Create a custom configuration pipeline
With configuration pipelines, you can control collector behavior remotely and at scale. Configuration pipelines are made up of a unique name, a content body, and matching attributes. This page explains how to write your own Alloy configuration pipelines in the Grafana Fleet Management interface.
Before you begin
To create configuration pipelines in Fleet Management, you should:
- Have a Grafana Cloud account.
- Have administrator privileges and the ability to create and edit access policies.
- Update Grafana Alloy to the most current version.
Fleet Management must be used with Alloy collectors and is recommended for use with Alloy v1.7.2 or later.
If you’re using an earlier version, make sure to include the
--stability.level=public-previewflag when running Alloy. - Understand the key terms and concepts of Fleet Management and how the service works.
Define the configuration pipeline
In your Grafana Cloud stack, click Connections > Collector > Fleet Management and then switch to the Remote configuration tab.
Click Create configuration pipeline.
Click Custom configuration and then Next.
Enter a unique name for the pipeline.
Insert one or more configuration snippets to create a pipeline. You can create your own using Alloy configuration syntax or select one of the snippets for Grafana Cloud integrations.
Make sure the pipeline is complete. Each pipeline must be self contained and have the necessary components to send telemetry over the network to persistent storage.
Note
Components can be reused across pipelines with an advanced Fleet Management feature: pipeline export injection.
If you want to label the telemetry you collect, inject collector attributes into the pipeline.
Scroll down to click Test configuration pipeline to validate the configuration syntax. The pipeline editor provides real-time feedback on the syntactic validity of the configuration content. If an error is reported, you can make the fix yourself or click the Assistant button and select Fix errors in Assistant.
Note
If you don’t see the Grafana Assistant button or the button is disabled, Assistant has not been enabled on your stack. Contact your stack administrator for more details.
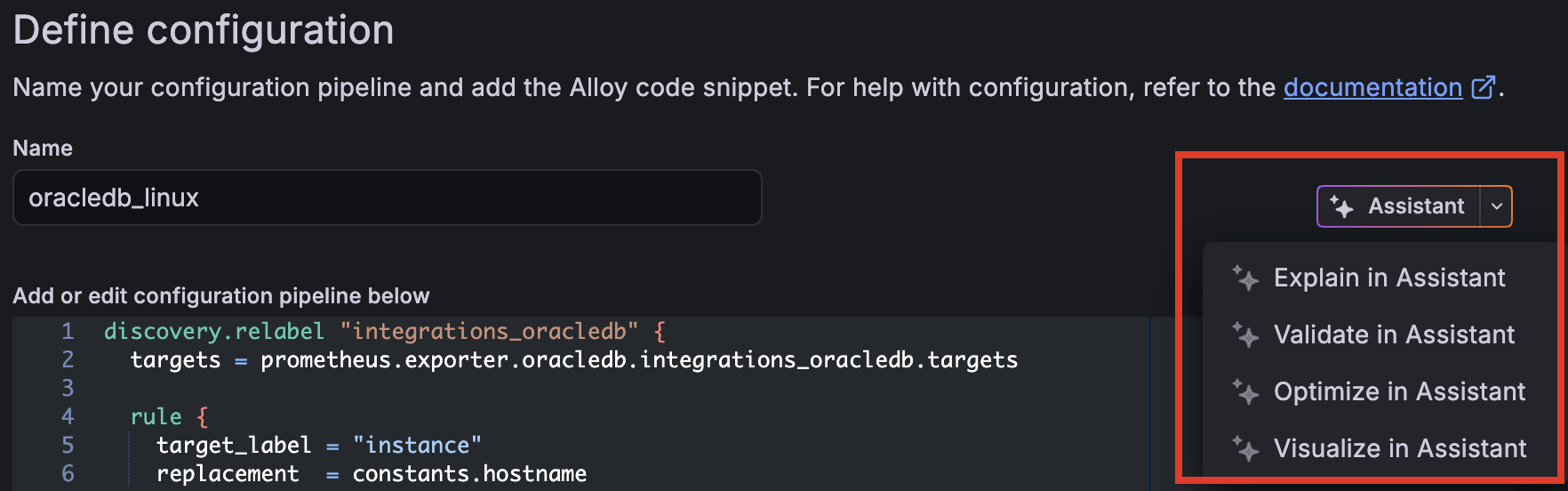
To understand how your pipeline works, the different components in use, and potential areas for optimization, click the Assistant button. You can choose to have Grafana Assistant explain the pipeline, validate the syntax or fix errors if there are any, optimize the configuration, or create a diagram of the pipeline.
![One section of the Define configuration page in the Fleet Management interface in Grafana Cloud where a menu shows the tasks that Grafana Assistant can perform on the selected configuration pipeline. The four options are Explain in Assistant, Validate in Assistant, Optimize in Assistant, and Visualize in Assistant.]()
Click Next to assign the configuration pipeline to collectors or click Save to save an incomplete pipeline.
Assign the configuration pipeline
Configuration pipelines are incomplete until you add matching attributes that assign them to collectors.
Note
If you saved an incomplete configuration, click the Edit icon from the Configuration pipeline list to return to the Define a configuration pipeline page.
Click Next on the Define a configuration pipeline page.
Use the dropdown menus to create a matching attribute. The Collector list updates in real time to show you which collectors have been assigned the configuration pipeline. Only active collectors are displayed in this list by default. Inactive collectors are not shown, but you can include them by updating the status filter.
Continue adding matching attributes as needed.
GetConfigpolling requests to the API can accept a maximum of 15 attributes.Click Save to activate the configuration pipeline and return to the Configuration pipeline list.
Activate or deactivate a configuration pipeline with a click of the Active switch.
Assigning the matching attribute profiling_enabled=true.
Next steps
Now that you’ve started remotely configuring your fleet, learn how to streamline your workflows and track historical changes to your configuration pipelines.