This is documentation for the next version of Grafana documentation. For the latest stable release, go to the latest version.
Data source management
Grafana supports many different storage backends for your time series data (data source). Refer to data sources for more information about using data sources in Grafana. Only users with the organization admin role can add data sources.
For links to data source-specific documentation, see Data sources.
Data source permissions
You can configure data source permissions to allow or deny certain users the ability to query, edit, or administrate a data source. Each data source’s configuration includes a Permissions tab where you can restrict data source permissions to specific users, service accounts, teams, or roles.
- The
querypermission allows users to query the data source. - The
editpermission allows users to query the data source, edit the data source’s configuration and delete the data source. - The
adminpermission allows users to query and edit the data source, change permissions on the data source and enable or disable query caching for the data source.
Note
Available in Grafana Enterprise and Grafana Cloud.
By default, data sources in an organization can be queried by any user in that organization. For example, a user with the Viewer role can issue any possible query to a data source, not just queries that exist on dashboards to which they have access. Additionally, by default, data sources can be edited by the user who created the data source, as well as users with the Admin role.
Assign data source permissions to users, service accounts, teams, or roles
You can assign data source permissions to users, service accounts, teams, and roles which will allow access to query, edit, or administrate the data source.
- Click Connections in the left-side menu.
- Under Your connections, click Data sources.
- Select the data source to which you want to assign permissions.
- On the Permissions tab, click Add a permission.
- Select User, Service Account, Team, or Role.
- Select the entity for which you want to modify permissions.
- Select the Query, Edit, or Admin permission.
- Click Save.
Edit data source permissions for users, service accounts, teams, or roles
- Click Connections in the left-side menu.
- Under Your connections, click Data sources.
- Select the data source for which you want to edit permissions.
- On the Permissions tab, find the User, Service Account, Team, or Role permission you want to update.
- Select a different option in the Permission dropdown.
Remove data source permissions for users, service accounts, teams, or roles
- Click Connections in the left-side menu.
- Under Your connections, click Data sources.
- Select the data source from which you want to remove permissions.
- On the Permissions tab, find the User, Service Account, Team, or Role permission you want to remove.
- Click the X next to the permission.
Query and resource caching
When you enable query and resource caching, Grafana temporarily stores the results of data source queries and resource requests. When you or another user submit the same query or resource request again, the results will come back from the cache instead of from the data source.
When using Grafana, a query pertains to a request for data frames to be modified or displayed. A resource relates to any HTTP requests made by a plugin, such as the Amazon Timestream plugin requesting a list of available databases from AWS. For more information on data source queries and resources, please see the developers page on backend plugins.
The caching feature works for all backend data sources. You can enable the cache globally in Grafana’s configuration, and configure a cache duration (also called Time to Live, or TTL) for each data source individually.
Note
Available in Grafana Enterprise and Grafana Cloud.
The following cache backend options are available: in-memory, Redis, and Memcached.
Note
Storing cached queries in-memory can increase Grafana’s memory footprint. In production environments, a Redis or Memcached backend is highly recommended.
When a panel queries a data source with cached data, it will either fetch fresh data or use cached data depending on the panel’s interval. The interval is used to round the query time range to a nearby cached time range, increasing the likelihood of cache hits. Therefore, wider panels and dashboards with shorter time ranges fetch new data more often than narrower panels and dashboards with longer time ranges.
A panel’s interval is visible in the query options. It is calculated as follows: time range / max data points. Max data points are calculated based on the width of the panel. For example, a wide panel with 1000 data points on a dashboard with a time range of last 7 days will retrieve fresh data every 10 minutes: 7d / 1000 = 10m. In this example, cached data for this panel will be served for up to 10 minutes before Grafana needs to query the data source again for new data.
You can configure a panel to retrieve data more often by increasing the Max data points setting in the panel’s query options.
Caching benefits
By reducing the number of queries and requests sent to data sources, caching can provide the following benefits:
- Faster dashboard load times, especially for popular dashboards.
- Reduced API costs.
- Reduced likelihood that APIs will rate-limit or throttle requests.
Data sources that work with query caching
Query caching works for Grafana’s built-in data sources, and backend data source plugins that extend the DataSourceWithBackend class in the plugins SDK.
Note
Logs Insights for the CloudWatch data source does not support query caching due to the way logs are requested from AWS.
To verify that a data source works with query caching, follow the instructions below to Enable and Configure query caching. If caching is enabled in Grafana but the Caching tab is not visible for the given data source, then query caching is not available for that data source.
Note
Some data sources, such as Elasticsearch, Prometheus, and Loki, cache queries themselves, so Grafana query caching does not significantly improve performance. However, resource caching may help. Refer to plugin resources for details.
Enable and configure query caching
You must be an Org admin or Grafana admin to enable query caching for a data source. For more information on Grafana roles and permissions, refer to About users and permissions.
By default, data source queries are not cached. To enable query caching for a single data source:
- Click Connections in the left-side menu.
- Under Your Connections, click Data sources.
- In the data source list, click the data source that you want to turn on caching for.
- Go to the Cache tab.
- Click Enable.
- (Optional) Choose custom TTLs for the data source’s queries and resources caching. If you skip this step, then Grafana uses the default TTL.
You can optionally override a data source’s configured TTL for individual dashboard panels. This can be useful when you have queries whose results change more or less often than the configured TTL. In the Edit Panel view, select the caching-enabled data source, expand the Query options, and enter your the TTL in milliseconds.
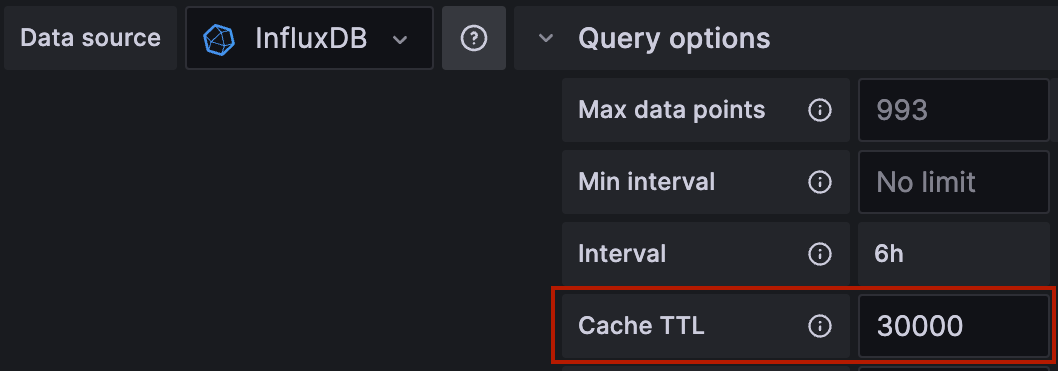
Note
If query caching is enabled and the Cache tab is not visible in a data source’s settings, then query caching is not available for that data source.
To configure global settings for query caching, refer to the caching section of Configure Grafana Enterprise.
Disable query caching
To disable query caching for a single data source:
- Click Connections in the left-side menu.
- Under Your Connections, click Data sources.
- In the data source list, click the data source that you want to turn off caching for.
- On the Cache tab, click Disable.
To disable query caching for an entire Grafana instance, set the enabled flag to false in the caching section of Configure Grafana Enterprise. You will no longer see the Cache tab on any data sources, and no data source queries will be cached.
Clear cache
If you experience performance issues or repeated queries become slower to execute, consider clearing your cache.
Note
This action impacts all cache-enabled data sources. If you are using Memcached, the system clears all data from the Memcached instance.
- Click Connections in the left-side menu.
- Under Your Connections, click Data sources.
- In the data source list, click the data source that you want to clear the cache for.
- In the Cache tab, click Clear cache.
Sending a request without cache
If a data source query request contains an X-Cache-Skip header, then Grafana skips the caching middleware, and does not search the cache for a response. This can be particularly useful when debugging data source queries using cURL.



