Build a mental model of IRM
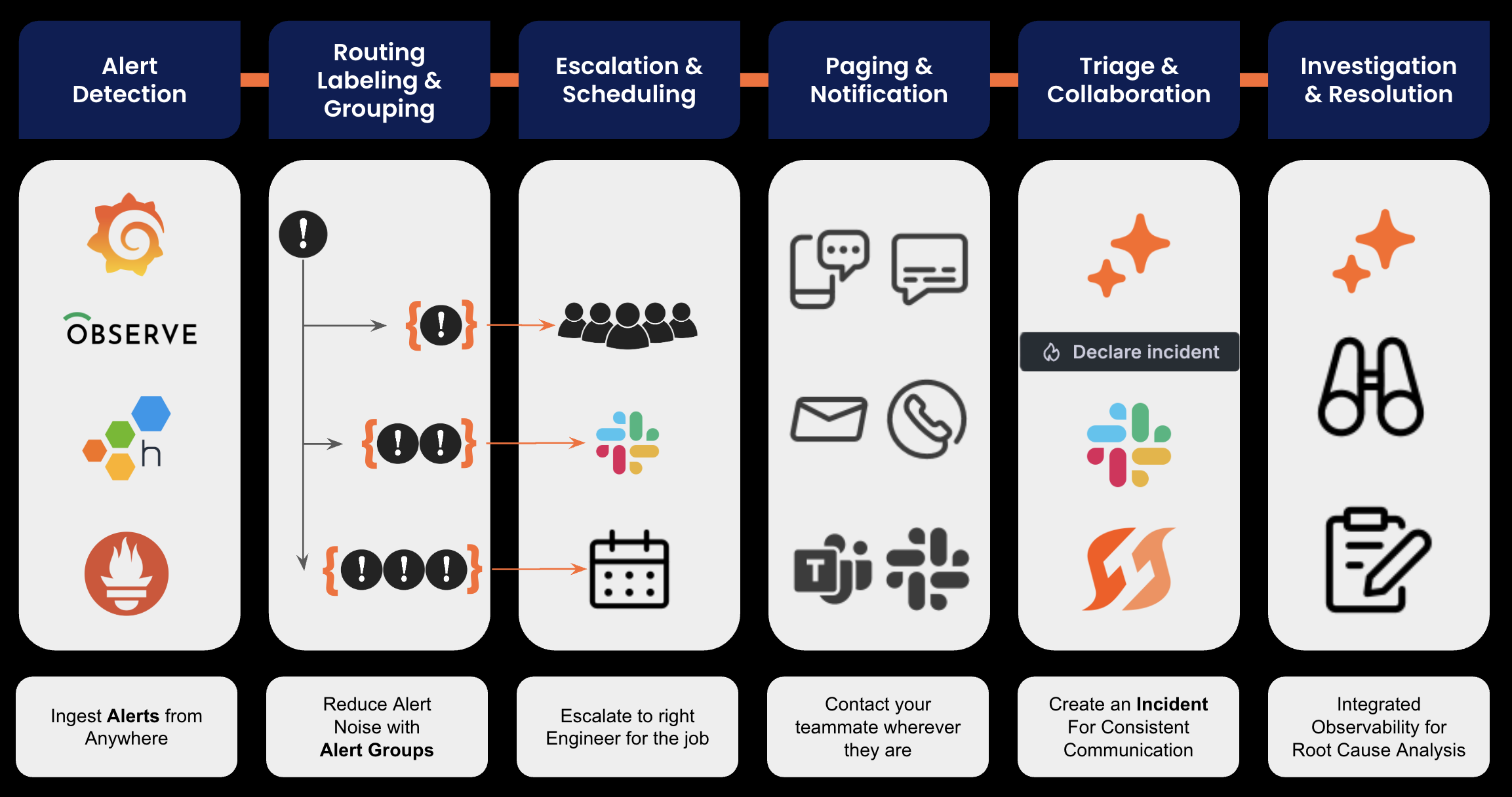
Understanding how IRM components work together helps you design effective incident response workflows. IRM consists of five core components that process alerts from detection to resolution: integrations, routes, escalation chains, schedules, and notification rules.
Each component serves a specific purpose and together they ensure alerts and incidents reach the right people through the appropriate channels.
The following diagram illustrates the different components of IRM and how they work together as alerts flow through IRM:
Familiarize yourself with these components before you configure them in the next milestones:
- Integrations connect alert and event sources to IRM. Common types include Grafana Alerting, external monitoring tools, ticketing systems, custom webhooks, and API based connections.
- Routes apply conditional rules to direct alerts from an integration to specific escalation chains. Every integration has a default route that processes all alerts; add more routes for conditional logic (labels, severity, service, or content).
- Escalation chains define a sequence of notification steps: who is notified, when, and with what importance. They set initial targets, wait intervals, escalation steps, and notification importance.
- Schedules manage on-call rotations and determine who is currently responsible. Use them in escalation chains to notify the current on-call responder automatically.
- Notification rules define user-specific notification methods (SMS, phone call, mobile push, email) with timing and escalation behavior.
In the next milestone, you connect Grafana Alerting as an alert source in IRM.
