State timeline
A state timeline visualization displays data in a way that shows state changes over time. In a state timeline, the data is presented as a series of bars or bands called state regions. State regions can be rendered with or without values, and the region length indicates the duration or frequency of a state within a given time range.
For example, if you’re monitoring the CPU usage of a server, you can use a state timeline to visualize the different states, such as “LOW,” “NORMAL,” “HIGH,” or “CRITICAL,” over time. Each state is represented by a different color and the lengths represent the duration of time that the server remained in that state:

The state timeline visualization is useful when you need to monitor and analyze changes in states or statuses of various entities over time. You can use one when you need to:
- Monitor the status of a server, application, or service to know when your infrastructure is experiencing issues over time.
- Identify operational trends over time.
- Spot any recurring issues with the health of your applications.
Configure a state timeline
With Grafana Play, you can explore and see how it works, learning from practical examples to accelerate your development. This feature can be seen on Grafana State Timeline & Status History.
Supported data formats
The state timeline visualization works best if you have data capturing the various states of entities over time, formatted as a table. The data must include:
- Timestamps - Indicate when each state change occurred. This could also be the start time for the state change. You can also add an optional timestamp to indicate the end time for the state change.
- Entity name/identifier - Represents the name of the entity you’re trying to monitor.
- State value - Represents the state value of the entity you’re monitoring. These can be string, numerical, or boolean states.
Each state ends when the next state begins or when there is a null value.
Example 1
The following example has a single time column and includes null values:
The data is converted as follows, with the null and empty values visualized as gaps in the state timeline:
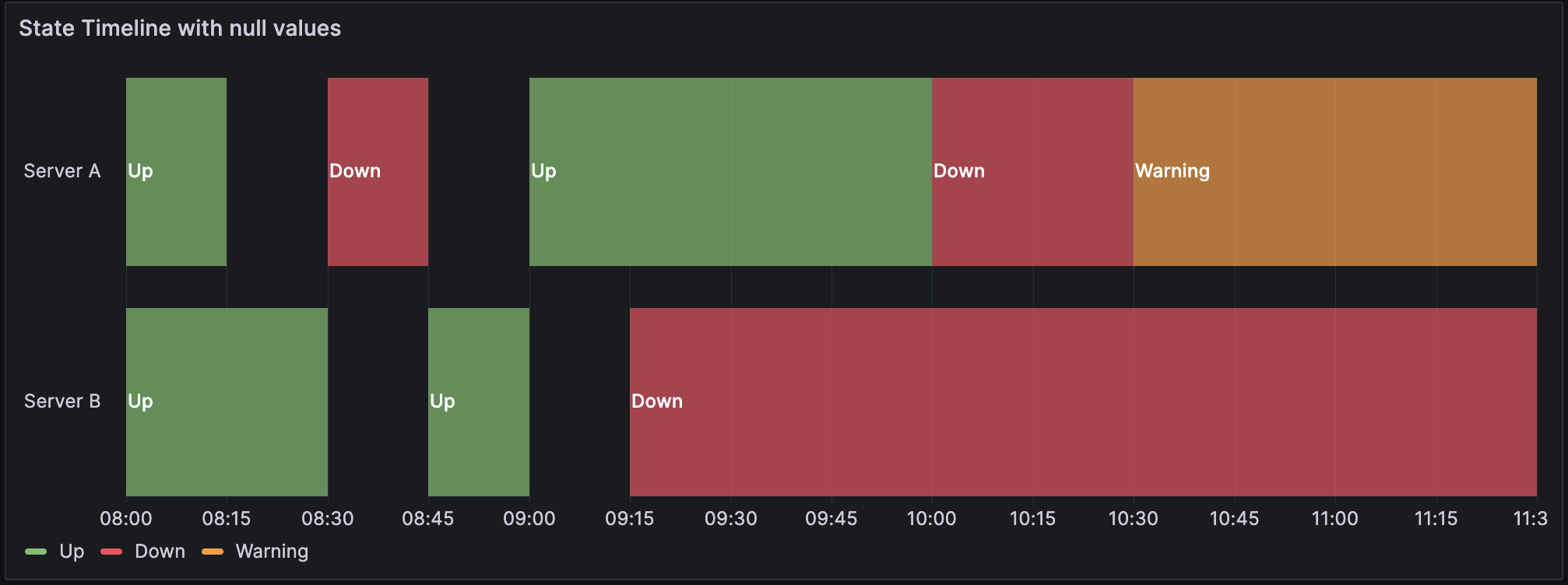
Example 2
The following example has two time columns and doesn’t include any null values:
The data is converted as follows:
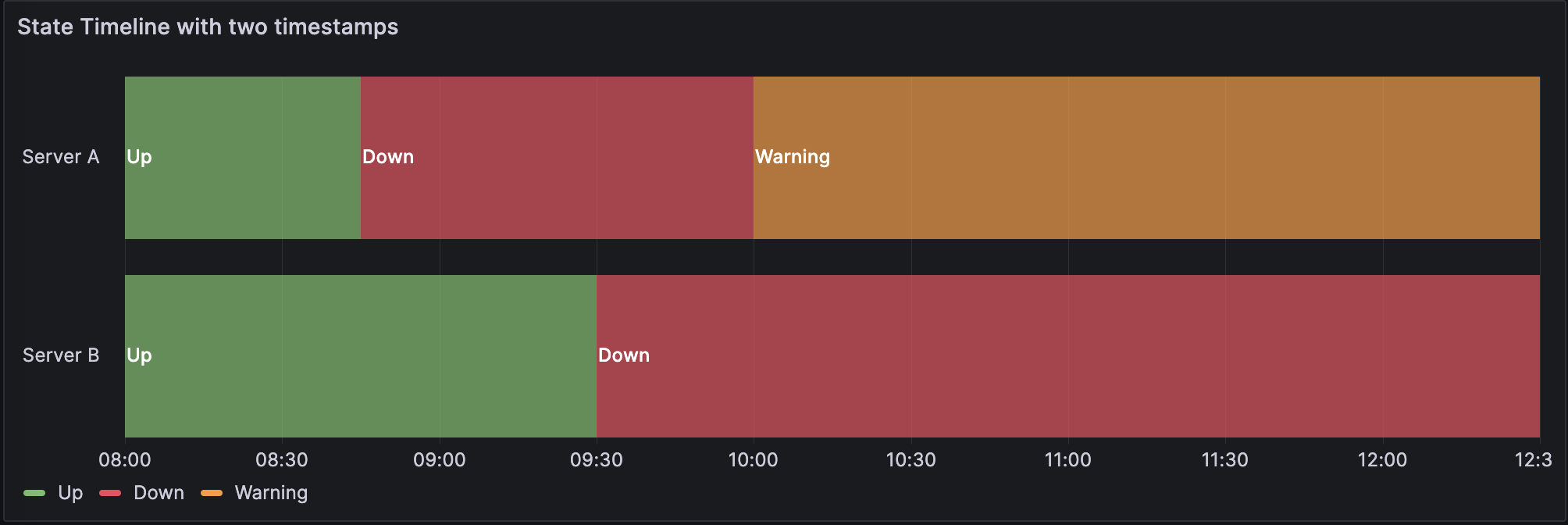
If your query results aren’t in a table format like the preceding examples, especially for time-series data, you can apply specific transformations to achieve this.
Time series data
You can also create a state timeline visualization using time series data. To do this, add thresholds, which turn the time series into discrete colored state regions.
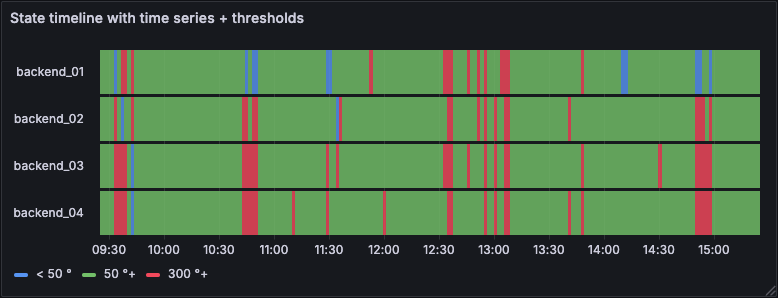
Zoom panel time range
You can zoom the panel time range in and out, which in turn, changes the dashboard time range.
Zoom in - Click and drag on the panel to zoom in on a particular time range.
Zoom out - Double-click anywhere on the panel to zoom out the time range.
When you zoom out, the range doubles with each double-click, adding equal time to each side of the range. For example, if the original time range is from 9:00 to 9:59, the time range changes as follow with each double-click:
- Next range: 8:30 - 10:29
- Next range: 7:30 - 11:29
For screen recordings showing these interactions, refer to the Panel overview documentation.
Configuration options
The following section describes the configuration options available in the panel editor pane for this visualization. These options are, as much as possible, ordered as they appear in Grafana.
Panel options
In the Panel options section of the panel editor pane, set basic options like panel title and description, as well as panel links. To learn more, refer to Configure panel options.
State timeline options
Use these options to refine the visualization.
Page size (enable pagination)
The Page size option lets you paginate the state timeline visualization to limit how many series are visible at once. This is useful when you have many series. With paginated results, the visualization displays a subset of all series on each page:
Connect null values
Choose how null values, which are gaps in the data, appear on the graph. Null values can be connected to form a continuous line or set to a threshold above which gaps in the data are no longer connected.
- Never - Time series data points with gaps in the data are never connected.
- Always - Time series data points with gaps in the data are always connected.
- Threshold - Specify a threshold above which gaps in the data are no longer connected. This can be useful when the connected gaps in the data are of a known size and/or within a known range, and gaps outside this range should no longer be connected.
Disconnect values
Choose whether to set a threshold above which values in the data should be disconnected.
- Never - Time series data points in the data are never disconnected.
- Threshold - Specify a threshold above which values in the data are disconnected. This can be useful when desired values in the data are of a known size and/or within a known range, and values outside this range should no longer be connected.
Legend options
When the legend option is enabled it can show either the value mappings or the threshold brackets. To show the value mappings in the legend, it’s important that the Color scheme as referenced in Color scheme is set to Single color or Classic palette. To see the threshold brackets in the legend set the Color scheme to From thresholds.
For more information about the legend, refer to Configure a legend.
Visibility
Toggle the switch to turn the legend on or off.
Mode
Use these settings to define how the legend appears in your visualization.
- List - Displays the legend as a list. This is a default display mode of the legend.
- Table - Displays the legend as a table.
Placement
Choose where to display the legend.
- Bottom - Below the graph.
- Right - To the right of the graph.
Width
Control how wide the legend is when placed on the right side of the visualization. This option is only displayed if you set the legend placement to Right.
Tooltip options
Tooltip options control the information overlay that appears when you hover over data points in the visualization.
Tooltip mode
When you hover your cursor over the visualization, Grafana can display tooltips. Choose how tooltips behave.
- Single - The hover tooltip shows only a single series, the one that you are hovering over on the visualization.
- All - The hover tooltip shows all series in the visualization. Grafana highlights the series that you are hovering over in bold in the series list in the tooltip.
- Hidden - Do not display the tooltip when you interact with the visualization.
Use an override to hide individual series from the tooltip.
Values sort order
When you set the Tooltip mode to All, the Values sort order option is displayed. This option controls the order in which values are listed in a tooltip. Choose from the following:
- None - Grafana automatically sorts the values displayed in a tooltip.
- Ascending - Values in the tooltip are listed from smallest to largest.
- Descending - Values in the tooltip are listed from largest to smallest.
Axis options
Standard options
Standard options in the panel editor pane let you change how field data is displayed in your visualizations. When you set a standard option, the change is applied to all fields or series. For more granular control over the display of fields, refer to Configure overrides.
To learn more, refer to Configure standard options.
Data links and actions
Data links allow you to link to other panels, dashboards, and external resources and actions let you trigger basic, unauthenticated, API calls. In both cases, you can carry out these tasks while maintaining the context of the source panel.
For each data link, set the following options:
- Title
- URL
- Open in new tab
- One click - Opens the data link with a single click. Only one data link can have One click enabled at a time.
For each action, define the following API call settings:
To learn more, refer to Configure data links and actions.
Value mappings
Value mapping is a technique you can use to change how data appears in a visualization.
For each value mapping, set the following options:
- Condition - Choose what’s mapped to the display text and (optionally) color:
- Value - Specific values
- Range - Numerical ranges
- Regex - Regular expressions
- Special - Special values like
Null,NaN(not a number), or boolean values liketrueandfalse
- Display text
- Color (Optional)
- Icon (Canvas only)
To learn more, refer to Configure value mappings.
Thresholds
A threshold is a value or limit you set for a metric that’s reflected visually when it’s met or exceeded. Thresholds are one way you can conditionally style and color your visualizations based on query results.
For each threshold, set the following options:
To learn more, refer to Configure thresholds.
Field overrides
Overrides allow you to customize visualization settings for specific fields or series. When you add an override rule, it targets a particular set of fields and lets you define multiple options for how that field is displayed.
Choose from the following override options:
To learn more, refer to Configure field overrides.



