Important: This documentation is about an older version. It's relevant only to the release noted, many of the features and functions have been updated or replaced. Please view the current version.
Using Prometheus in Grafana
Grafana includes built-in support for Prometheus.
Adding the data source to Grafana
- Open the side menu by clicking the Grafana icon in the top header.
- In the side menu under the
Dashboardslink you should find a link namedData Sources. - Click the
+ Add data sourcebutton in the top header. - Select
Prometheusfrom the Type dropdown.
NOTE: If you’re not seeing the
Data Sourceslink in your side menu it means that your current user does not have theAdminrole for the current organization.
Data source options
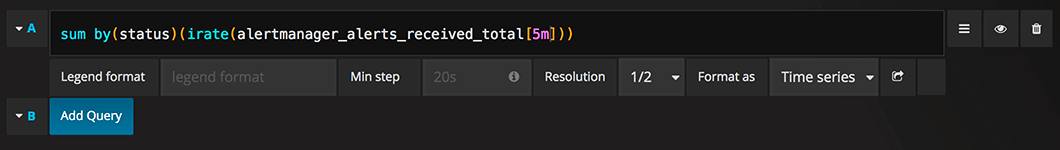
Query editor
Open a graph in edit mode by click the title > Edit (or by pressing e key while hovering over panel).
Templating
Instead of hard-coding things like server, application and sensor name in you metric queries you can use variables in their place. Variables are shown as dropdown select boxes at the top of the dashboard. These dropdowns makes it easy to change the data being displayed in your dashboard.
Checkout the Templating documentation for an introduction to the templating feature and the different types of template variables.
Query variable
Variable of the type Query allows you to query Prometheus for a list of metrics, labels or label values. The Prometheus data source plugin
provides the following functions you can use in the Query input field.
For details of metric names, label names and label values are please refer to the Prometheus documentation.
Using variables in queries
There are two syntaxes:
$<varname>Example: rate(http_requests_total{job=~"$job"}[5m])[[varname]]Example: rate(http_requests_total{job=~"[[job]]"}[5m])
Why two ways? The first syntax is easier to read and write but does not allow you to use a variable in the middle of a word. When the Multi-value or Include all value
options are enabled, Grafana converts the labels from plain text to a regex compatible string. Which means you have to use =~ instead of =.
Annotations
Annotations allows you to overlay rich event information on top of graphs. You add annotation queries via the Dashboard menu / Annotations view.
Prometheus supports two ways to query annotations.
- A regular metric query
- A Prometheus query for pending and firing alerts (for details see Inspecting alerts during runtime)
The step option is useful to limit the number of events returned from your query.
Getting Grafana metrics into Prometheus
Since 4.6.0 Grafana exposes metrics for Prometheus on the /metrics endpoint. We also bundle a dashboard within Grafana so you can get started viewing your metrics faster. You can import the bundled dashboard by going to the data source edit page and click the dashboard tab. There you can find a dashboard for Grafana and one for Prometheus. Import and start viewing all the metrics!
Configure the Datasource with Provisioning
It’s now possible to configure datasources using config files with Grafana’s provisioning system. You can read more about how it works and all the settings you can set for datasources on the provisioning docs page
Here are some provisioning examples for this datasource.
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: Prometheus
type: prometheus
access: proxy
url: http://localhost:9090