Configure value mappings
In addition to field overrides, value mapping is a technique you can use to change how data appears in a visualization.
For example, the mapping applied in the following image causes the visualization to display the text Cold, Good, and Hot in blue, green, and red for ranges of temperatures rather than actual temperature values. Using value mappings this way can make data faster and easier to understand and interpret.
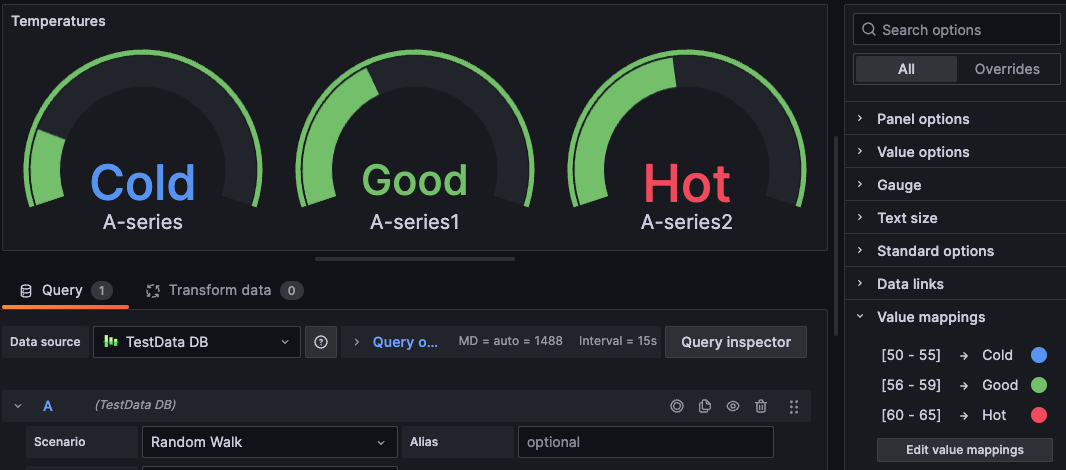
Value mappings bypass unit formatting set in the Standard options section of panel editor, like color or number of decimal places displayed. When value mappings are present in a panel, Grafana displays a summary of them in the Value mappings section of the editor panel.
Supported visualizations
You can configure value mappings for the following visualizations:
Types of value mappings
Grafana supports the following value mapping types:
Value
A Value mapping maps specific values to text and a color. For example, you can configure a mapping so that all instances of the value 10 appear as Perfection! rather than the number. Use Value mapping when you want to format a single value.

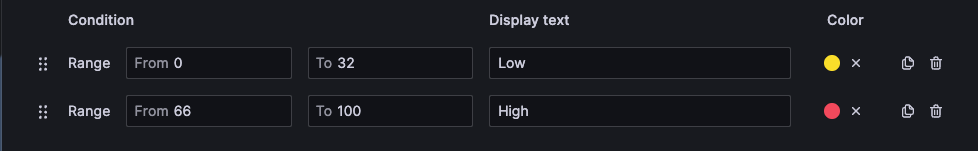
Range
A Range mapping maps numerical ranges to text and a color. For example, if a value is within a certain range, you can configure a range value mapping to display Low or High rather than the number. Use Range mapping when you want to format multiple, continuous values.
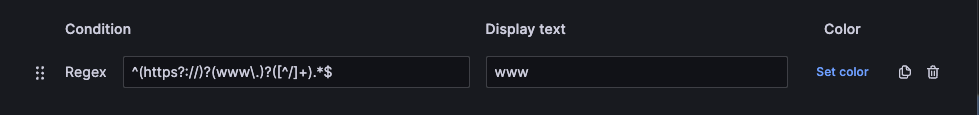
Regex
A Regex mapping maps regular expressions to text and a color. For example, if a value is www.example.com, you can configure a regular expression value mapping so that Grafana displays www and truncates the domain. Use the Regex mapping when you want to format the text and color of a regular expression value.
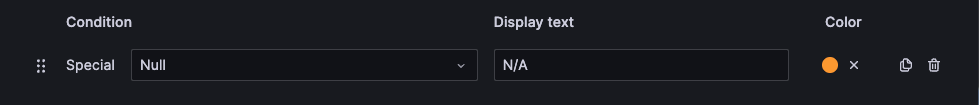
Special
A Special mapping maps special values like Null, NaN (not a number), and boolean values like true and false to text and color. For example, you can configure a special value mapping so that null values appear as N/A. Use the Special mapping when you want to format uncommon, boolean, or empty values.
Examples
Refer to the following examples to learn more about value mapping.
Time series example
The following image shows a time series visualization with value mappings. Value mapping colors aren’t applied to this visualization, but the display text is shown on the axis.
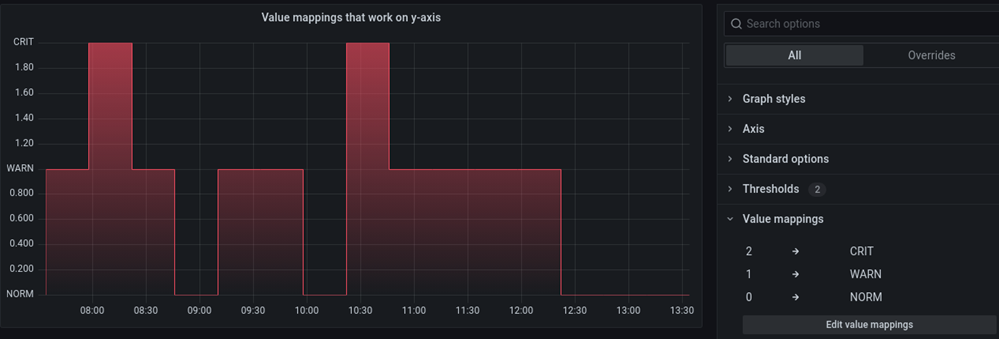
Stat example
The following image shows a stat visualization with value mappings and text colors applied. You can hide the sparkline so it doesn’t interfere with the values.
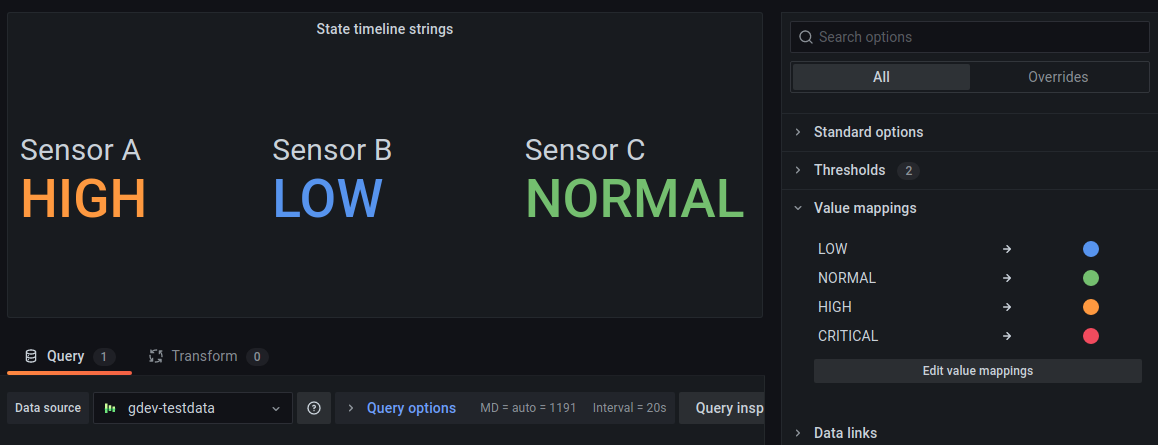
Bar gauge example
The following image shows a bar gauge visualization with value mappings. Note that the value mapping colors are applied to the text, but not to the gauges.
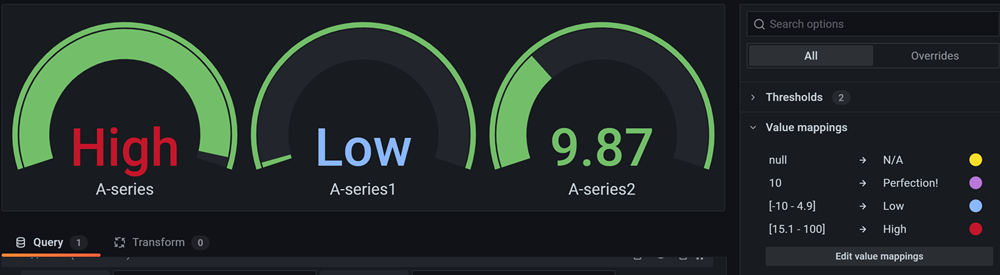
Table example
The following image shows a table visualization with value mappings. If you want value mapping colors displayed on the table, then set the cell display mode to Color text or Color background.
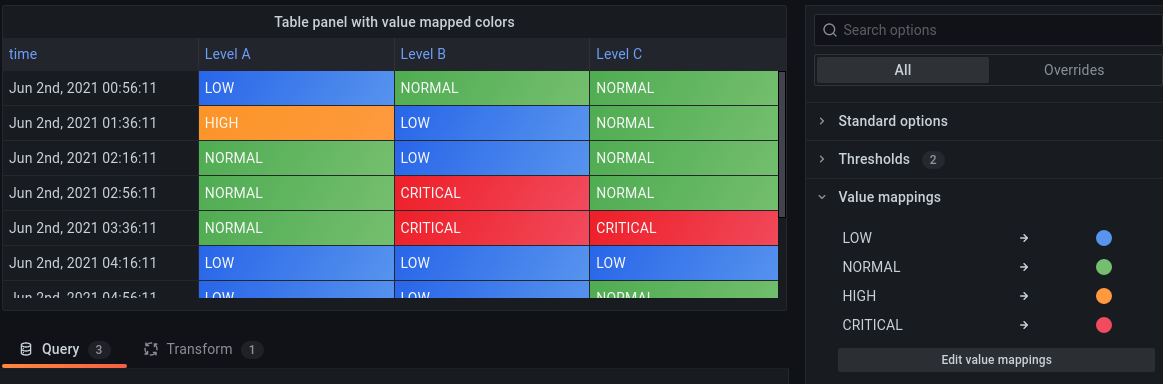
Add a value mapping
Navigate to the panel you want to update.
Hover over any part of the panel you want to work on to display the menu on the top right corner.
Click the menu and select Edit.
Scroll to the Value mappings section and expand it.
Click Add value mappings.
Click Add a new mapping and then select one of the following:
- Value - Enter a single value to match.
- Range - Enter the beginning and ending values of a range to match.
- Regex - Enter a regular expression pattern to match.
- Special - Select a special value to match.
(Optional) Enter display text.
(Optional) Set the color.
(Optional) Set an icon (canvas visualizations only).
Click Update to save the value mapping.
After you’ve added a mapping, the Edit value mappings button replaces the Add value mappings button. Click the edit button to add or update mappings.
- Click Save dashboard.
- Click Back to dashboard and then Exit edit.



