Azure Private Link and Fleet Management
Send telemetry data from your Azure Virtual Network to Grafana Cloud and Grafana Fleet Management using Azure Private Link so you can:
- Reduce your Azure egress costs.
- Improve security by keeping your data within the Azure network.
To use this feature, configure a Private Endpoint in your Azure Virtual Network. Your local agents can use this endpoint to route data to Grafana Cloud with Azure Private Link.
Before you begin
To use Azure Private Link, you must:
- Have a Grafana Cloud stack hosted on Azure and an Azure Virtual Network.
- Know the DNS name of every Grafana Cloud service you want to send data to.
- Provide to Grafana Support a list of Subscription IDs you plan to connect to Grafana Cloud.
Check if your stack is hosted on Azure
To check where your stack is hosted, follow these steps:
- Navigate to your account in Grafana Cloud and click Details for your stack.
- Click Details for a given service, such as Prometheus or Loki.
- If the region matches one of the Azure regions where Grafana Cloud is hosted, then your stack is hosted on Azure. If your stack is not hosted on Azure, you can create a new stack, forward telemetry to it, and query it from your existing stack.
Find the DNS name for Fleet Management
You can find the DNS name in the Fleet Management application.
In your Grafana Cloud stack, click Connections > Collector > Fleet Management in the left-side menu.
On the Fleet Management interface, switch to the API tab.
Find the URL in the Base URL section. For example:
https://fleet-management-prod-001.grafana.netTrim the URL by removing the protocol and the
grafana.net. For example, the base URL in the previous example should be trimmed tofleet-management-prod-001. This is the DNS name to use when you set up a Private Endpoint.
Find the DNS names of other Grafana Cloud services
You can find service DNS names in your Grafana Cloud account.
Navigate to your account in Grafana Cloud and click Details for your stack.
Click Details for a Cloud service you plan to use.
Look for the base URL of the service. For example, the base URL for a Prometheus service looks like
https://prometheus-prod-001-prod-us-east-0.grafana.net/api/prom/Trim the URL by removing the protocol, the
grafana.netand everything that comes after it. For example, the base URL in the previous example should be trimmed toprometheus-prod-001-prod-us-east-0. This is the DNS endpoint to use when you set up a Private Endpoint.Repeat steps 2-4 for each Cloud service you plan to use. To take advantage of all Fleet Management features, make sure to identify the endpoints for Prometheus and Loki, at a minimum. If you have other
grafana.netservices routed through your virtual network, you need to find those endpoints as well.
Provide Subscription IDs to support
Before setting up Azure Private Link, contact Grafana Support with the list of Subscription IDs you plan to connect to Grafana Cloud services.
After Grafana Support confirms your Subscription IDs have been added to the Private Link allowlist, you can set up the connection.
Other regions
Azure Private Link supports cross-regional connections by default. If your infrastructure is hosted in a different Azure region than the one where Grafana is hosted, you can still use Private Link.
Set up a Private Endpoint on an Azure Virtual Network
Create a Private Endpoint in the Azure console, or provision one using Terraform.
Use the Azure Console
Open your Azure Console and search for or navigate to Private Endpoints.
![Select Private Endpoint > Endpoints]()
Choose Create.
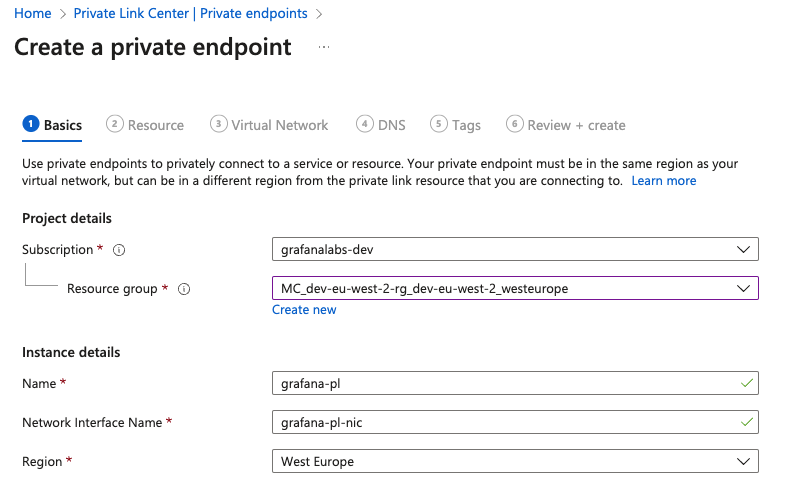
Select the subscription and resource group where your virtual network is.
Give the endpoint a name, for example,
grafana-pl.![Enter name]()
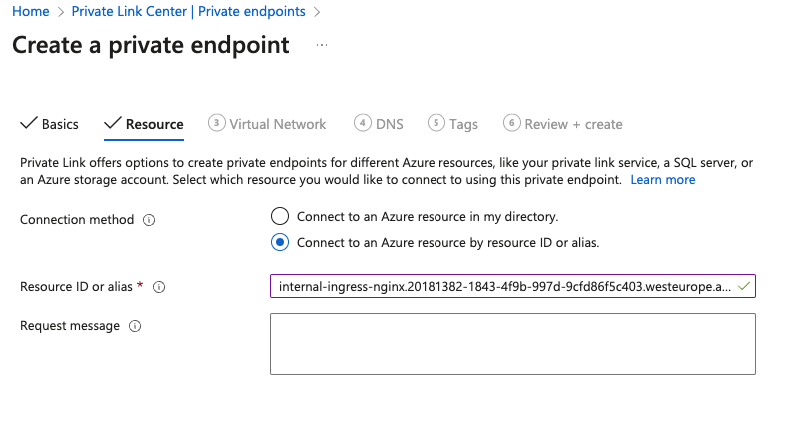
Continue to the Resource tab and select Connect to an Azure resource by resource ID or alias.
In the Resource ID or alias field, enter the service alias from your Grafana Cloud stack. The following table shows all service aliases of Azure regions available in Grafana Cloud. If you don’t know which region your stack is in, check your Cloud portal.
![Select service]()
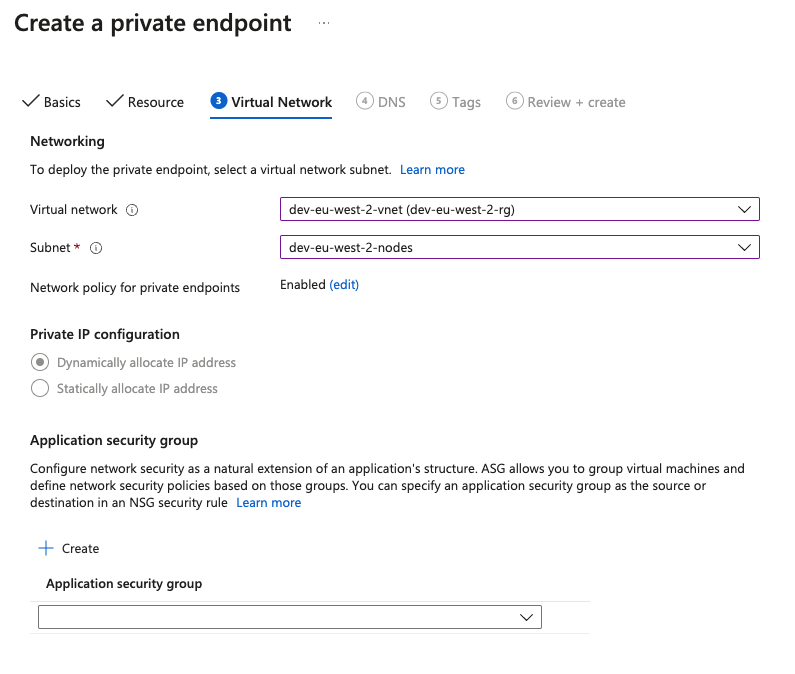
Continue to Virtual Network. Select your Virtual Network and Subnet.
![Network]()
Choose Review + Create and proceed to create the resource. The Private Endpoint is created and after a few minutes, Connection status should show as
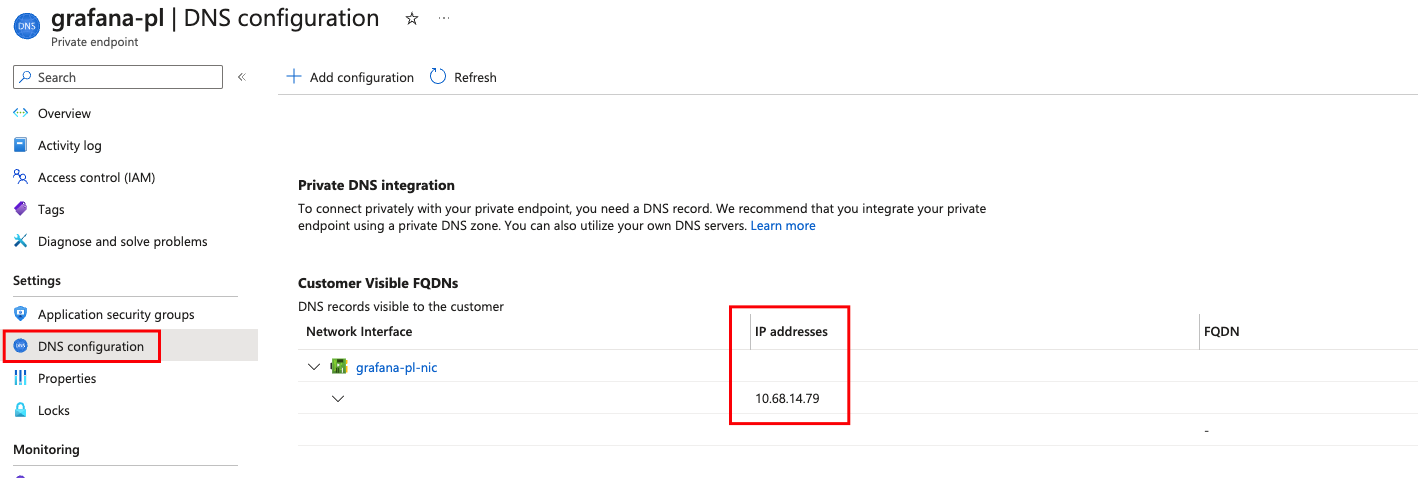
Approved. If status stays asAwaiting Approval, the Subscription ID from where you are connecting is not included in the allowlist. Contact Grafana Support to request the approval of the connection.Under DNS Configuration, copy the local IP address of the private endpoint. You will need this IP later.
![IP Address]()
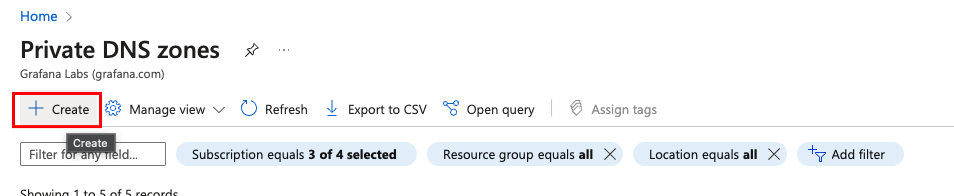
Navigate to Private DNS zones and click Create.
![Create DNS Zone]()
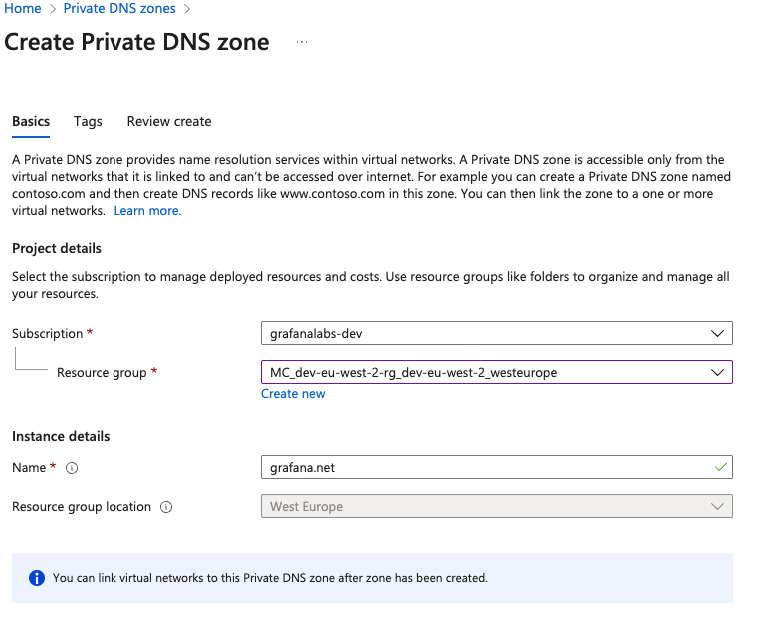
Select the subscription and resource group.
In Instance Details > Name, enter
grafana.netand then proceed to create.![DNS Zone]()
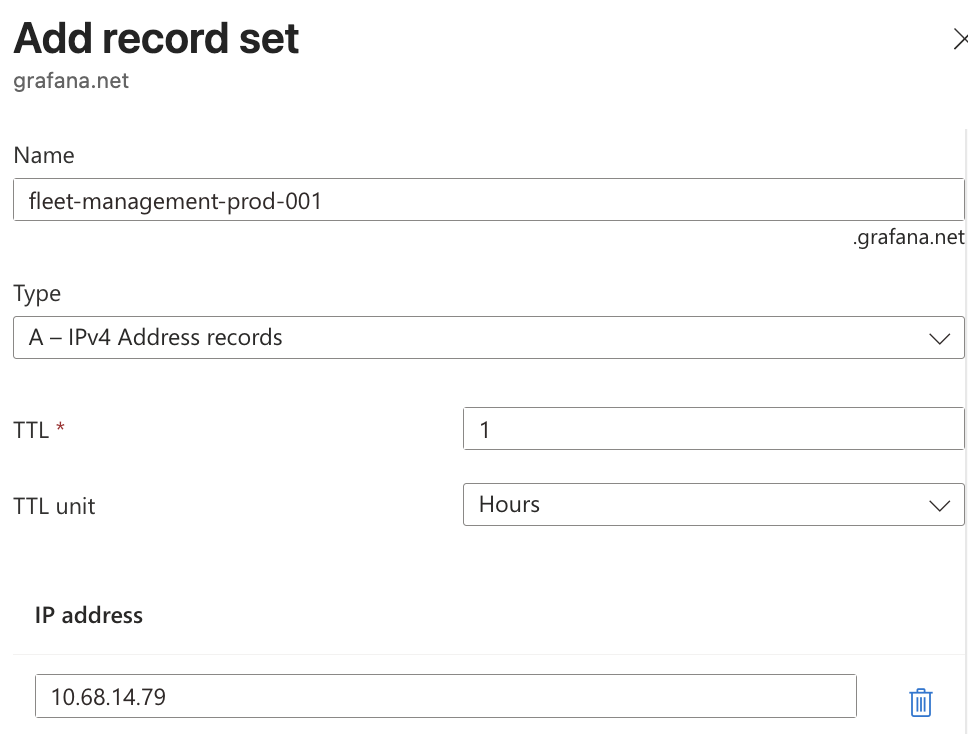
Return to Private DNS Zone overview and add a Record Set.
In Name, introduce the DNS name of the endpoint, for example
fleet-management-prod-001. Repeat these two steps for every endpoint you want to connect using Private Link. You can find service endpoints in your Fleet Management application and Grafana Cloud portal.Note
When configuring the Azure Virtual Network, you need to connect a Private Endpoint for all
grafana.netendpoints in use, not just Fleet Management.To take advantage of all Fleet Management features, configure the Fleet Management, Prometheus, and Loki endpoints, at minimum. You should also configure all instances using the virtual network because those endpoints route requests to
grafana.netthrough the matching Private DNS zone and unconnected endpoints cannot route properly.If you plan to use remote configuration, make note of the DNS name for each service, so you can secure telemetry connections.
In IP Address, enter the local IP Address of the Private Endpoint that you copied earlier and then click Add.
![Record Set]()
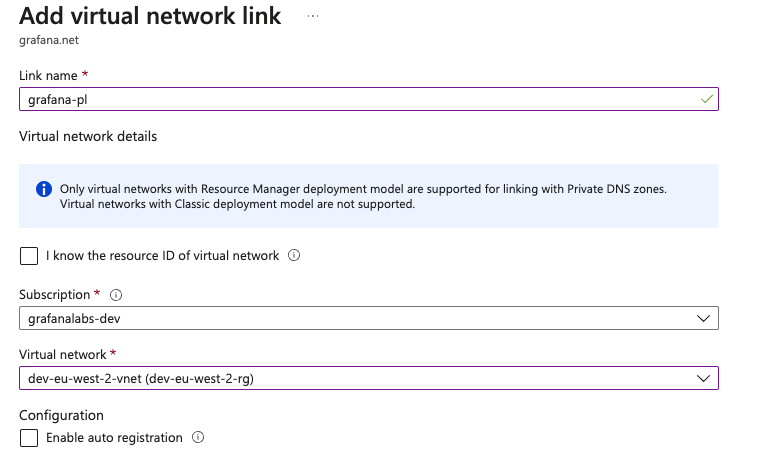
Navigate to Virtual network links, then click Add.
Name the network link, for example
grafana-pl.Select your subscription and Virtual Network.
![Virtual Network Link]()
After you create this link, all endpoints with a DNS entry resolve to the Private Endpoint IP, so their data is sent to Grafana Cloud using Private Link.
Use Terraform
Use the following snippet to automate Private Endpoint setup in Azure using Terraform. You can find the service alias of your region in the table in the previous section.
locals {
region = "<your azure region>"
resource_group_name = "<your resource group name>"
vnet_id = "<your virtual network id>"
subnet_id = "<your subnet id>"
privatelink_service_alias = "<private link service alias provided by Grafana>"
}
resource "azurerm_private_endpoint" "privatelink_grafana" {
name = "grafana-pl"
location = local.region
resource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
subnet_id = local.subnet_id
private_service_connection {
name = "grafana-pl"
is_manual_connection = true
request_message = "connection request from <customer name>"
private_connection_resource_alias = local.privatelink_service_alias
}
}
resource "azurerm_private_dns_zone" "privatelink_grafana" {
name = "grafana.net"
resource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
}
resource "azurerm_private_dns_zone_virtual_network_link" "privatelink_grafana" {
name = "grafana-pl"
resource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
private_dns_zone_name = azurerm_private_dns_zone.privatelink_grafana.name
virtual_network_id = local.vnet_id
}
resource "azurerm_private_dns_a_record" "privatelink_grafana_logs" {
name = "logs-prod-us-central2"
zone_name = azurerm_private_dns_zone.privatelink_grafana.name
resource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ttl = 300
records = [azurerm_private_endpoint.privatelink_grafana.private_service_connection[0].private_ip_address]
}
resource "azurerm_private_dns_a_record" "privatelink_grafana_metrics" {
name = "prometheus-us-central2"
zone_name = azurerm_private_dns_zone.privatelink_grafana.name
resource_group_name = local.resource_group_name
ttl = 300
records = [azurerm_private_endpoint.privatelink_grafana.private_service_connection[0].private_ip_address]
}Secure telemetry connections
Self-monitoring pipelines and integration pipelines contain hardcoded destination URLs to Grafana Cloud services such as Prometheus and Loki. By default, these pipelines send data over the public internet. To route this data through your Azure Private Link connection, you need to update the destination URLs in each configuration pipeline.
To update pipeline URLs:
- Find the private DNS names you created for each Grafana Cloud service.
- In your Grafana Cloud instance, navigate to Connections > Collector > Fleet Management.
- Switch to the Remote configuration tab.
- For each self-monitoring pipeline, such as
self_monitoring_metrics, and any integration pipelines you have:- Click the Edit icon in a pipeline row.
- Look for URL references to Grafana Cloud services (for example,
prometheus-*.grafana.netorlogs-*.grafana.net). - Update these URLs to use the private DNS names for your Grafana Cloud services.
- Save the configuration pipeline.
- Repeat for each pipeline with hardcoded URLs.