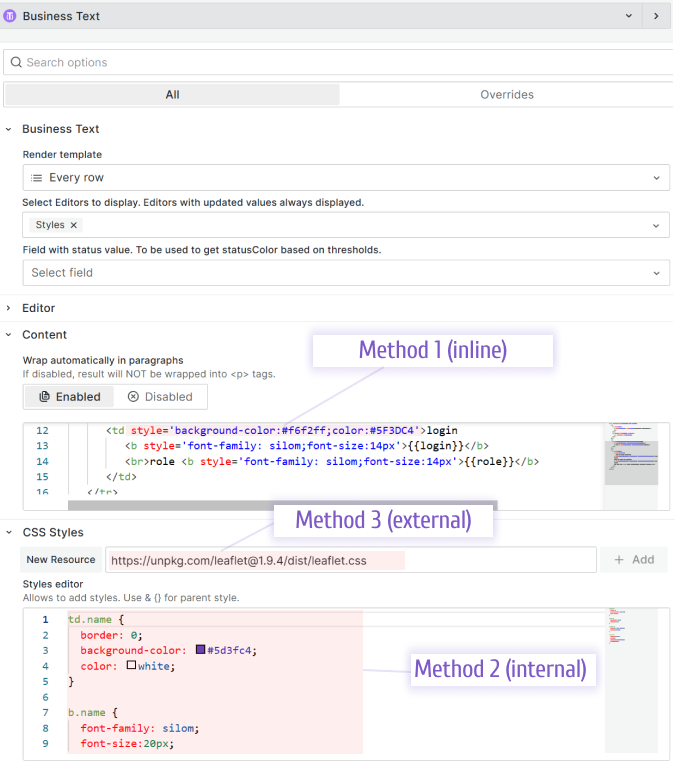
Styles
Apply CSS styling using inline, internal, or external methods with support for dashboard variables and syntax highlighting.
Methods to include CSS
You can apply styles using one, all, or any combination of the following methods:
- Inline: Specify CSS commands directly in the Content.
- Internal: Specify CSS in the Style editor with CSS syntax highlighting.
- External: Import an external CSS file. To prevent loading third-party URLs, store CSS files in the public folder on your Grafana instance:
- For an external Grafana instance:
https://GRAFANA-URL/public/grafanaCSS.css - For a local Grafana instance:
/public/grafanaCSS.css
- For an external Grafana instance:
Dashboard variables
Dashboard variables are replaced automatically in all CSS style methods.
Note
The Business Text panel supports dashboard variables starting from version 3.0.0 and dashboard variables in CSS styles starting from version 4.0.0.
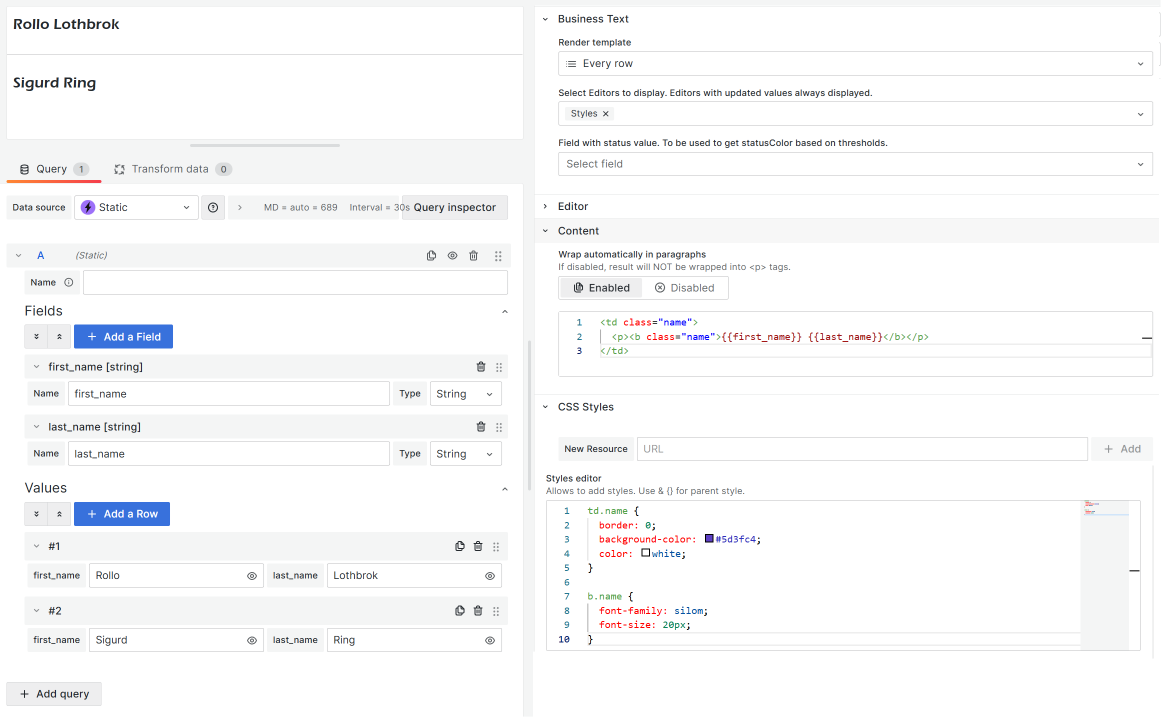
Internal method: Example 1
You can define your styles and use them in a template (Content, Default Content).
Code for a template:
<td class="name">
<p><b class="name">{{first_name}} {{last_name}}</b></p>
</td>Code for the Styles editor:
td.name {
border: 0;
background-color: #5d3fc4;
color: white;
}
b.name {
font-family: silom;
font-size: 20px;
}
Internal method: Example 2
This example demonstrates a simple styling approach. You can display the status of your devices or servers as green or red dots in a table.
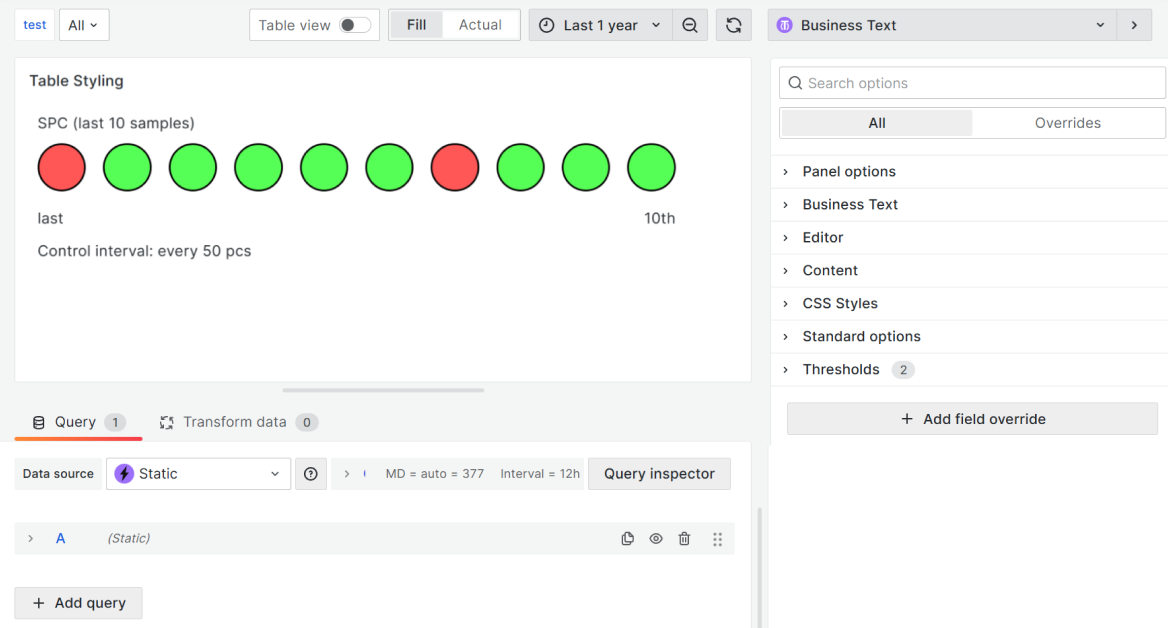
To display this on your dashboard, copy the Content and CSS Styles parameters from the following sections.
Content
<table>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td style="width: 10%;" colspan="10" class="header">
SPC (last 10 samples)
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td style="width: 10%;"><span class="dot_niO"></span></td>
<td style="width: 10%;"><span class="dot_iO"></span></td>
<td style="width: 10%;"><span class="dot_iO"></span></td>
<td style="width: 10%;"><span class="dot_iO"></span></td>
<td style="width: 10%;"><span class="dot_iO"></span></td>
<td style="width: 10%;"><span class="dot_iO"></span></td>
<td style="width: 10%;"><span class="dot_niO"></span></td>
<td style="width: 10%;"><span class="dot_iO"></span></td>
<td style="width: 10%;"><span class="dot_iO"></span></td>
<td style="width: 10%;"><span class="dot_iO"></span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td style="text-align: left;" colspan="5">last</td>
<td style="text-align: right;" colspan="5">10th</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td style="width: 10%;" colspan="5" class="down">
Control interval: every 50 pcs
</td>
<td style="text-align: right;" colspan="5"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>CSS Styles
.dot_iO {
height: 45px;
width: 45px;
background-color: #56ff56;
border-radius: 50%;
border: 2px solid black;
display: inline-block;
}
.dot_niO {
height: 45px;
width: 45px;
background-color: #ff5656;
border-radius: 50%;
border: 2px solid black;
display: inline-block;
}
table {
border-style: unset !important;
}
tr td {
border-style: unset !important;
}External method: Example
For the external method example, refer to the Leaflet.js interactive maps.
Override
You can see all the defined default styles in the source code.
import { css } from '@emotion/css';
import { GrafanaTheme2 } from '@grafana/data';
import { HIGHLIGHT_DARK, HIGHLIGHT_LIGHT } from '../../constants';
/**
* Styles
*/
export const getStyles = (theme: GrafanaTheme2) => {
/**
* Frame
*/
const frame = css`
border-bottom: 1px solid ${theme.colors.border.medium};
margin-bottom: ${theme.spacing(2)};
padding: ${theme.spacing(1)};
&:last-child {
margin-bottom: 0;
border-bottom: 0;
}
img {
max-width: 100%;
}
li {
margin-left: ${theme.spacing(2)};
}
a {
color: ${theme.colors.text.link};
}
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
th,
td {
padding: ${theme.spacing(0.5)} ${theme.spacing(1)};
border-top: 1px solid ${theme.colors.border.medium};
border-left: 1px solid ${theme.colors.border.medium};
}
th {
font-weight: ${theme.typography.fontWeightMedium};
background: ${theme.colors.background.secondary};
}
border-bottom: 1px solid ${theme.colors.border.medium};
border-right: 1px solid ${theme.colors.border.medium};
}
blockquote {
margin: ${theme.spacing(2)} 0;
border-left: 5px solid ${theme.colors.border.strong};
padding: ${theme.spacing(1)};
padding-left: ${theme.spacing(2)};
p {
font-size: ${theme.typography.body.fontSize};
color: ${theme.colors.text.secondary};
}
}
`;
/**
* Loading Bar
*/
const loadingBar = css`
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
`;
/**
* Highlight
*/
const highlight = theme.isDark ? HIGHLIGHT_DARK : HIGHLIGHT_LIGHT;
return {
frame,
highlight,
loadingBar,
};
};Padding and margins
To display content without padding and margins, you need to override the parent CSS style.
& {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}Code syntax highlight
The code syntax highlighting is based on the highlight.js library, which supports key programming languages.
Styling
The Accessibility (A11Y) syntax highlighting style for light and dark themes is included. You can override it in the styles editor by copying one of the styles from the project source files.
/*!
Theme: a11y-light
Author: @ericwbailey
Maintainer: @ericwbailey
Based on the Tomorrow Night Eighties theme: https://github.com/isagalaev/highlight.js/blob/master/src/styles/tomorrow-night-eighties.css
*/
.hljs {
background: #fefefe;
color: #545454;
}
/* Comment */
.hljs-comment,
.hljs-quote {
color: #696969;
}
/* Red */
.hljs-variable,
.hljs-template-variable,
.hljs-tag,
.hljs-name,
.hljs-selector-id,
.hljs-selector-class,
.hljs-regexp,
.hljs-deletion {
color: #d91e18;
}
/* Orange */
.hljs-number,
.hljs-built_in,
.hljs-literal,
.hljs-type,
.hljs-params,
.hljs-meta,
.hljs-link {
color: #aa5d00;
}
/* Yellow */
.hljs-attribute {
color: #aa5d00;
}
/* Green */
.hljs-string,
.hljs-symbol,
.hljs-bullet,
.hljs-addition {
color: #008000;
}
/* Blue */
.hljs-title,
.hljs-section {
color: #007faa;
}
/* Purple */
.hljs-keyword,
.hljs-selector-tag {
color: #7928a1;
}
.hljs-emphasis {
font-style: italic;
}
.hljs-strong {
font-weight: bold;
}
@media screen and (-ms-high-contrast: active) {
.hljs-addition,
.hljs-attribute,
.hljs-built_in,
.hljs-bullet,
.hljs-comment,
.hljs-link,
.hljs-literal,
.hljs-meta,
.hljs-number,
.hljs-params,
.hljs-string,
.hljs-symbol,
.hljs-type,
.hljs-quote {
color: highlight;
}
.hljs-keyword,
.hljs-selector-tag {
font-weight: bold;
}
}