MCP server for tracing
Note
Grafana Cloud Traces MCP server is currently in public preview. Grafana Labs offers limited support, and breaking changes might occur prior to the feature being made generally available.
Grafana Cloud Traces includes a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that provides AI assistants and Large Language Models (LLMs) with direct access to distributed tracing data through TraceQL queries and other endpoints.
This integration lets you connect LLM-powered tools like Claude Code or Cursor to Grafana Cloud Traces, enabling you to use natural language prompts to:
- Explore services and understand their interactions
- Diagnose and investigate errors
- Optimize performance and reduce latency
The MCP server is built in and is available for all Grafana Cloud Traces users. You don’t need to install any additional plugins to use the MCP server.
For examples on how you can use the MCP server, refer to LLM-powered insights into your tracing data: introducing MCP support in Grafana Cloud Traces.
For more information on MCP, refer to the MCP documentation.
Before you begin
To set up the MCP server, you need a Grafana Cloud stack with Grafana and Grafana Tempo or Grafana Cloud Traces configured and receiving tracing data.
Configure the MCP server for your AI tool
These steps provide a general overview of how to configure the MCP server for an AI tool like Claude Code. The specific commands and configuration steps vary depending on the AI tool you are using.
The examples in this section use Claude Code. Refer to your AI tool’s documentation for your specific instructions.
Locate your stack’s URL, user, and password (token)
When you configure the MCP server, you need to provide the URL, user, and password (token) for your Grafana Cloud stack.
Refer to Locate your stack’s URL, user, and password for more details.
- Navigate to your Grafana Cloud stack.
- Select Details next to your stack.
- Locate Tempo and select Send Traces or Details.
- Locate the Using Grafana with Tempo section.
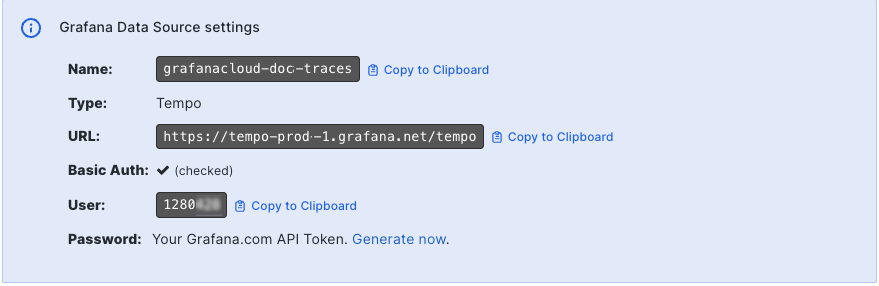
- Copy your user ID number and the stack’s URL. The URL is in the format
https://<your-stack-id>.grafana.net/tempo. - Copy the API token. If you don’t have a token, click Generate now to create a new API token with
readscopes.![Locate the SDK or Grafana Alloy configuration values]()
Add authentication to LLM agent
Your AI or LLM agent needs to be authenticated to access your tracing data. Refer to your LLM agent’s documentation on how to configure it to use basic authentication.
Here’s an example with Claude Code:
Open your terminal or command prompt.
Use the following command to create an environment variable containing your base64-encoded user ID and API token. Replace
<user>with your Grafana Cloud User ID and<token>with your generated API token:export GCT_AUTH=$(echo -n '<user>:<token>' | base64)
Configure the MCP server in your AI tool
Next, you need to configure your AI tool to access your tracing data.
Use the appropriate command to add your Grafana Cloud MCP server to your AI tool, using the URL, user, and password (token) you located in the previous steps. For example, to configure Claude Code, you would use the
claude mcp addcommand and replace<URL>with the Tempo URL you noted in step 1. The URL should be in the format:https://<your-stack-id>.grafana.net/tempo/api/mcp.claude mcp add tempo https://<URL>/api/mcp -t http -H 'Authorization: Basic ${GCT_AUTH}'Verify that your AI tool is connected to Cloud Traces or Tempo. For example, in Claude Code, you can use the
claude mcp listcommand to list the available MCP servers, their URLs, and connection status.