What's new from Grafana Labs
Grafana Labs products, projects, and features can go through multiple release stages before becoming generally available. These stages in the release life cycle can present varying degrees of stability and support. For more information, refer to release life cycle for Grafana Labs.
Loading...
Area of interest:
Cloud availability:
Cloud editions:
Self-managed availability:
Self-managed editions:
No results found. Please adjust your filters or search criteria.
There was an error with your request.
Removal of old Tempo Search tab
In Grafana v10.1, we added a Tempo search editor powered by TraceQL (search tab). We also recommended using this new editor over the older non-TraceQL powered editor.
(Re-)introducing “Keep Last State” to Grafana managed alert rules.
You can now choose to keep the last evaluated state of an alert rule when that rule produces “No Data” or “Error” results. Simply choose the “Keep Last State” option for no data or error handling when editing a rule. Refer to the Alerting documentation on state and health of alert rules for more information.
We are happy to announce Cloud Logs Export is now Generally Available to all Grafana Cloud users!
Cloud Logs Export lets users ship logs to their own object storage (AWS, GCP, Azure) for low-cost, long term retention. If you need to retain logs for long periods of time, without a need to frequently query them, Cloud Logs is the most cost effective way to do that.
Dashboards, when accessed by users with the Viewer role, are now using the Scenes library. Those users shouldn’t see any difference in the dashboards apart from two small changes to the user interface (UI): the variables UI has slightly changed and the time picker is now part of the dashboard container.
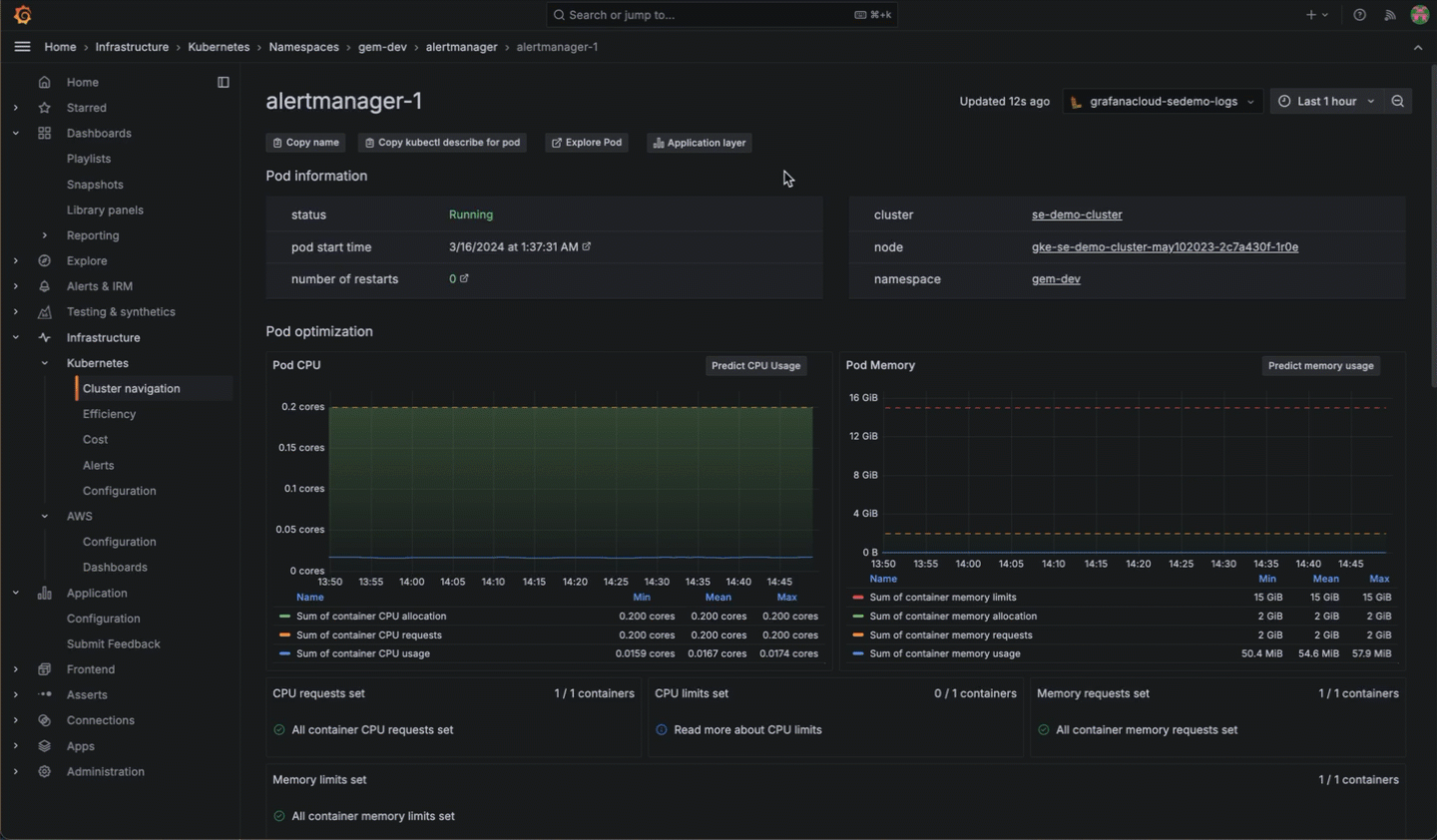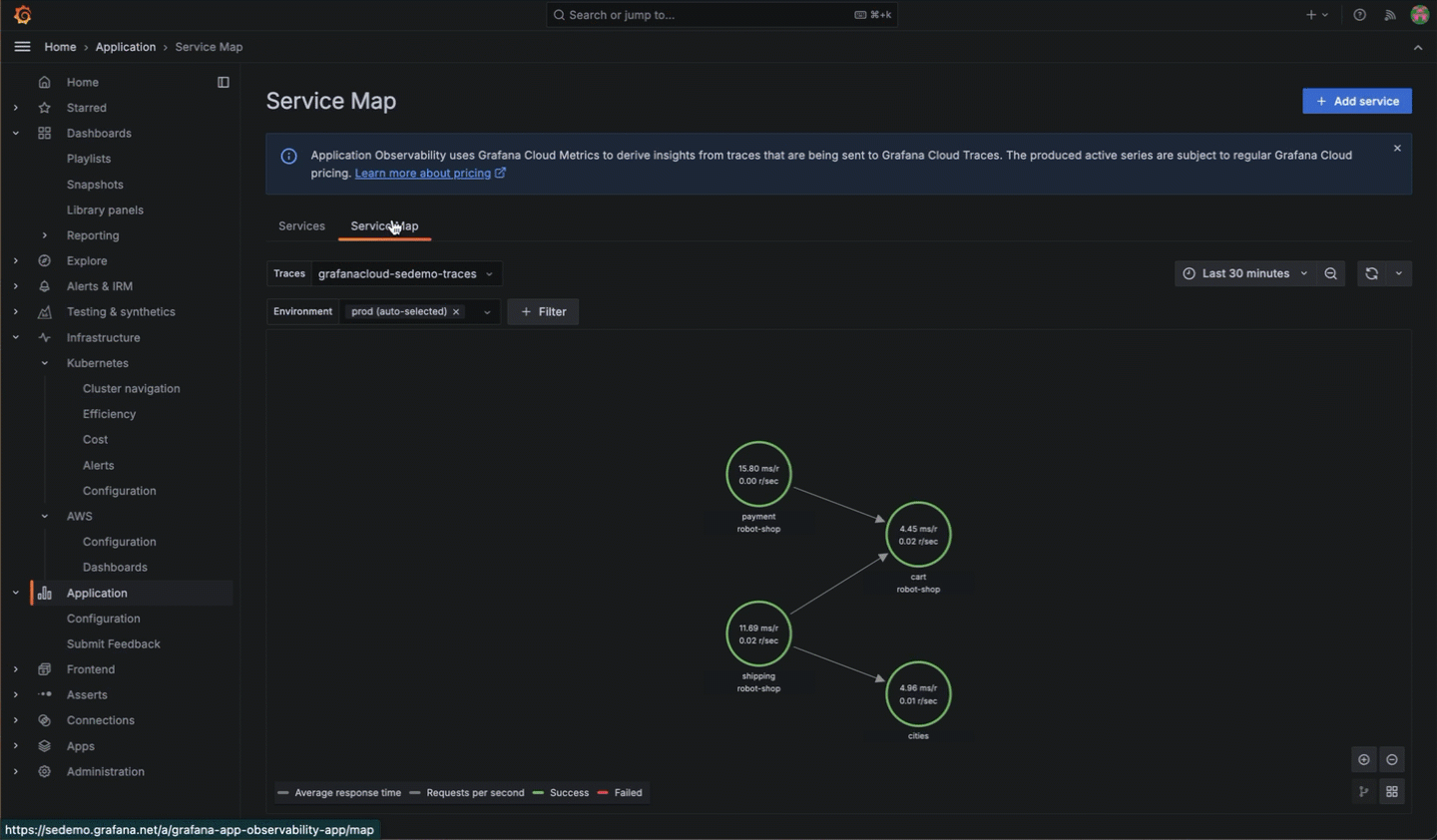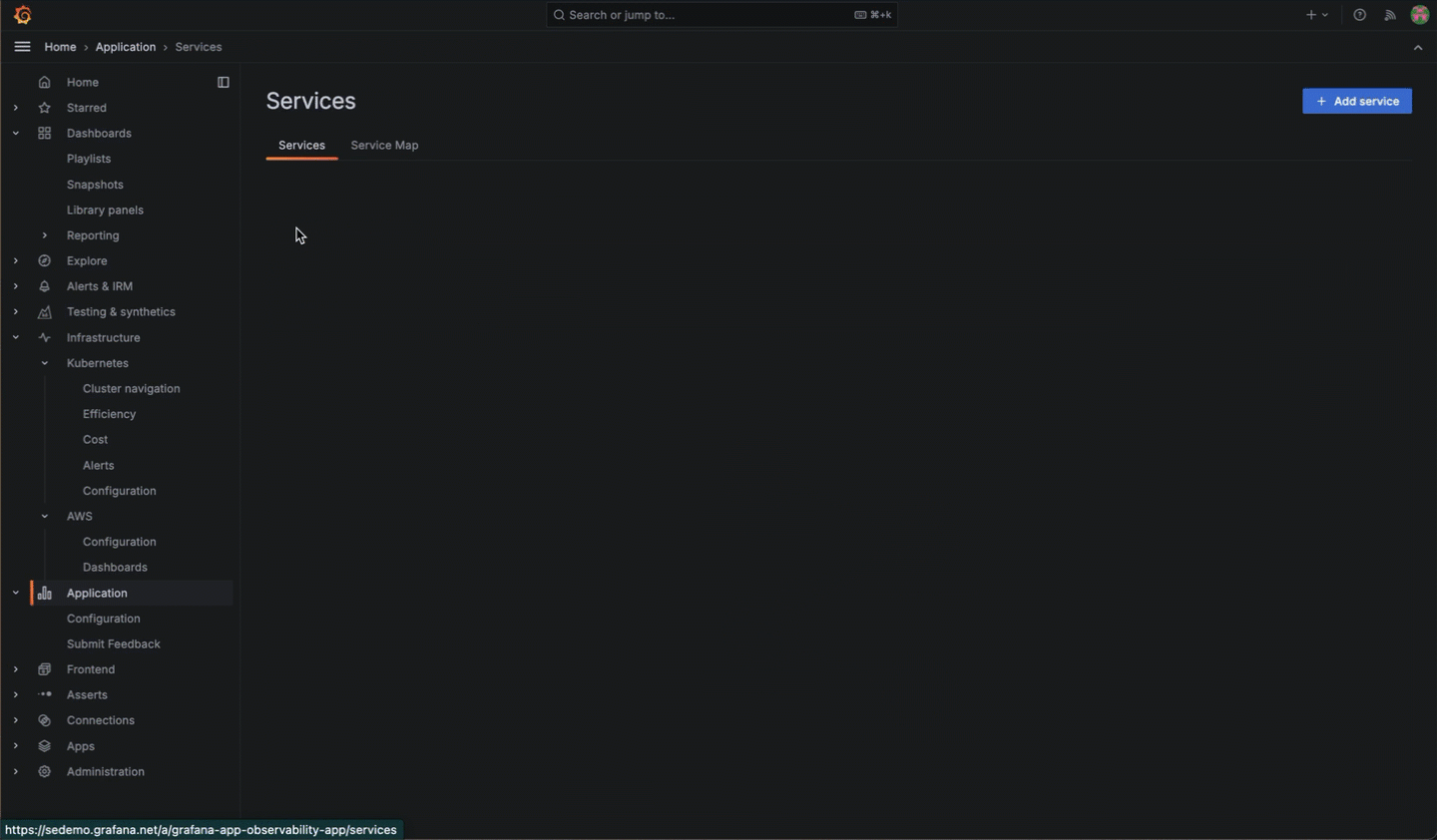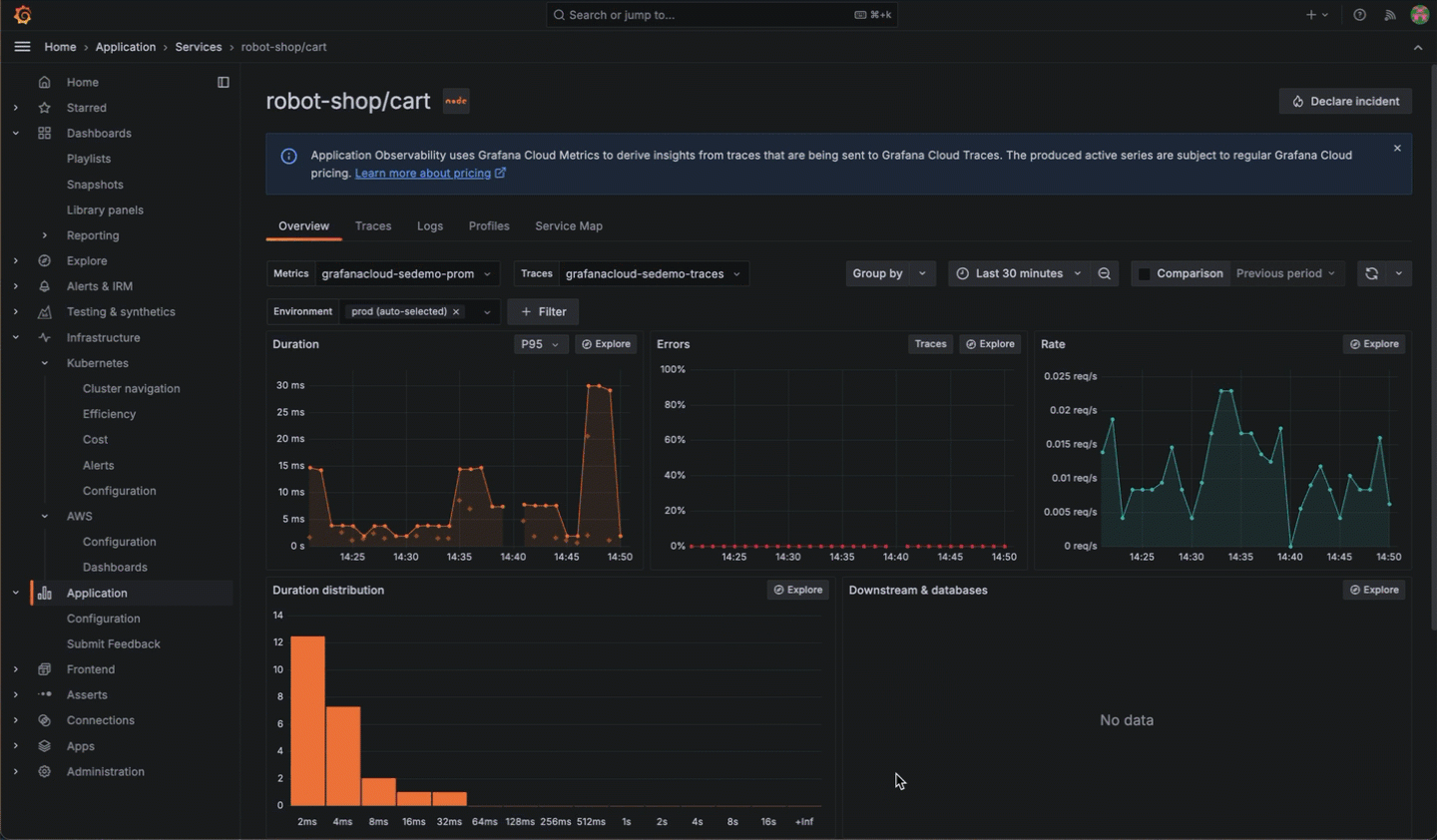
Directly from Kubernetes Monitoring, you can click into the Asserts RCA Workbench to see what is occurring between components and their relationships.
 (Release 2.0.4)
(Release 2.0.4)
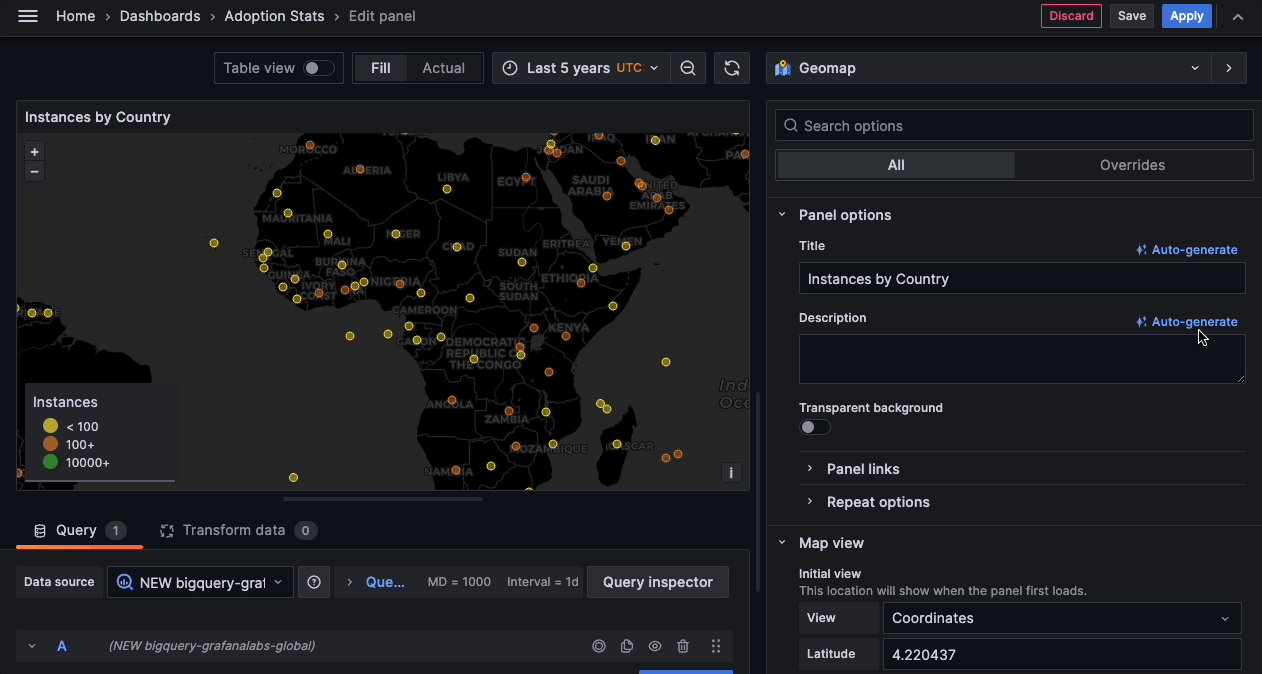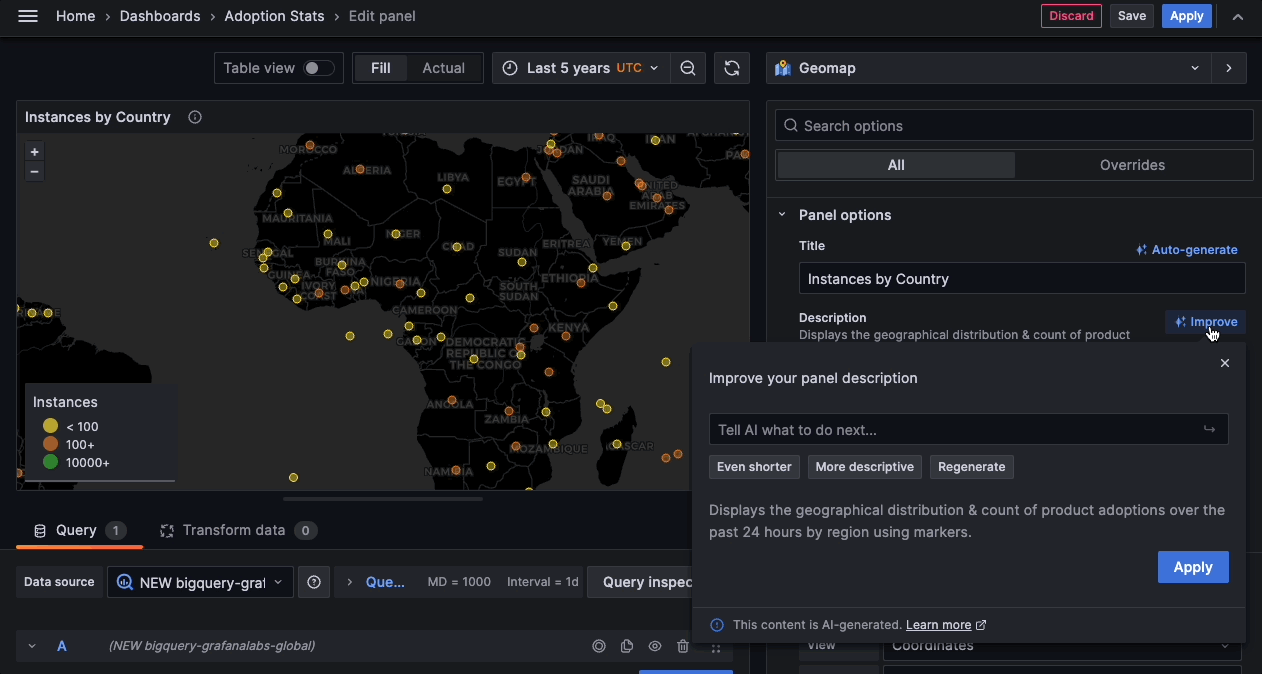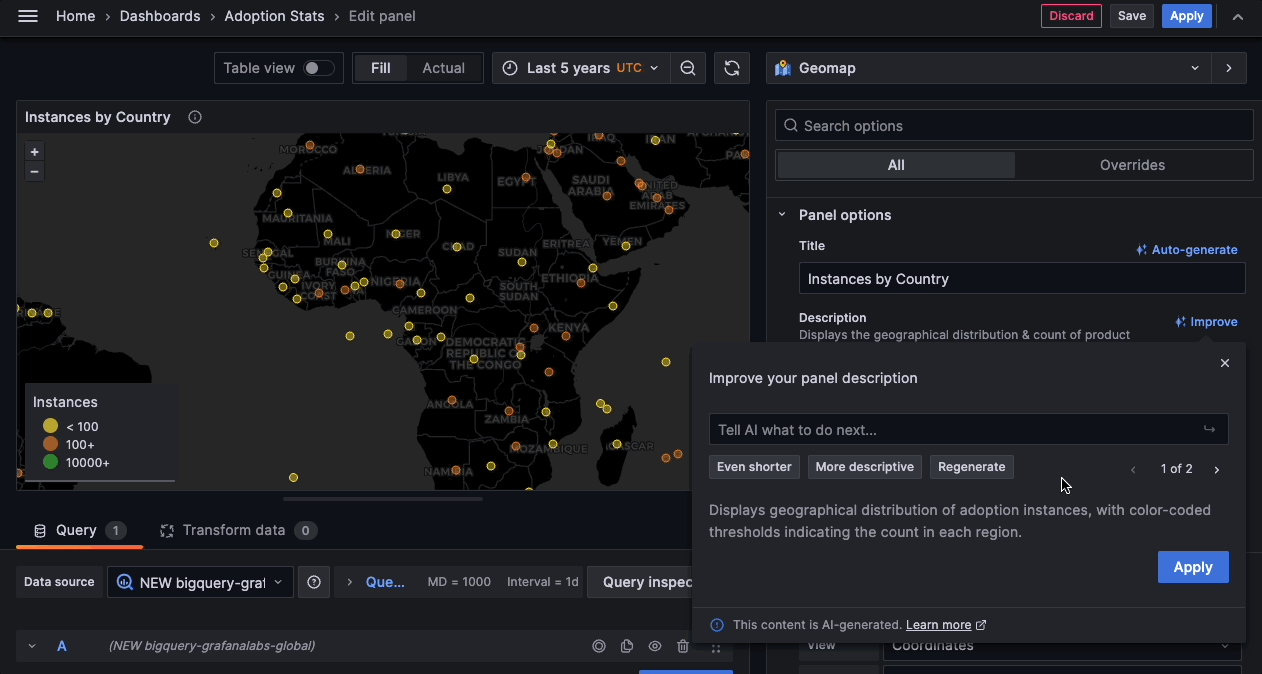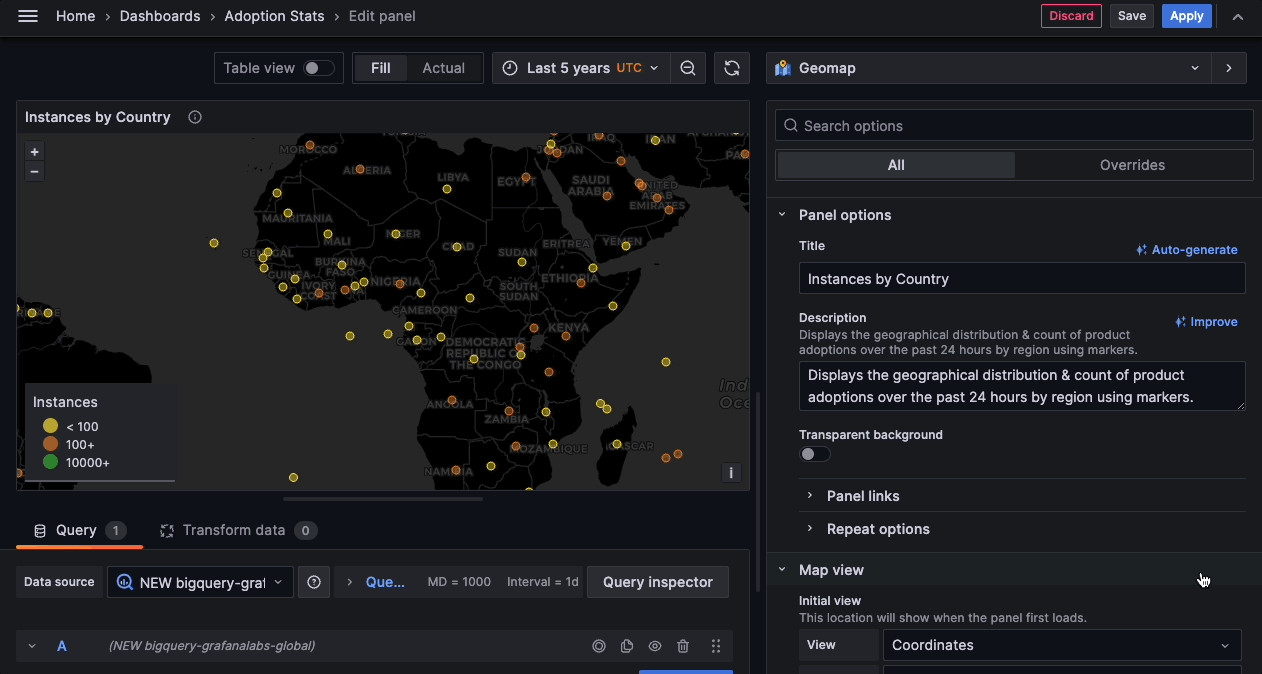
You can now use generative AI to assist you in your Grafana dashboards. So far generative AI can help you generate panel and dashboard titles and descriptions - You can now generate a title and description for your panel or dashboard based on the data you’ve added to it. This is useful when you want to quickly visualize your data and don’t want to spend time coming up with a title or description.
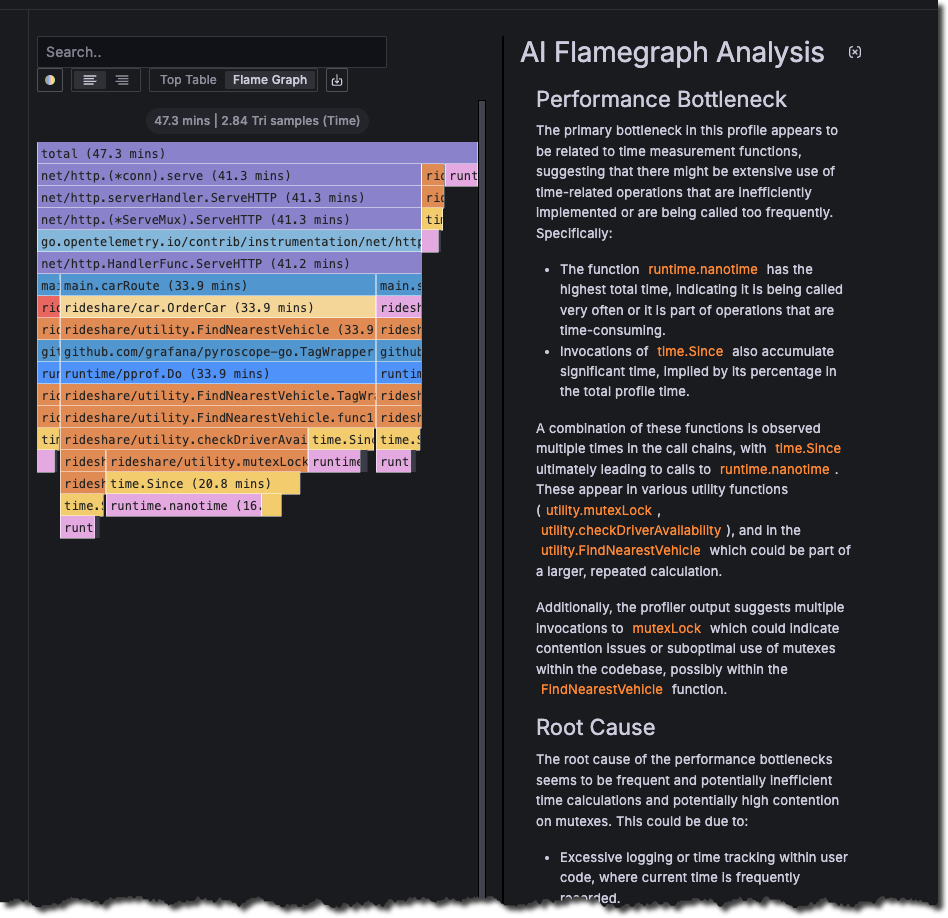
Flamegraph AI in Grafana Cloud Profiles is now GA
Flamegraph AI helps you understand your profiling data by using a large-language model (LLM) to assist with data interpretation.
On any Pod or workload detail page, you can navigate directly to Application Observability to see more data about the application.
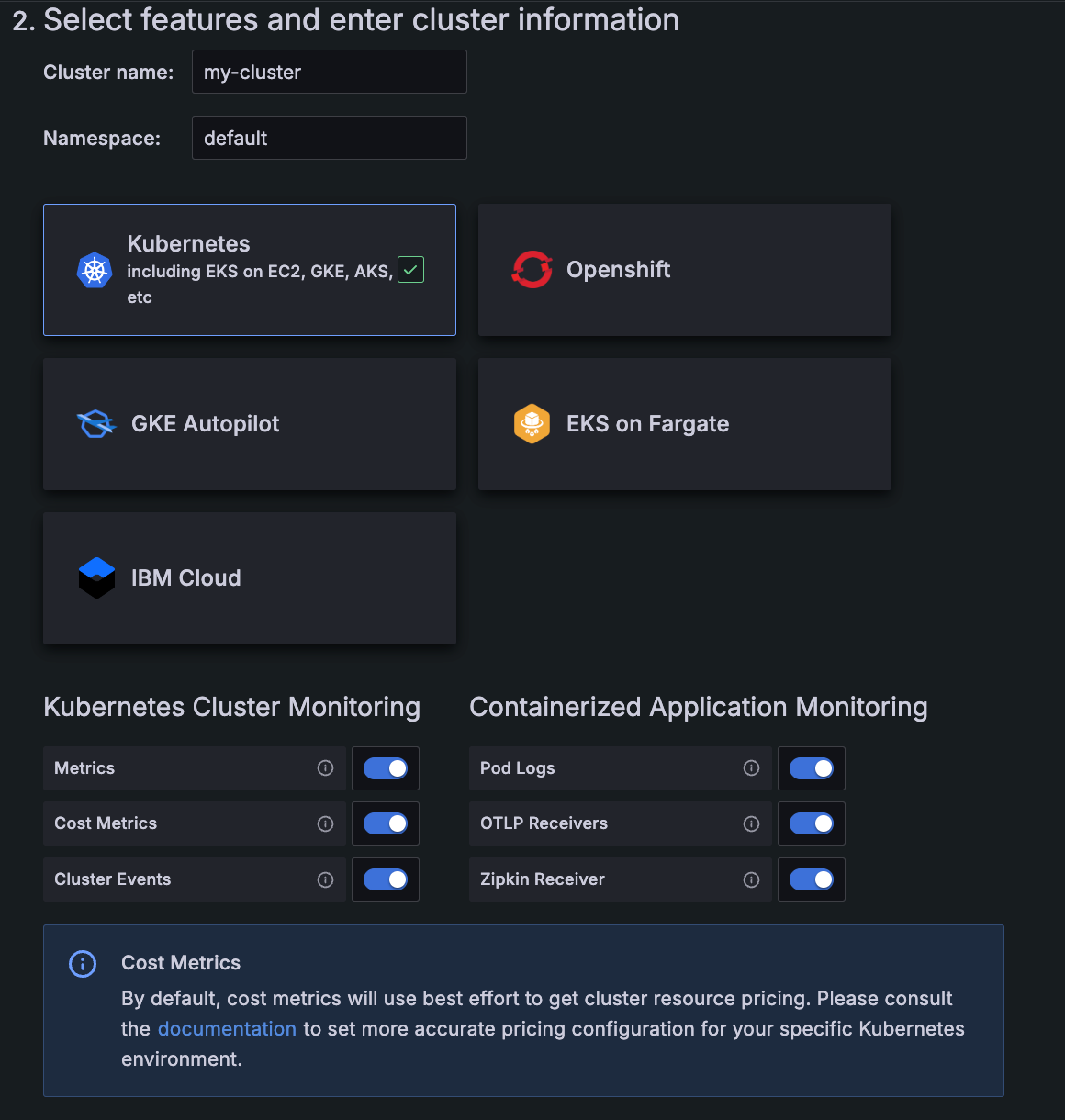
 (Release 2.0.3)
(Release 2.0.3)
When you use the easy configuration process with Grafana Kubernetes Monitoring Helm chart, you can switch on the use of OTLP and Zipkin receivers for containerized application monitoring.
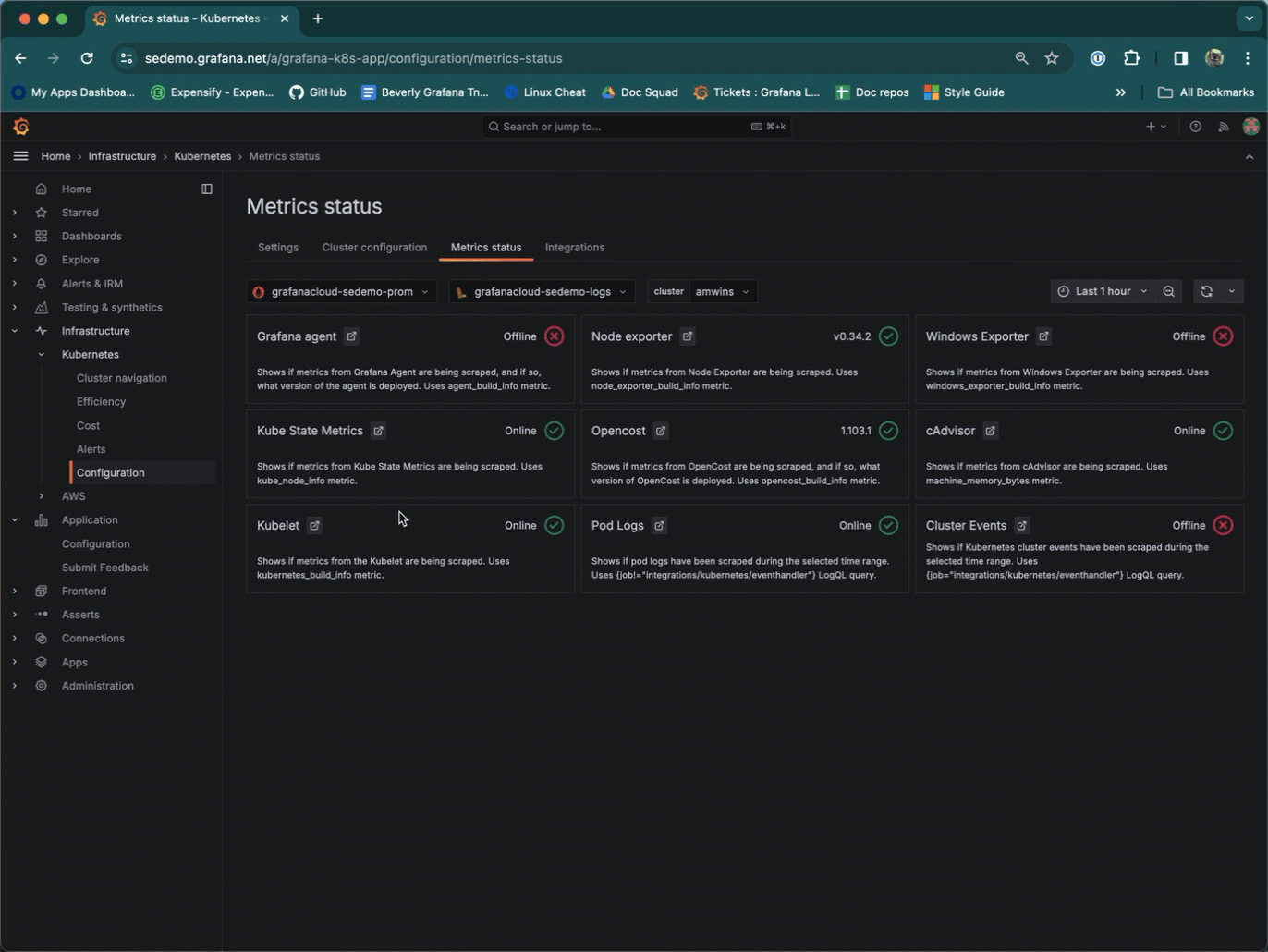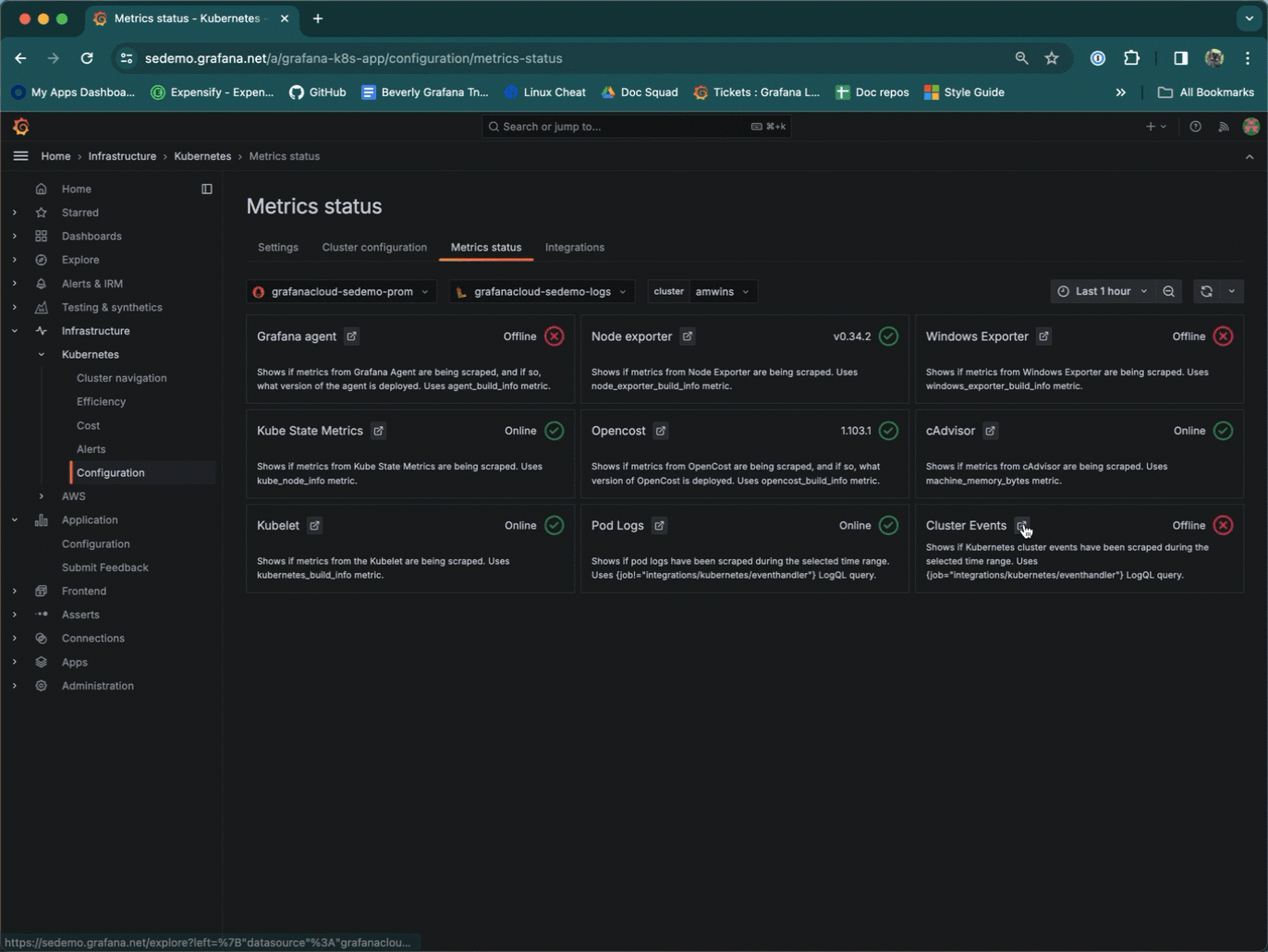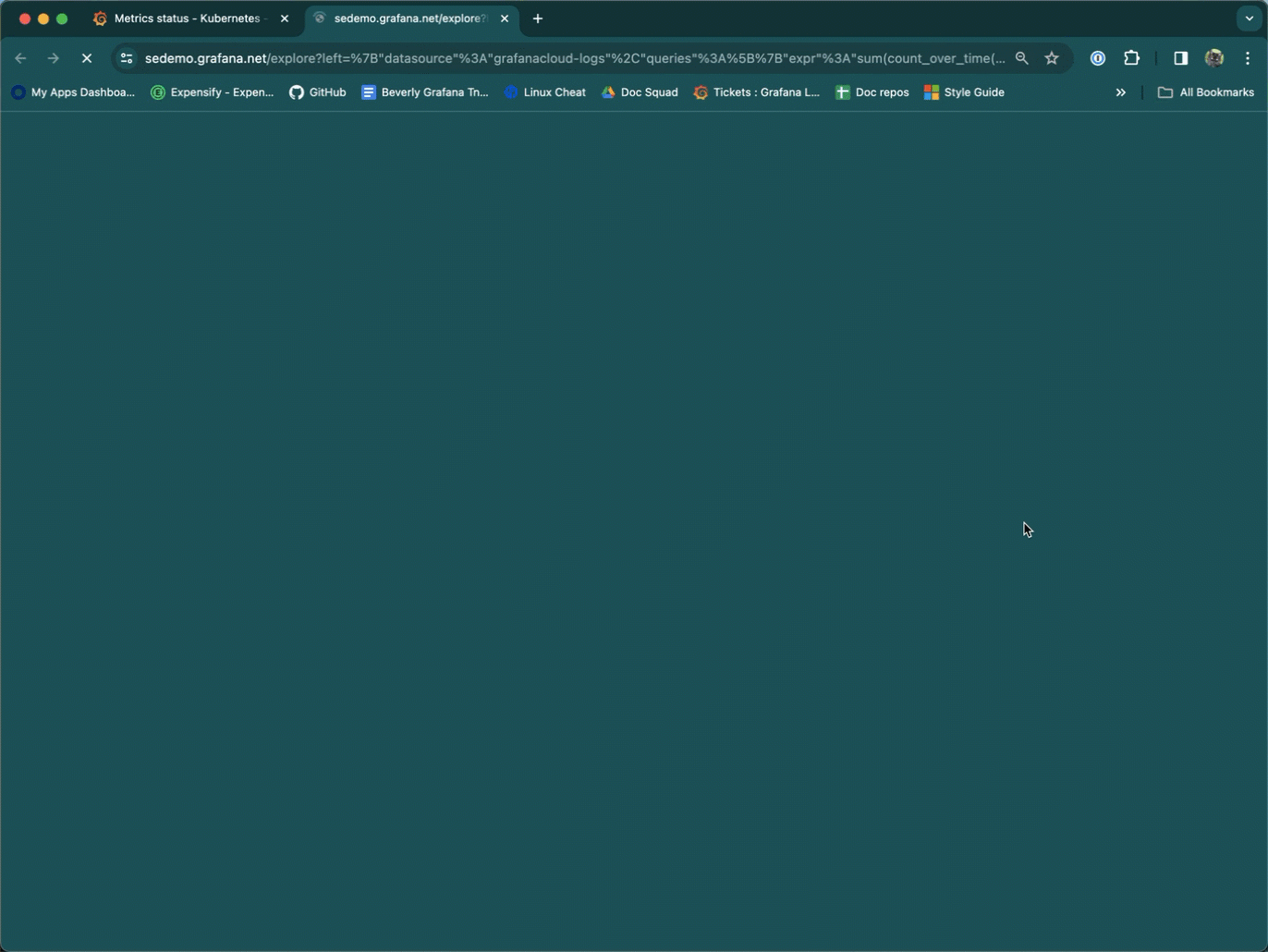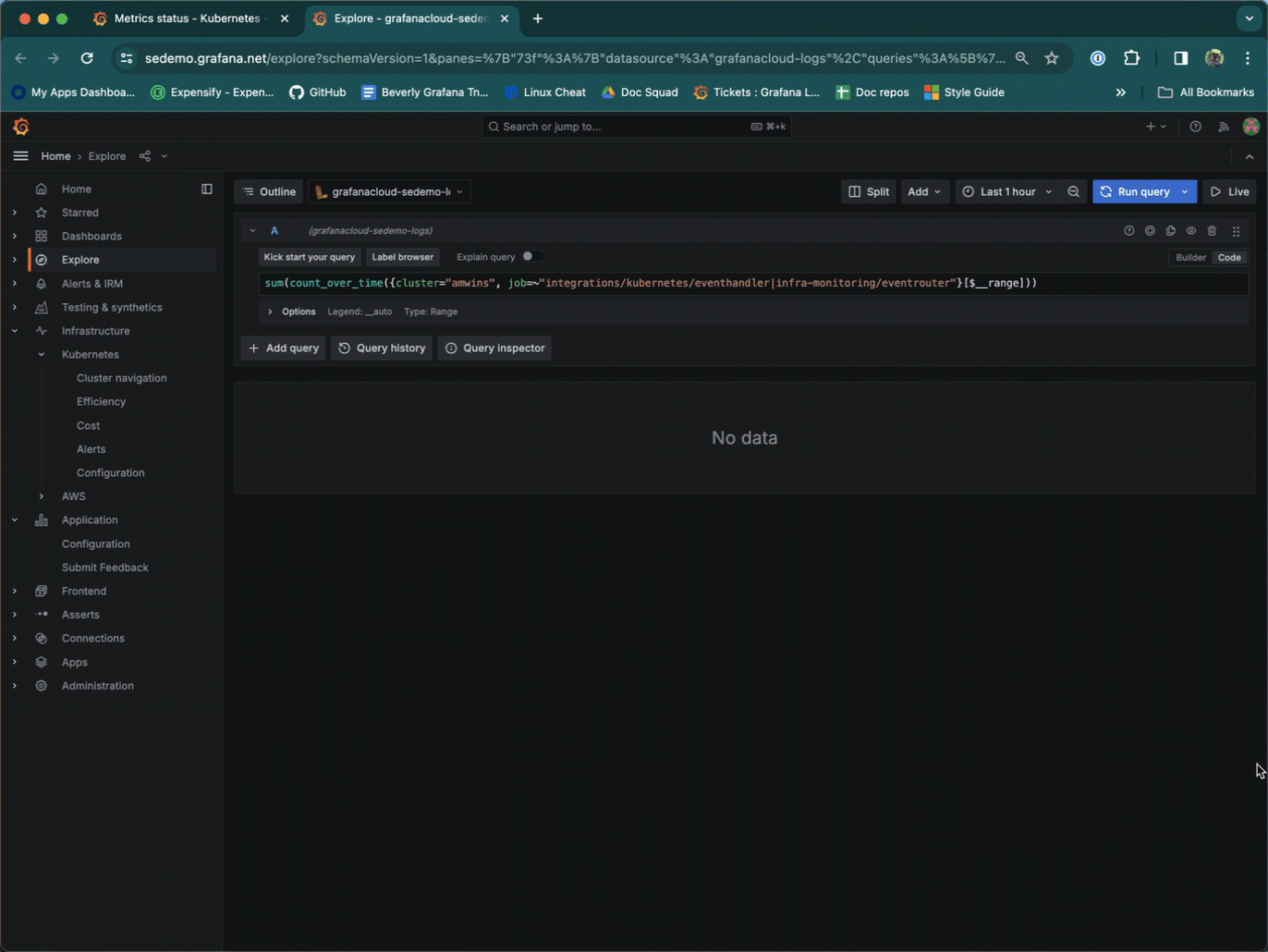
Click the Explore icon to view the query and additional tools available for you to further explore and query your data.
You can explore a query from the Metrics status tab.
Users looking to migrate to the new Grafana Alerting product can do so with confidence with the Grafana Alerting migration preview tool. The migration preview tool allows users to view, edit, and delete migrated rules prior cutting over, with the option to roll back to Legacy Alerting.
Grafana Alerting previously evaluated rules at the start of the evaluation interval. This created a sudden spike of resource utilization, impacting data sources. Rule evaluation is now spread over the entire interval for smoother performance utilization of data sources.
We’ve added the option to manage library panel permissions through role-based access control (RBAC). With this feature, you can choose who can create, edit, and read library panels. RBAC provides a standardized way of granting, changing, and revoking access when it comes to viewing and modifying Grafana resources, such as dashboards, reports, and administrative settings.
This feature simplifies your options for configuring where your notifications are sent when an alert rule fires. Choose an existing contact point directly from within the alert rule creation form without the need to label match notification policies. You can also set optional muting, grouping, and timing settings directly in the alert rule.
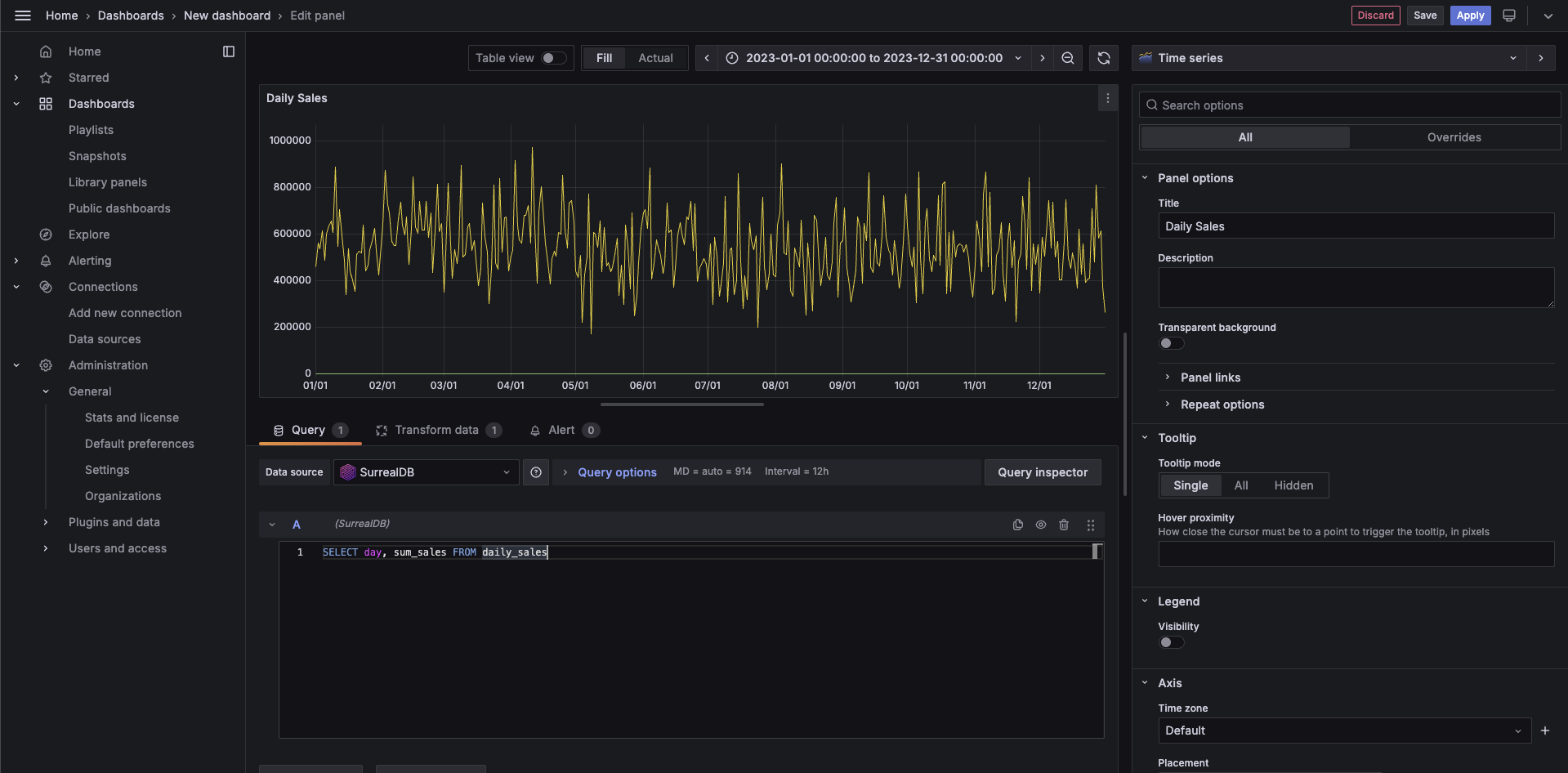
A SurrealDB data source has been added to the Plugin Catalog, enabling the integration of SurrealDB, a real-time, multi-model database, with Grafana’s visualization capabilities. This datasource allows users to directly query and visualize data from SurrealDB within Grafana, using SurrealDB’s query language.