Monitor user actions
Track your users’ key interactions with your application using Faro’s User Actions instrumentation. User actions let you follow end-to-end user journeys and attach context to related signals, such as HTTP requests and performance metrics, as users interact with your app.
Overview
A user action represents an end user’s interaction with your product, for example, clicking a button or submitting a form. User actions can start automatically or manually and are linked with signals such as measurements, logs, and errors. This linkage helps you monitor critical paths, identify issues, and measure feature adoption.
Create a user action
You can create user actions in two ways.
Automatically
A user action starts when a user clicks or presses Space/Enter on an HTML element that includes the data-faro-user-action-name attribute.
You can customize this attribute name. Refer to Configuration for more details.
Manually
Use the Faro Web SDK faro.api.startUserAction method to start a user action programmatically and include custom options.
User action lifecycle
After creation, all signals generated during the user action’s lifetime include an action attribute. For example, a performance resource event looks like this:
{
"name": "faro.performance.resource",
"domain": "browser",
"attributes": {
"name": "http://localhost:3000/",
"duration": "45",
"tcpHandshakeTime": "1"
...
},
"timestamp": "2025-07-17T08:09:34.051Z",
"trace": {
"trace_id": "77ae1ba7a590bb8c085deacb83907e87",
"span_id": "83e4ec9b0511a4ec"
},
"action": {
"parentId": "CdK96bsFeT",
"name": "fetch-success"
}
}User actions follow two main lifecycle paths.
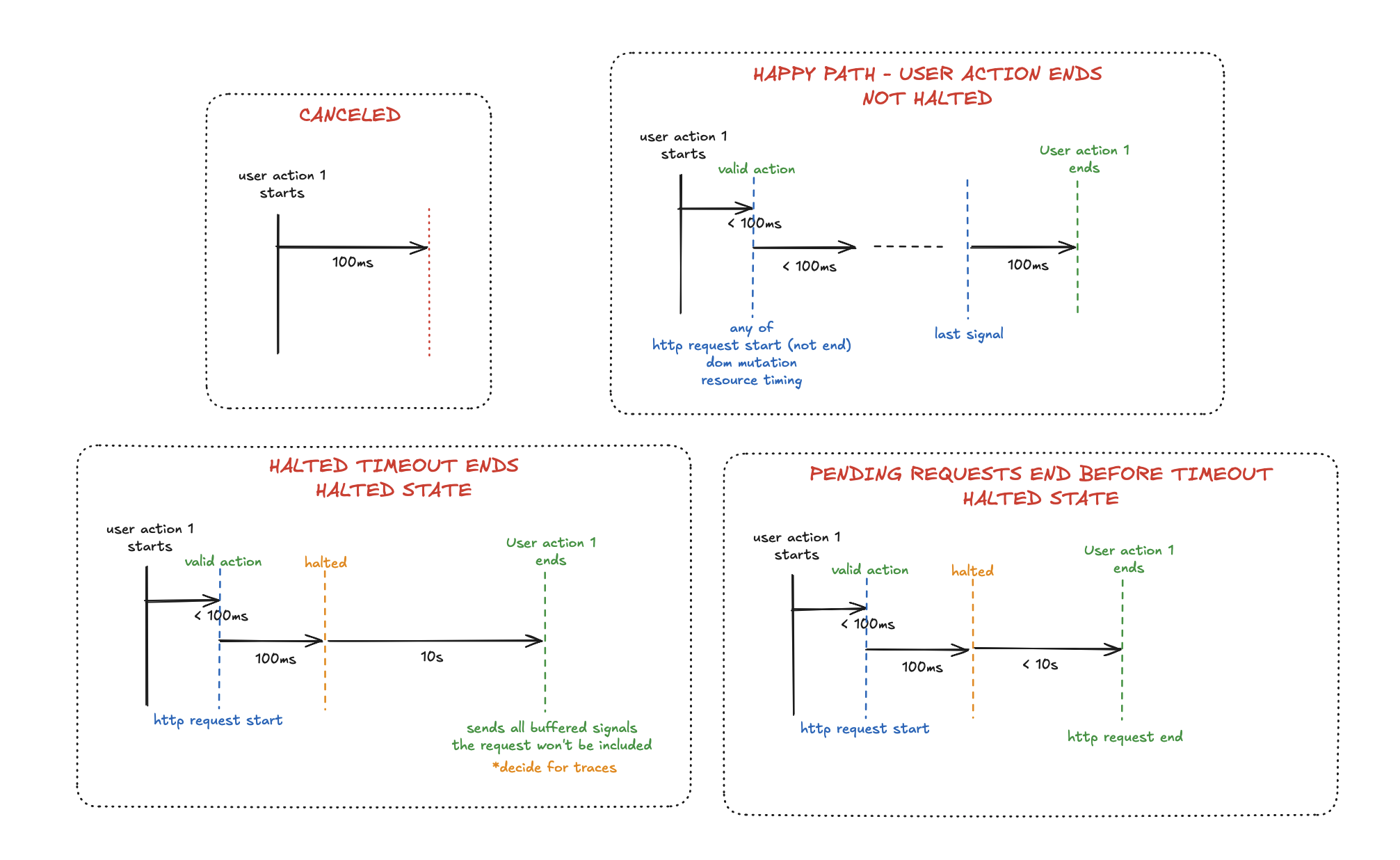
Completion
- An action completes automatically 100 ms after the last linked event is received. Each new event resets the timer.
- Events include timing attributes such as, such as
userActionStartTime,userActionEndTime, anduserActionDuration. - Cancellation after halt: If open HTTP requests remain after the 100 ms mark, the action halts for up to 10s (configurable) to allow slow or long-running network requests to finish. The action completes once all requests close or the timeout is reached.
Cancellation
- If no qualifying events occur within 100 ms of user action creation, the action is canceled and ignored.
- Cancellation after halt: If a halted action times out before requests close, it is also canceled.
Configuration
User Action instrumentation is enabled by default in the Faro SDK.
If you use custom instrumentation, manually include the UserActionInstrumentation:
import { UserActionInstrumentation } from '@grafana/faro-web-sdk';
const instrumentations = [
// ...other instrumentations
new UserActionInstrumentation(),
];The data attribute name defaults to data-faro-user-action-name for automatic actions. To override it, use the dataAttributeName option in the userActionsInstrumentation configuration:
initializeFaro({
// ... other config
userActionsInstrumentation: {
dataAttributeName: 'myAttribute', // must be camelCase
},
});Then, in your HTML:
<button data-my-attribute="add-to-cart">Add to cart</button>Clicking this button starts a new user action named add-to-cart.
Manual user action API
Use the startUserAction method for advanced control and customization:
startUserAction(
name: string,
attributes?: Record<string, string>,
options?: StartUserActionOptions
)Parameters
Example usage
faro.api.startUserAction(
'checkout', // name of the user action
{ cartSize: '3', paymentMethod: 'card' }, // custom attributes attached to the user action
{ triggerName: 'customEvent', importance: importance: UserActionImportance.Critical } // custom config
);Best practices
- Use descriptive action names to make filtering and analysis easier.
- Attach relevant attributes to actions for enhanced context, for example, button name and page context.
- For highly custom interactions, prefer manual initiation with
startUserAction. - For
Single Page Applications (SPA)where event handlers might take more than 100ms to execute, use the manual initiation and avoid using the HTMLdata-attribute as it might have unexpected behavior.



