interval or $__interval.
OK: rate(http_requests_total[5m])
Better: rate(http_requests_total[$__rate_interval])Details: $__rate_interval is defined as max($__interval + Scrape interval, 4 * Scrape interval), where Scrape interval is the Min step setting (AKA queryinterval, a setting per PromQL query) if any is set. Otherwise, the Scrape interval setting in the Prometheus data source is used. (The Min interval setting in the panel is modified by the resolution setting and therefore doesn’t have any effect on _Scrape interval.) This article contains additional details.
Using variables in queries
There are two syntaxes:
$<varname>Example: rate(http_requests_total{job=~"$job"}[5m])[[varname]]Example: rate(http_requests_total{job=~"[[job]]"}[5m])
Why two ways? The first syntax is easier to read and write but does not allow you to use a variable in the middle of a word. When the Multi-value or Include all value
options are enabled, Grafana converts the labels from plain text to a regex compatible string. Which means you have to use =~ instead of =.
Ad hoc filters variable
Prometheus supports the special ad hoc filters variable type. It allows you to specify any number of label/value filters on the fly. These filters are automatically applied to all your Prometheus queries.
Annotations
Annotations allow you to overlay rich event information on top of graphs. You add annotation queries via the Dashboard menu / Annotations view.
Prometheus supports two ways to query annotations.
- A regular metric query
- A Prometheus query for pending and firing alerts (for details see Inspecting alerts during runtime)
The step option is useful to limit the number of events returned from your query.
Get Grafana metrics into Prometheus
Grafana exposes metrics for Prometheus on the /metrics endpoint. We also bundle a dashboard within Grafana so you can get started viewing your metrics faster. You can import the bundled dashboard by going to the data source edit page and click the dashboard tab. There you can find a dashboard for Grafana and one for Prometheus. Import and start viewing all the metrics!
For detailed instructions, refer to Internal Grafana metrics.
Prometheus API
The Prometheus data source works with other projects that implement the Prometheus query API including:
For more information on how to query other Prometheus-compatible projects from Grafana, refer to the specific project documentation.
Provision the Prometheus data source
You can configure data sources using config files with Grafana’s provisioning system. Read more about how it works and all the settings you can set for data sources on the provisioning docs page.
Here are some provisioning examples for this data source:
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: Prometheus
type: prometheus
# Access mode - proxy (server in the UI) or direct (browser in the UI).
access: proxy
url: http://localhost:9090
jsonData:
httpMethod: POST
exemplarTraceIdDestinations:
# Field with internal link pointing to data source in Grafana.
# datasourceUid value can be anything, but it should be unique across all defined data source uids.
- datasourceUid: my_jaeger_uid
name: traceID
# Field with external link.
- name: traceID
url: 'http://localhost:3000/explore?orgId=1&left=%5B%22now-1h%22,%22now%22,%22Jaeger%22,%7B%22query%22:%22$${__value.raw}%22%7D%5D'Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus
The Prometheus data source works with Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus. If you are using an AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) policy to control access to your Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus domain, then you must use AWS Signature Version 4 (AWS SigV4) to sign all requests to that domain. For more details on AWS SigV4, refer to the AWS documentation.
Note: Grafana version 7.3.5 or higher is required to use SigV4 authentication.
To connect the Prometheus data source to Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus using SigV4 authentication, refer to the AWS guide to Set up Grafana open source or Grafana Enterprise for use with AMP.
If you are running Grafana in an Amazon EKS cluster, follow the AWS guide to Query using Grafana running in an Amazon EKS cluster.
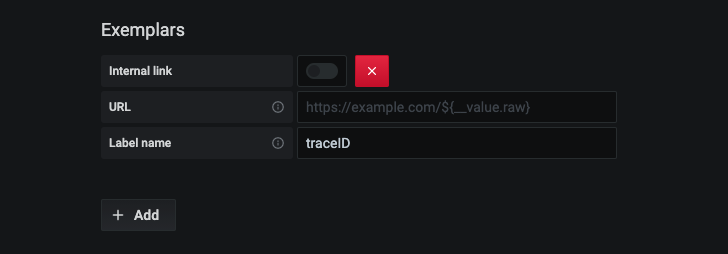
Configuring exemplars
Note: This feature is available in Prometheus 2.26+ and Grafana 7.4+.
Grafana 7.4 and later versions have the capability to show exemplars data alongside a metric both in Explore and Dashboards.
Exemplars are a way to associate higher cardinality metadata from a specific event with traditional timeseries data.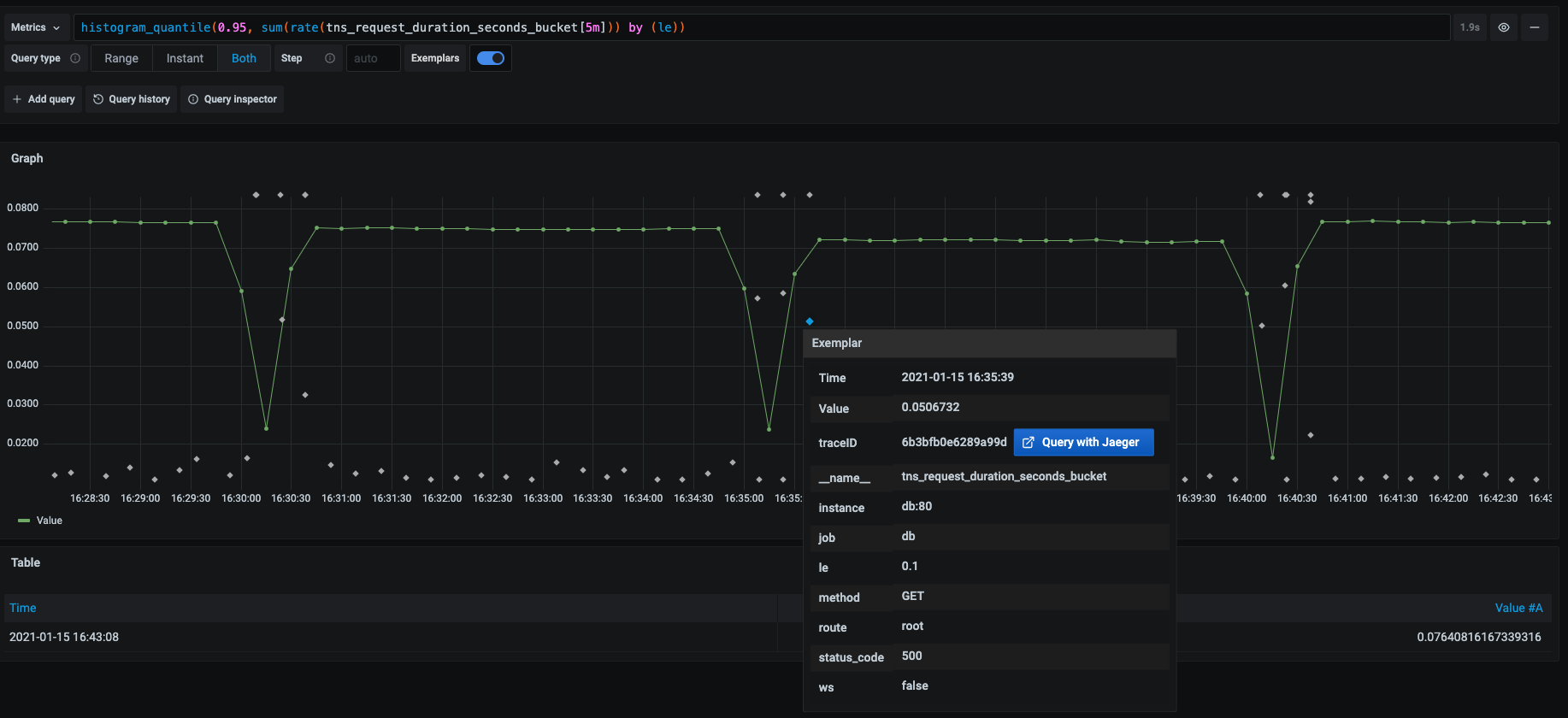
Configure Exemplars in the data source settings by adding external or internal links.