What's new from Grafana Labs
Grafana Labs products, projects, and features can go through multiple release stages before becoming generally available. These stages in the release life cycle can present varying degrees of stability and support. For more information, refer to release life cycle for Grafana Labs.
Loading...
Area of interest:
Cloud availability:
Cloud editions:
Self-managed availability:
Self-managed editions:
No results found. Please adjust your filters or search criteria.
There was an error with your request.
With this release, we’re rethinking our dashboard APIs and making the default a new model that is consistent, versioned, and resource-oriented.
We started the rollout in May. Since then, we’ve gathered feedback, measured impact, and improved testing. We’re now confident the APIs are stable and have made them the default.
We’re excited to announce the general availability of new alerting capabilities for Synthetic Monitoring. These new capabilities are available to all Grafana Cloud users.
You can now create alerts for each check in your Synthetic Monitoring application. For example, you can create an alert based on the number of check failures in a specific time window, with different settings for each one of your checks.
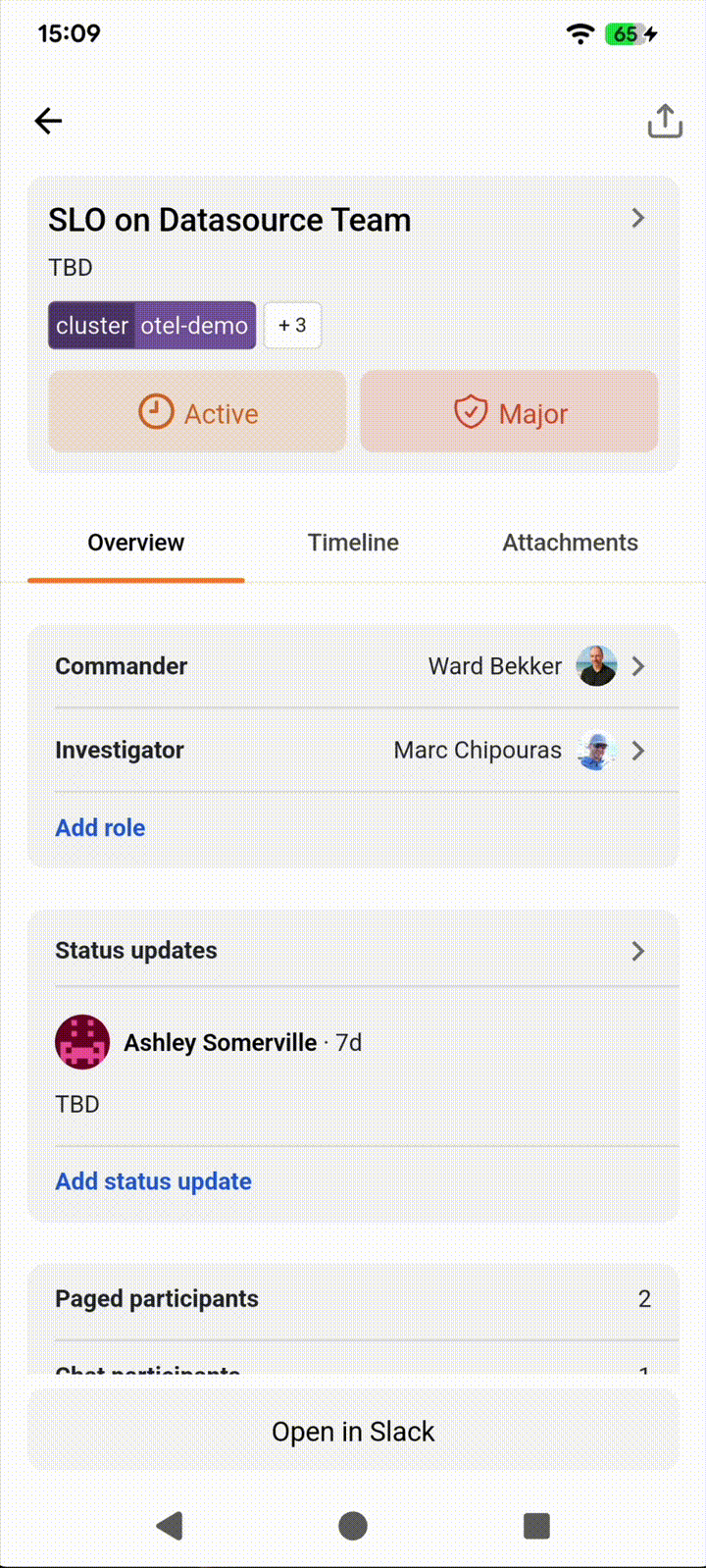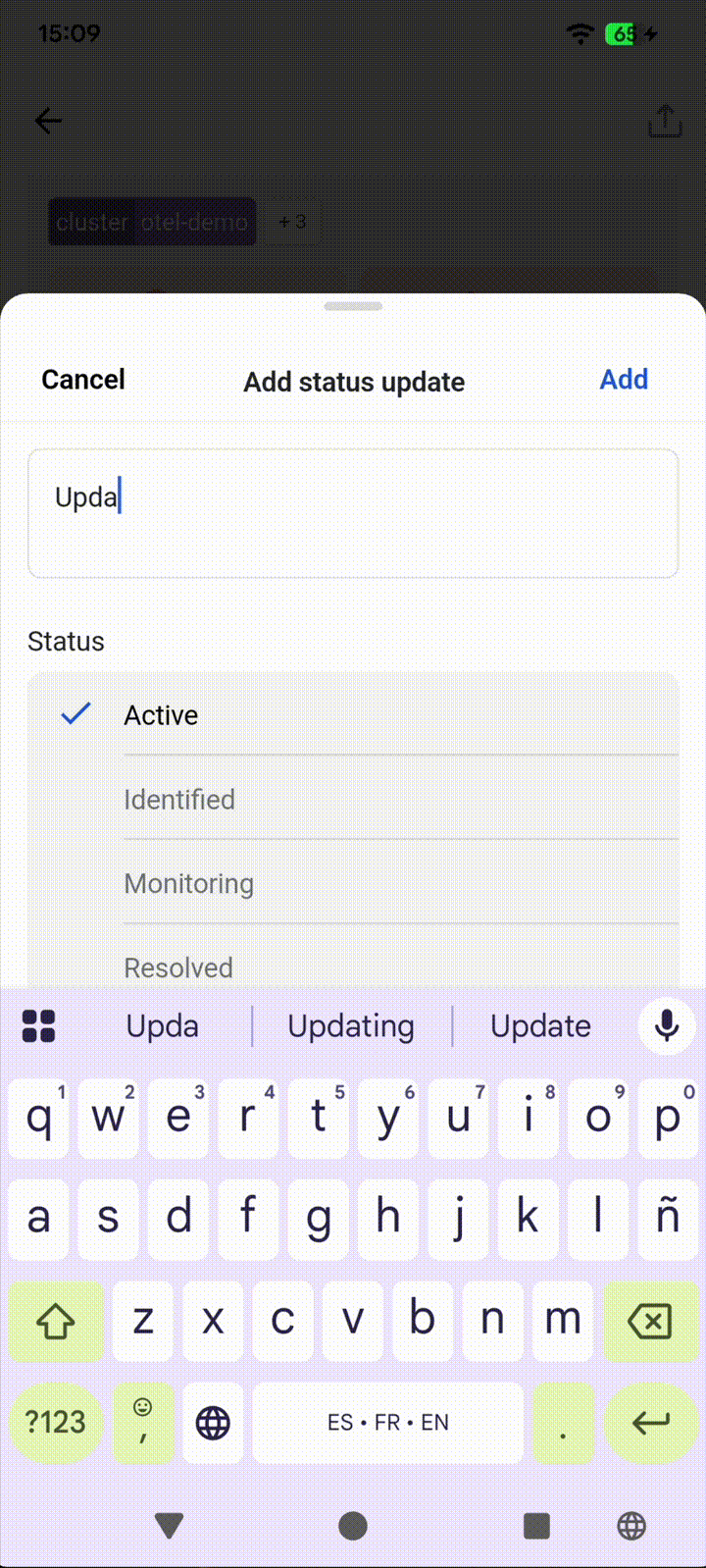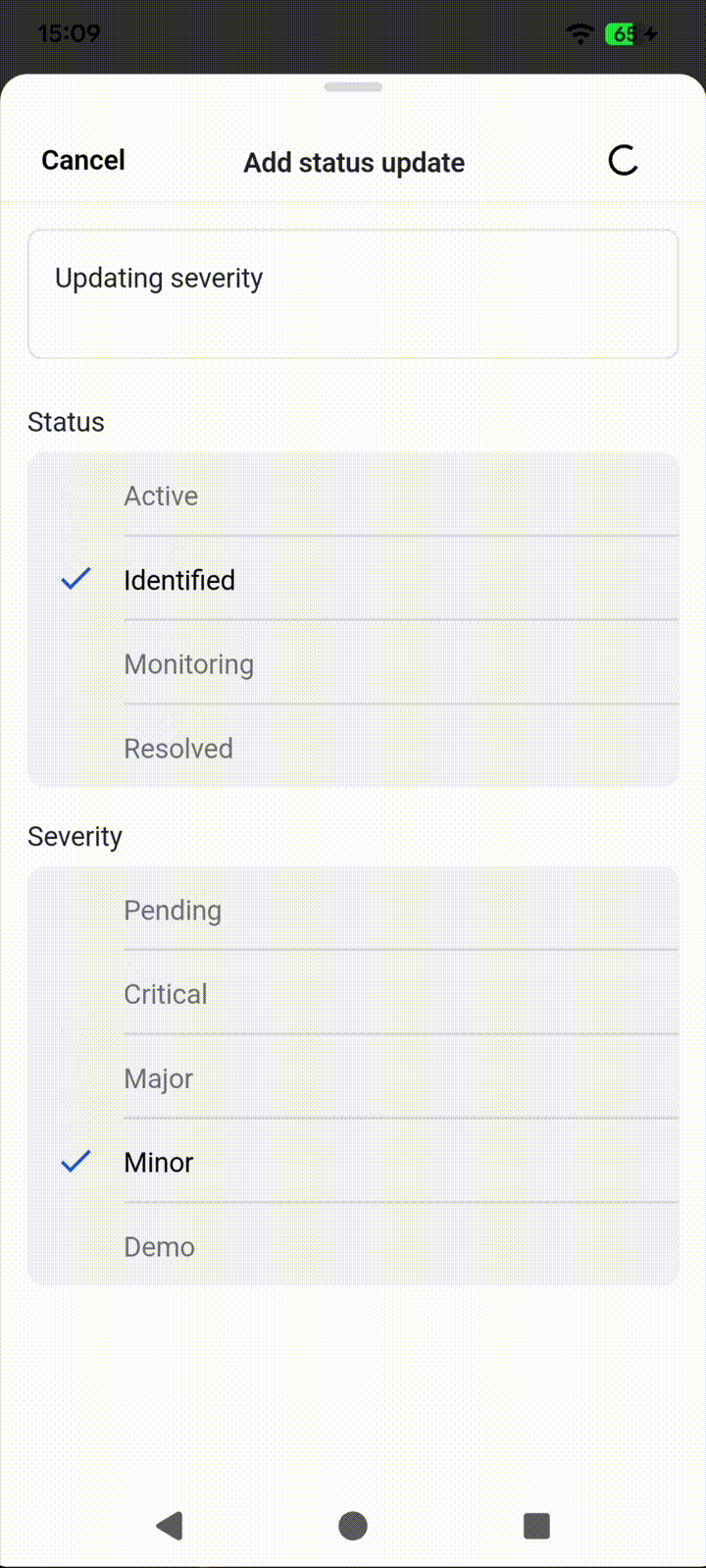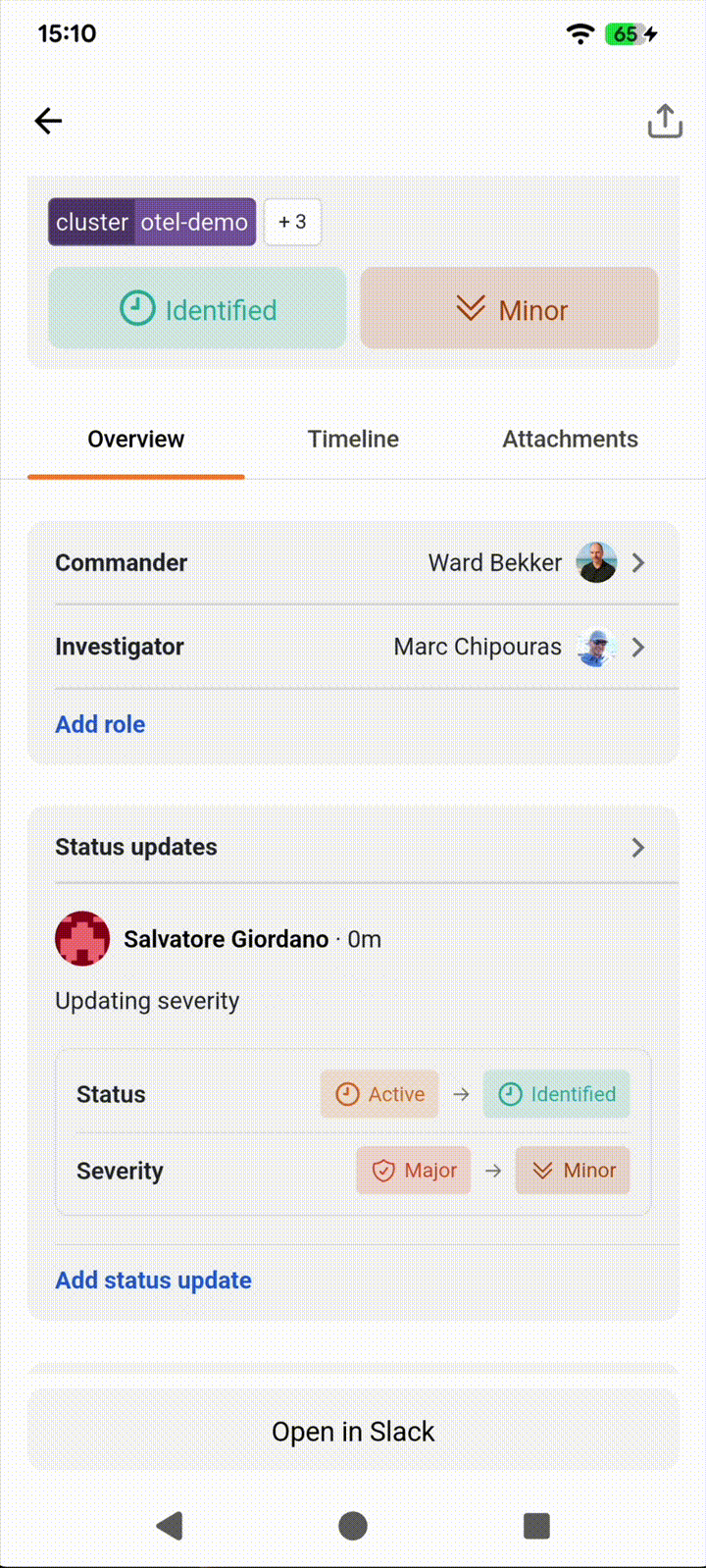
Status updates are crucial communication milestones during incident response, providing stakeholders with essential information about progress, status changes, and severity adjustments. Now you can view the complete timeline of key updates, see what changed and when, and contribute your own status updates with rich text content and “severity” or “status” modifications.
We are excited to announce the general availability of Amazon CloudWatch metric streams.
CloudWatch metric streams with Amazon Data Firehose offer you a less expensive, highly accurate way to import metrics from AWS into Grafana Cloud. As with CloudWatch metrics scrape, CloudWatch metric streams do not require you to deploy or maintain Alloy agents or servers and can be configured as code using Terraform or using a CloudFormation template.
You can now control the direction of connections between canvas elements by mapping the direction to a field value. A positive value draws the connection arrow forward, a negative value draws it in reverse, and a value of zero removes the directional arrow entirely. Alternatively, you can assign a fixed direction value.
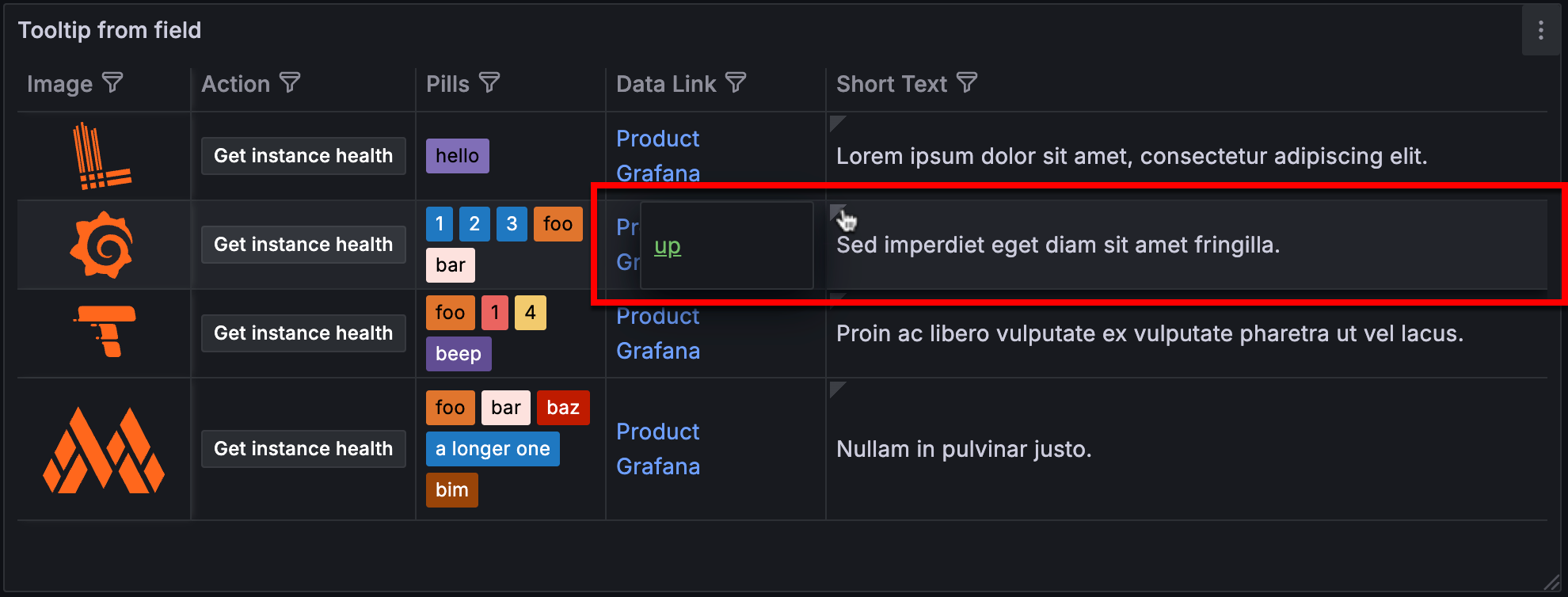
The Tooltip from field option in table visualizations allows you to use the values from another field (or column) in a tooltip.
When you toggle the switch on, you can select from a drop-down list any of the fields in the table to be used as the source of the tooltip content. All table fields are available for selection, whether visible or hidden.
We are excited to announce the general availability of k6 extensions in Grafana Cloud k6.
Grafana Assistant, Grafana’s AI tool within Grafana, is now available in Public Preview.
Grafana Assistant is an AI tool that can…
- … create dashboards.
- … write queries.
- … help you get onboarded.
- … support you in learning Grafana.
- … support in investigations and incidents.
Read our blog or watch a short video on how you can get started with Grafana Assistant.
The Jenkins data source allows you to query and visualize metrics such as projects, builds, build queues, nodes and load statistics from within Grafana.
This enterprise plugin includes two built-in dashboards to help you quickly get started visualizing Jenkins data:
We’re excited to announce the public preview release of secrets management for Synthetic Monitoring, available to all Grafana Cloud users.
Secrets management gives you a centralized place to securely store sensitive data like API keys, passwords, and tokens.
We’re excited to announce the integration of the Model Context Protocol (MCP) into Grafana Cloud Traces and into open-source Tempo (merged, available in Tempo 2.9). MCP, a standard developed by Anthropic, allows data sources to expose data and functionality to Large Language Models (LLMs) via an agent.
Grafana IRM outgoing webhooks now support incident events, providing a unified experience for automating alert group and incident workflows. You can configure webhooks from the Outgoing Webhooks tab and trigger requests based on key incident lifecycle events, such as when an incident is declared, updated, or resolved.
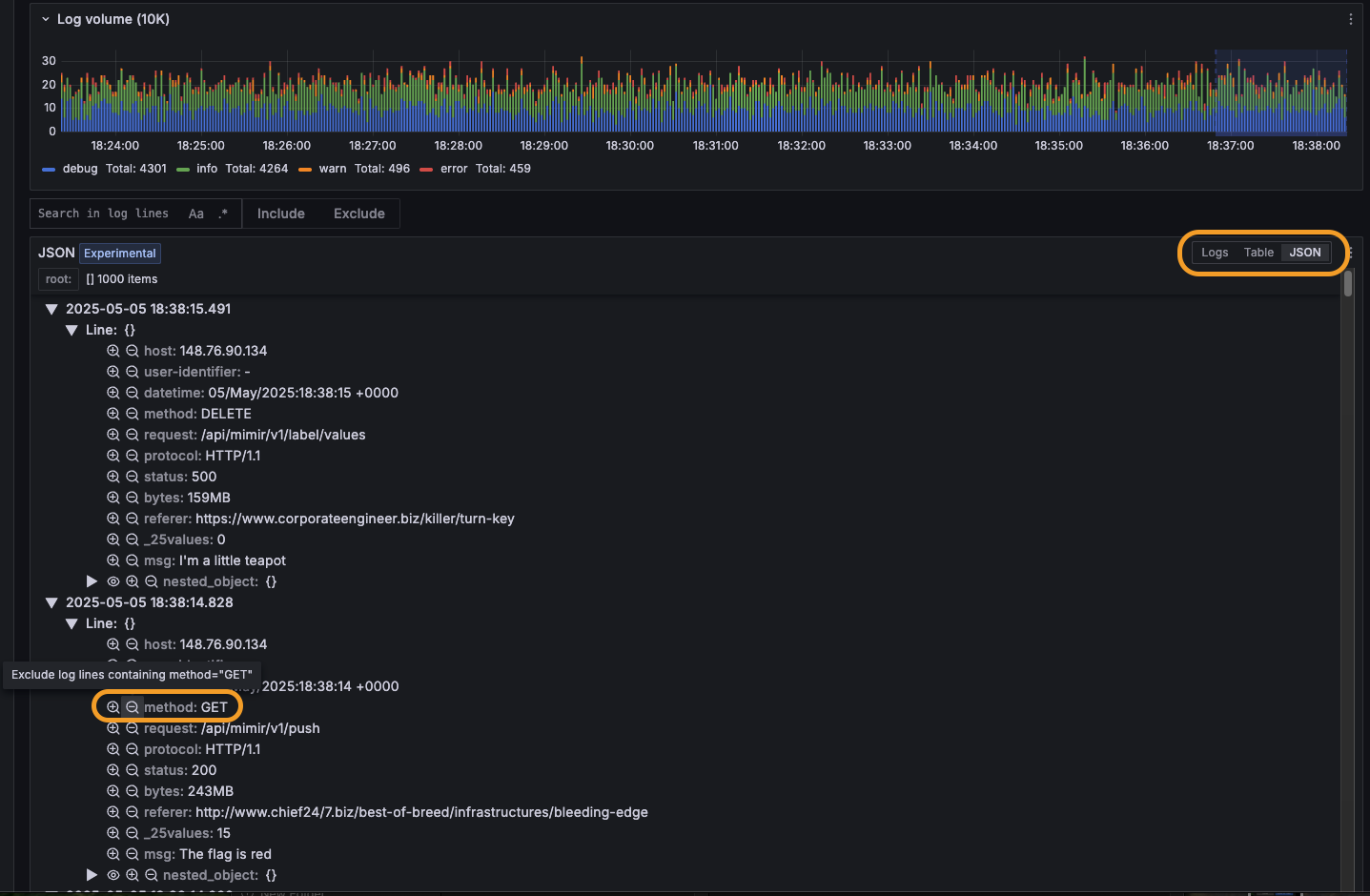
Using queryless experience of Metrics Drilldown to build an Alert Rule
The Challenge:
Creating effective alert rules often requires knowing exactly what query to write upfront. But sometimes you need to explore your data first — understanding how metrics behave across different label combinations, spotting patterns, and building confidence in your monitoring approach before committing to an alert rule.