Important: This documentation is about an older version. It's relevant only to the release noted, many of the features and functions have been updated or replaced. Please view the current version.
Table Panel

The table panel is very flexible, supporting both multiple modes for time series as well as for table, annotation and raw JSON data. It also provides date formatting and value formatting and coloring options.
To view table panels in action and test different configurations with sample data, check out the Table Panel Showcase in the Grafana Playground.
Querying Data
The table panel displays the results of a query specified in the Metrics tab. The result being displayed depends on the datasource and the query, but generally there is one row per datapoint, with extra columns for associated keys and values, as well as one column for the numeric value of the datapoint. You can change the behavior in the section Data to Table below.
Merge Multiple Queries per Table
Only available in Grafana v5.0+.
Sometimes it is useful to display the results of multiple queries in the same table on corresponding rows, e.g., when comparing capacity and actual usage of resources. In this example usage and capacity are metrics that will have corresponding datapoints, while their associated keys and values can be used to match them. (This matching is only available with the Table Transform set to Table.)
In its simplest case, both queries return time-series data with a numeric value and a timestamp. If the timestamps are the same, datapoints will be matched and rendered on the same row. Some datasources return keys and values (labels, tags) associated with the datapoint. These are being matched as well if they are present in both results and have the same value. The following datapoints will end up on the same row with one time column, two label columns (“host” and “job”) and two value columns:
Datapoint for query A: {time: 1, host: "node-2", job: "job-8", value: 3}
Datapoint for query B: {time: 1, host: "node-2", value: 4}The following two results cannot be matched and will be rendered on separate rows:
Different time
Datapoint for query A: {time: 1, host: "node-2", job: "job-8", value: 3}
Datapoint for query B: {time: 2, host: "node-2", value: 4}
Different label "host"
Datapoint for query A: {time: 1, host: "node-2", job: "job-8", value: 3}
Datapoint for query B: {time: 1, host: "node-9", value: 4}You can still merge both of the above cases by changing the conflicting column’s Type to hidden in the Column Styles.
Note that if each datapoint of your query results have multiple value fields like max, min, mean, etc., they will likely have different values and therefore will not match and render on separate rows. If you intend for rows to be merged but see them rendered on separate rows, check the query results in the Query Inspector for field values being identical across datapoints that should be merged into a row.
Options overview
The table panel has many ways to manipulate your data for optimal presentation.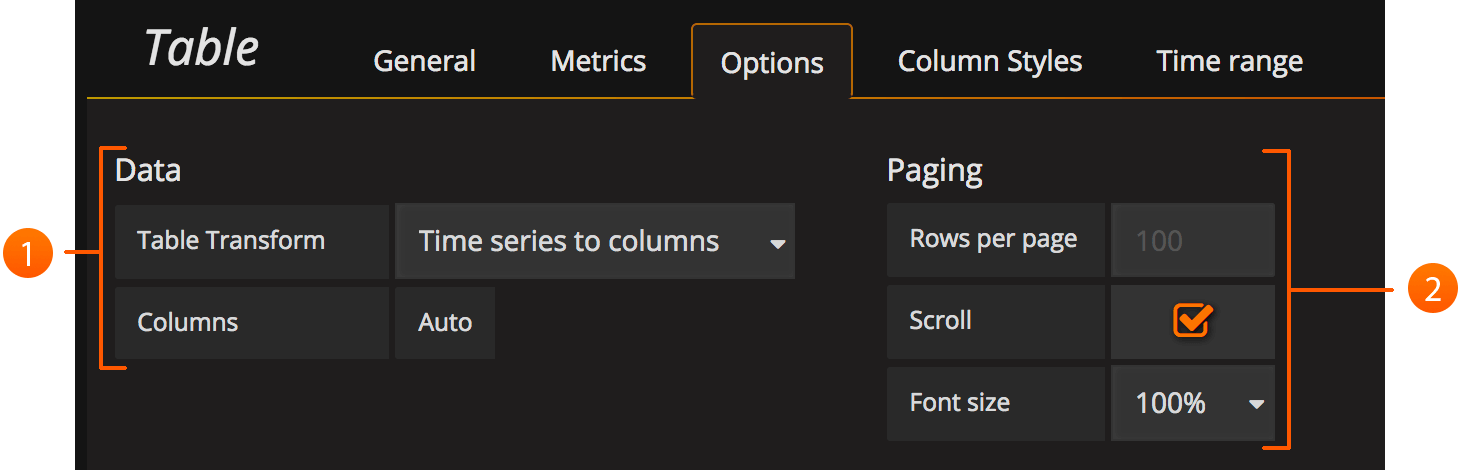
- Data: Control how your query is transformed into a table.
- Paging: Table display options.
Data to Table
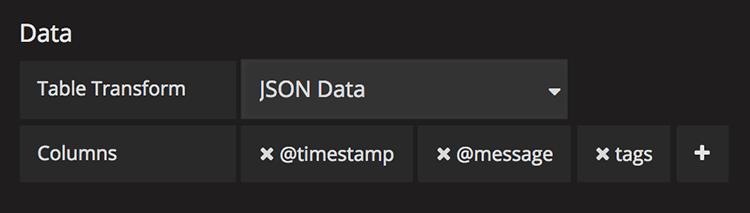
The data section contains the To Table Transform (1). This is the primary option for how your data/metric query should be transformed into a table format. The Columns (2) option allows you to select what columns you want in the table. Only applicable for some transforms.
Time series to rows
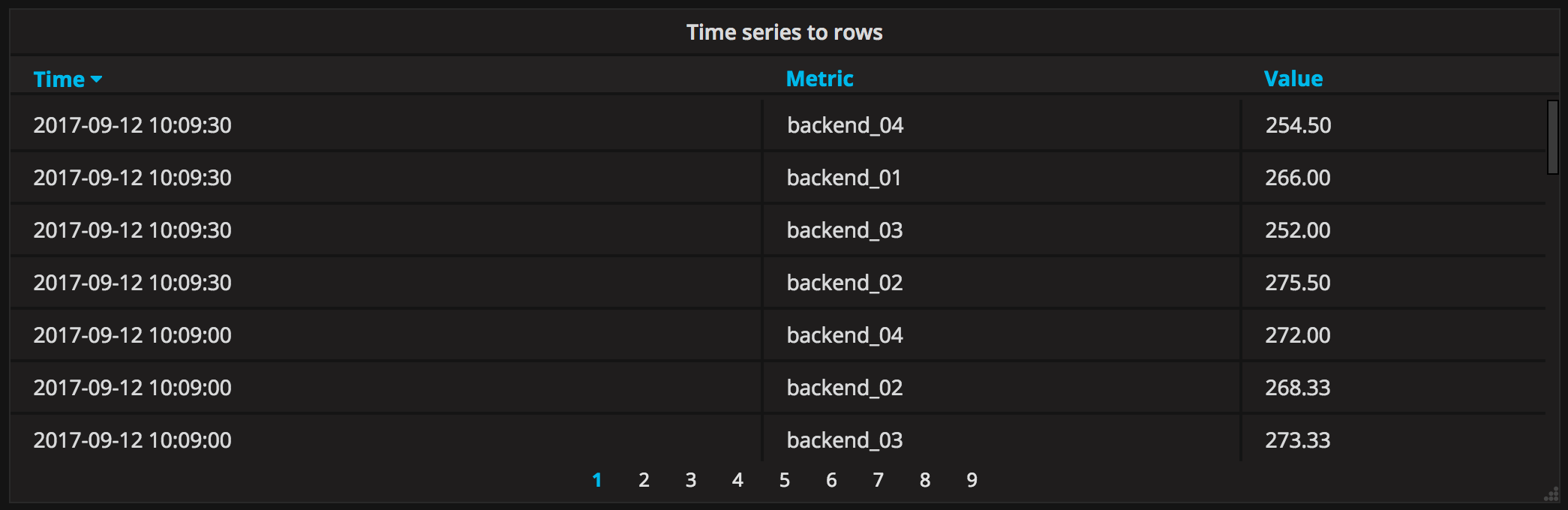
In the most simple mode you can turn time series to rows. This means you get a Time, Metric and a Value column. Where Metric is the name of the time series.
Time series to columns
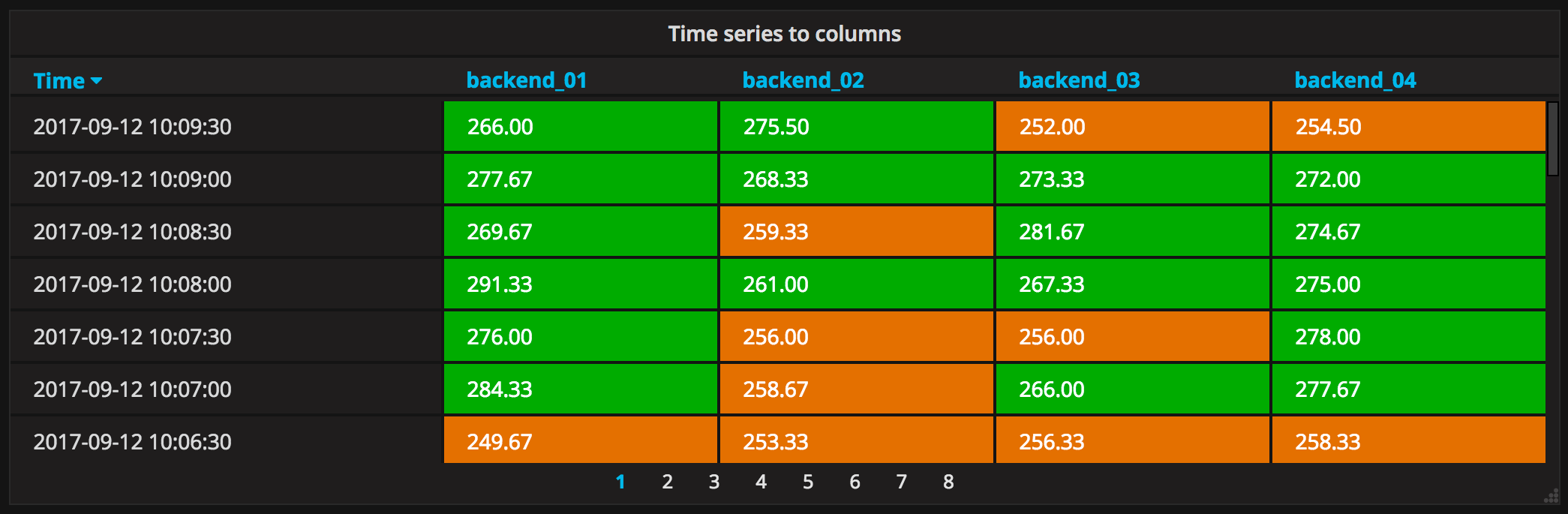
This transform allows you to take multiple time series and group them by time. Which will result in the primary column being Time and a column for each time series.
Time series aggregations
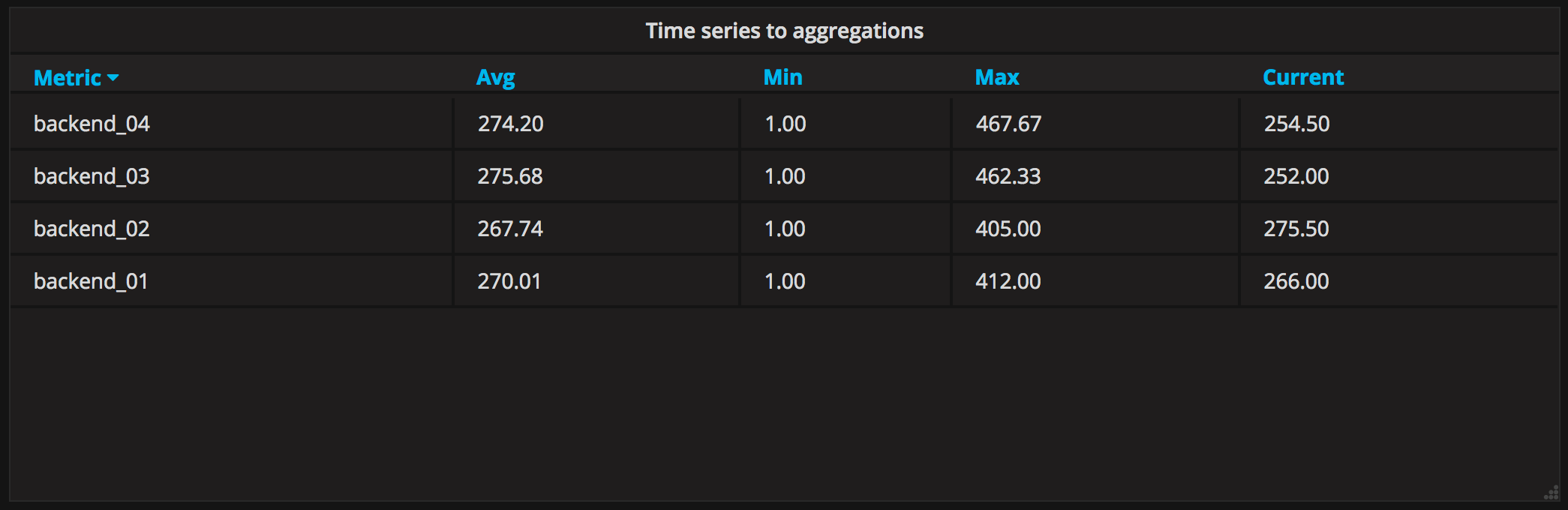
This table transformation will lay out your table into rows by metric, allowing columns of Avg, Min, Max, Total, Current and Count. More than one column can be added.
Annotations
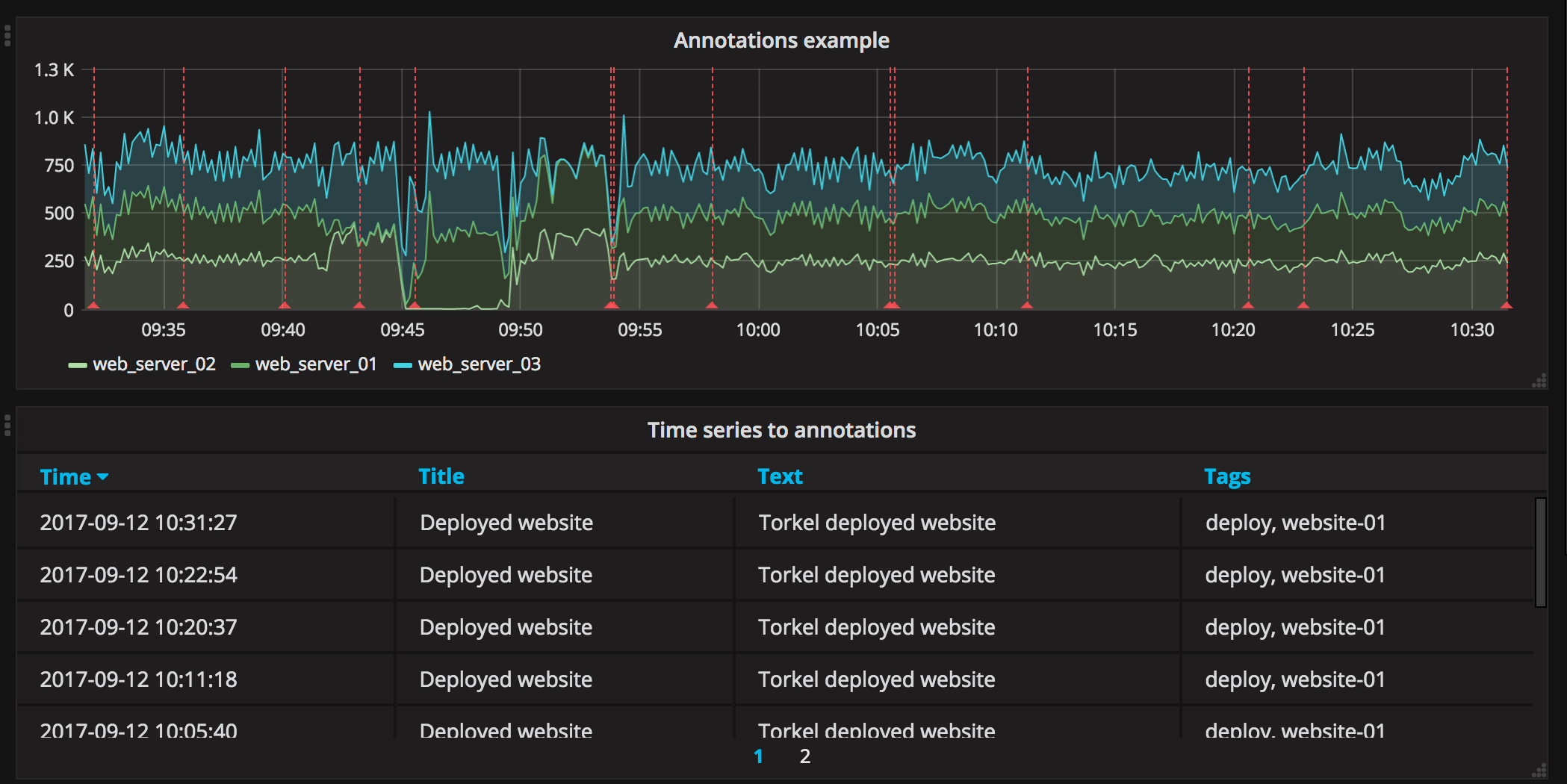
If you have annotations enabled in the dashboard you can have the table show them. If you configure this mode then any queries you have in the metrics tab will be ignored.
JSON Data
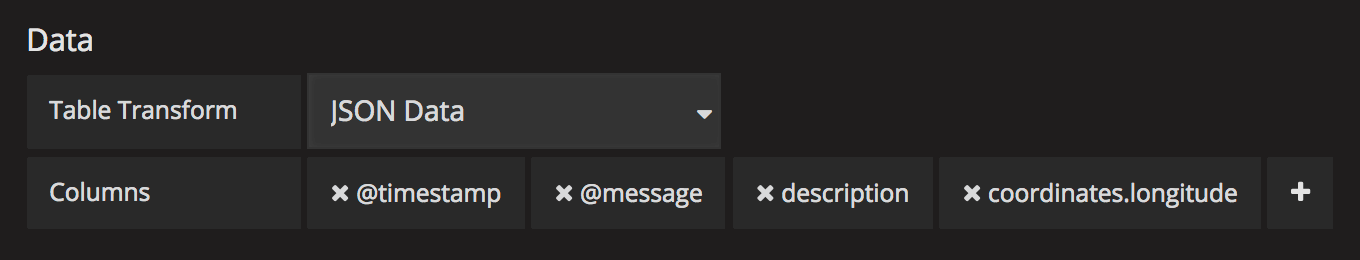
If you have an Elasticsearch Raw Document query or an Elasticsearch query without a date histogram use this transform mode and pick the columns using the Columns section.
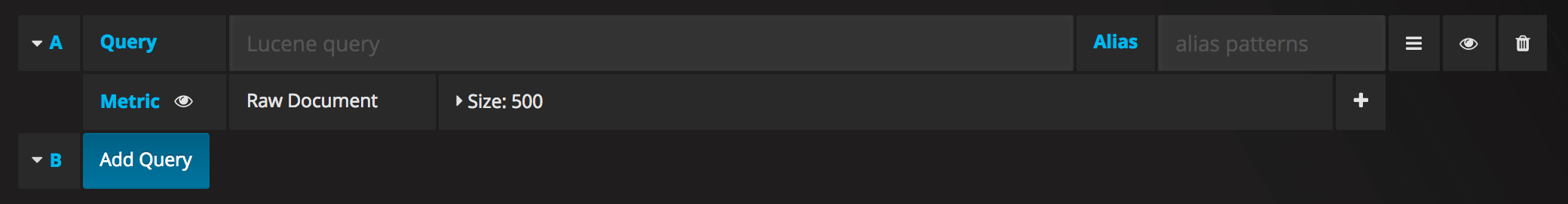
Table Display
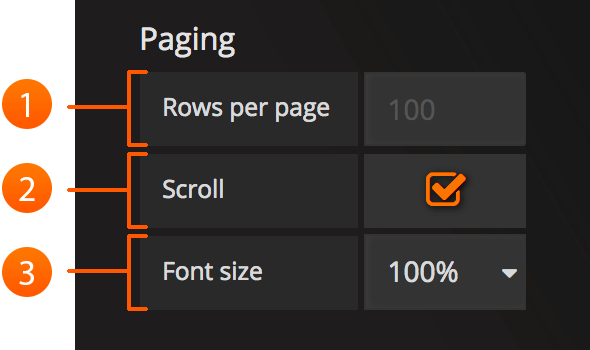
- Rows Per Page: The table display fields allow you to control how many rows per page there should be. For example, if your table had 95 records with a rows per page value of 10, your table would be split across 10 pages.
- Scroll: The scroll bar checkbox toggles the ability to scroll within the panel, when unchecked, the panel height will grow to display all rows.
- Font Size: The font size field allows you to increase or decrease the size for the panel, relative to the default font size.
Column Styles
The column styles allow you control how dates and numbers are formatted.
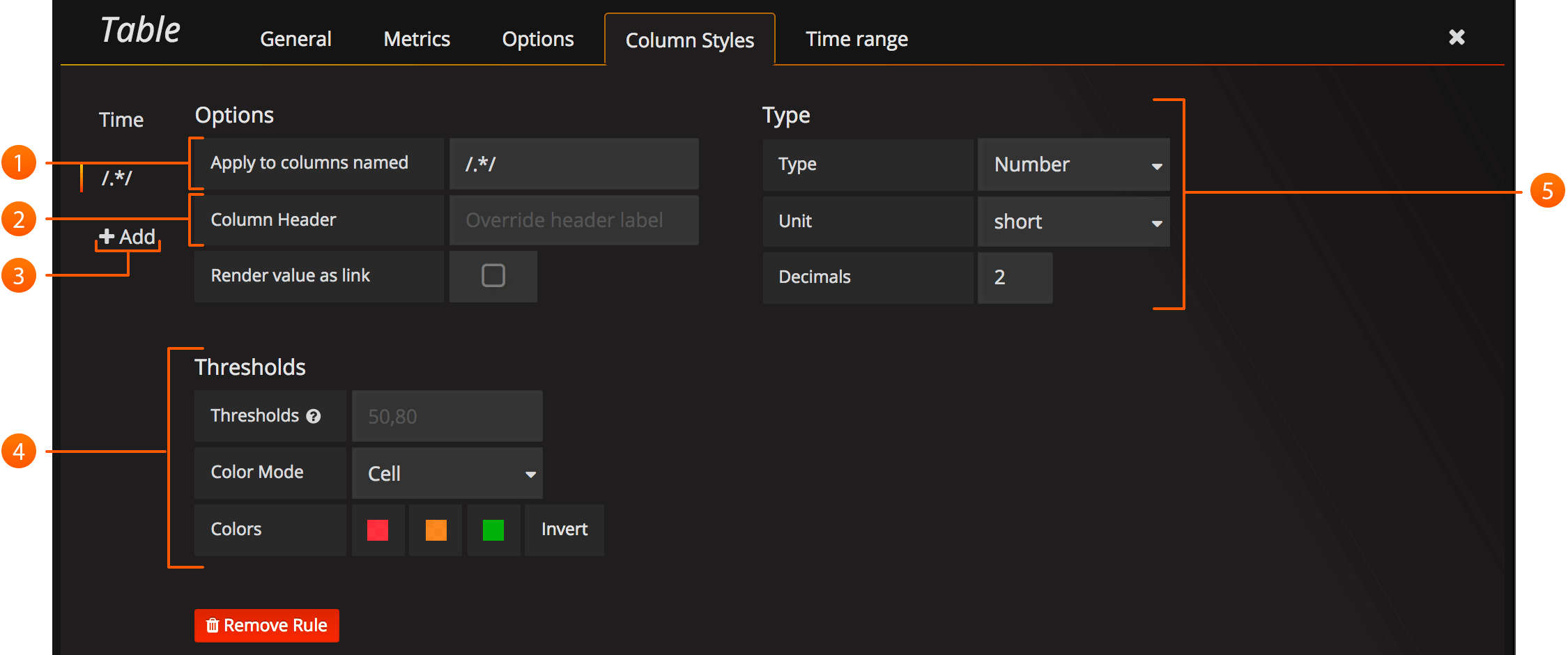
- Name or regex: The Name or Regex field controls what columns the rule should be applied to. The regex or name filter will be matched against the column name not against column values.
- Column Header: Title for the column, when using a Regex the title can include replacement strings like
$1. - Add column style rule: Add new column rule.
- Thresholds and Coloring: Specify color mode and thresholds limits.
- Type: The three supported types of types are Number, String and Date. Unit and Decimals: Specify unit and decimal precision for numbers. Format: Specify date format for dates.
String
Value/Range to text mapping
Only available in Grafana v5.1+.
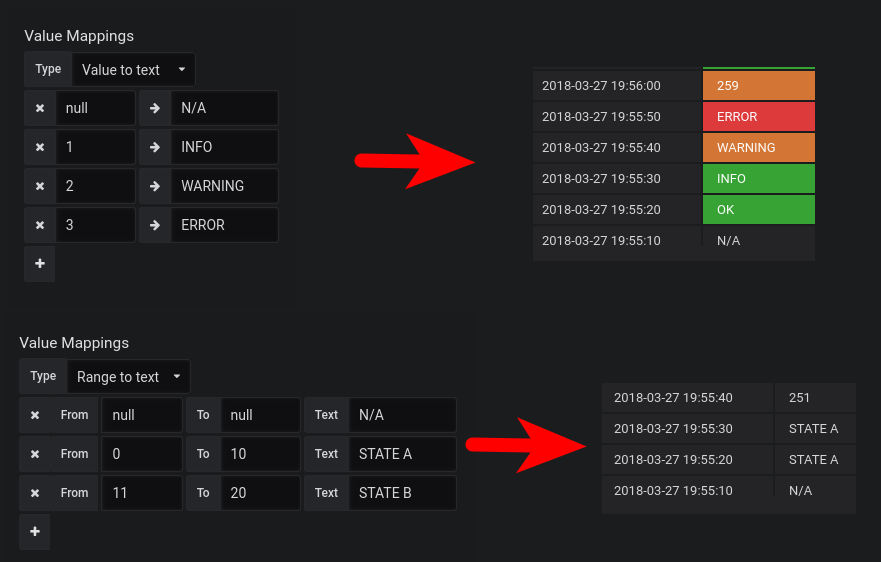
Value/range to text mapping allows you to translate numeric values into explicit text. The text will respect all styling, thresholds and customization defined for the value. This can be useful to translate the numeric values into a context-specific human-readable word or message.



