This is documentation for the next version of Grafana Mimir documentation. For the latest stable release, go to the latest version.
Configure owned series tracking
Note
Owned series tracking is an experimental feature in Grafana Mimir versions 2.12 and later.
In a distributed Grafana Mimir deployment, distributors use consistent hashing to determine which series should be routed to which ingester replicas or Kafka partitions. Because stale in-memory series in ingesters are only cleaned up during TSDB head compaction, the count of in-memory series is not suitable as a metric to drive automated ingester scaling; when a new replica is added, the in-memory series per ingester doesn’t drop until the next head compaction, and the scaler has no feedback about the impact of the scaling operation.
Additionally, since each ingester enforces only a fraction of a tenant’s in-memory series limits locally, increasing the ingester count, or a tenant’s shuffle-shard size, can result in ingesters rejecting samples due to exceeded local limits, even if the global limit isn’t breached. For example:
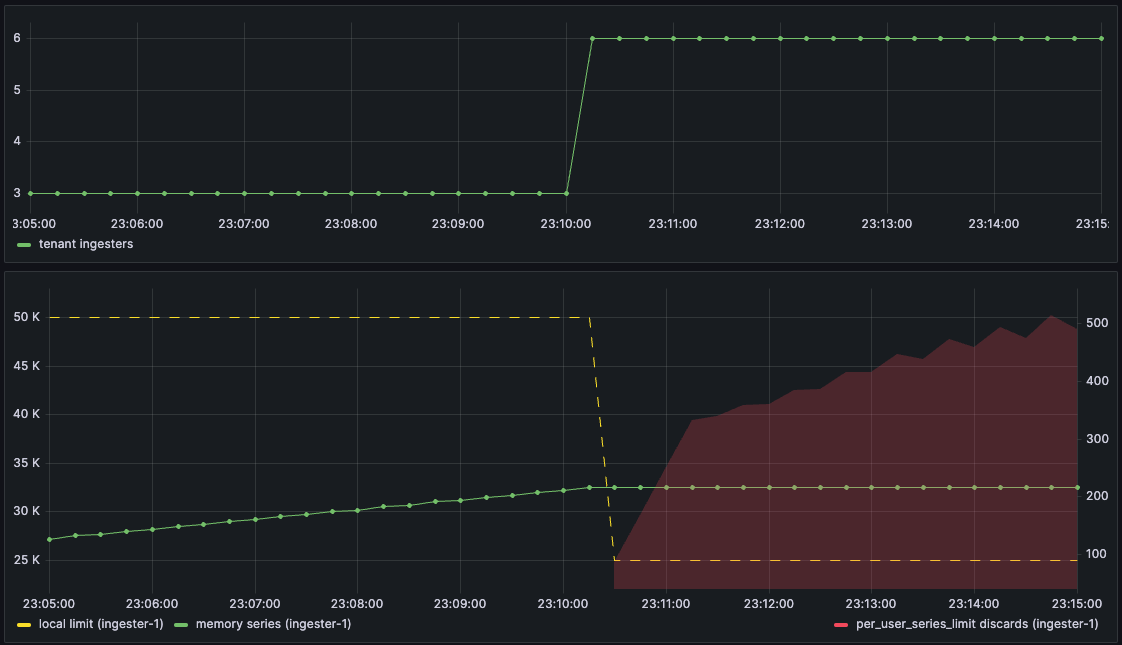
- Consider a tenant with a global series limit of 150k with series spread across 3 ingesters; the local limit on each ingester is 50k in-memory series.
- The tenant is sending ~90k series, so ~30k in-memory series per ingester.
- Now, the tenant is sharded across 6 ingesters, either by adding ingesters or increasing the tenant’s shuffle-shard size.
- The local limit on each ingester drops to 25k; the tenant’s 30k series on the original 3 ingesters exceed the new local limit, and those ingesters immediately start to discard samples.
Owned series tracking addresses these problems by counting, per tenant, the subset of in-memory series that hash to a particular ingester or partition, based on the current ring state and shard configuration. When you enable owned series tracking and use owned series for series limits, Mimir ingesters enforce limits against a tenant’s owned series count rather than the full count of in-memory series.
How owned series tracking works
Note
In ingest storage architecture, tokens are assigned to partitions rather than ingesters.
Ingesters are assigned tokens in a hash ring. For each token T assigned to an ingester, that ingester owns the range of hash values from the preceding assigned token through T-1. The preceding token can belong to any ingester in the ring. When shuffle-sharding is enabled, the token ranges owned by an ingester are different for each tenant, depending on which ingesters are part of the tenant’s sub-ring.
A series is owned by an ingester if the hash of its labels and tenant ID falls within a token range owned by that ingester. New series written to an ingester are automatically counted as owned by the ingester, since the distributors use the same algorithm to route series to ingesters.
Every ingester.owned-series-update-interval, each ingester’s owned series service iterates over each tenant and checks whether their owned series should be recomputed. Recomputation triggers are:
- Shard size changes
- Local series limit changes
- Token ranges changes
- Compaction events
If any of these conditions trigger an owned series recomputation, the ingester iterates over all of the series in the tenant’s TSDB and compares the series hash against the owned token ranges. If the hash falls within one of the token ranges, it is counted as still owned by the ingester; series with hashes that fall outside of the ranges are not counted, but remain in-memory until compaction.
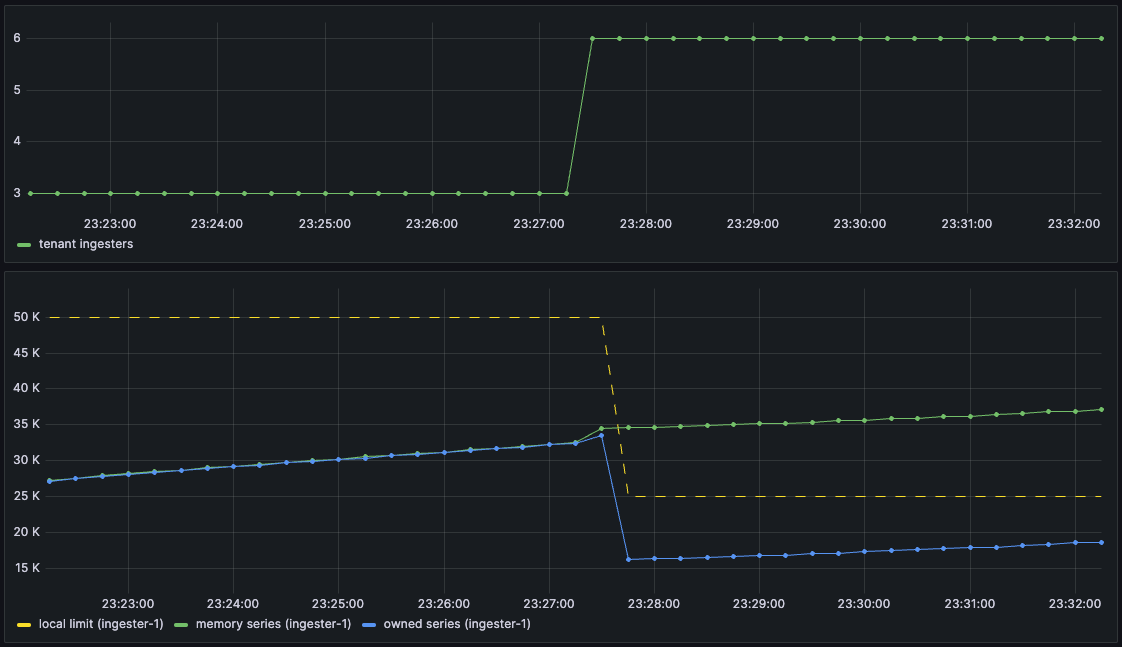
Because owned series are recomputed shortly after a change in the ring state, for instance, adding new ingesters, the owned series count is suitable to provide an autoscaler feedback about the impact of a scaling operation.
Additionally, if the recomputation is triggered by a series limit decrease, the owned series are recomputed before the new series limit takes effect. Series limit increases take effect immediately. This allows graceful handling of this situation, without dropping samples while the owned series are being recomputed.
Before you begin
Note
These steps are only required to use owned series tracking in classic architecture. They are not required with ingest storage architecture because series replication is handled by the Kafka partitions, rather than writing to multiple ingesters. However, zone-aware replication of ingesters is still recommended for high availability.
Due to the way token ranges are calculated, using owned series tracking requires you to complete the following tasks first:
- Enable zone-aware replication.
- Set the replication factor equal to the number of zones.
Configure owned series tracking and limits
Enable owned series tracking on ingesters. For example:
# Enable tracking of owned series based on ring state -ingester.track-ingester-owned-series=true # How often to check whether owned series need to be recomputed -ingester.owned-series-update-interval=15sVerify that owned series are being tracked per tenant by checking for
cortex_ingester_owned_seriesmetricsUse owned series, rather than in-memory series, to enforce per-tenant series limits. For example:
-ingester.use-ingester-owned-series-for-limits=true
For more information, refer to ingester in Grafana Mimir configuration parameters.
Monitor owned series
Ingesters expose the following metrics related to owned series: