This is documentation for the next version of Grafana k6 documentation. For the latest stable release, go to the latest version.
Grafana Cloud k6
Besides running cloud tests, you can also run a test locally and stream the results to Grafana Cloud k6.
When streaming the results to the cloud, the machine - where you execute the k6 CLI command - runs the test and uploads the results to the cloud-based solution. Then, you will be able to visualize and analyze the results on the web app in real-time.
Streaming results vs. running on cloud servers
Don’t confuse k6 cloud run --local-execution script.js (what this page is about) with k6 cloud run script.js.
Fundamentally the difference is the machine that the test runs on:
k6 cloud run --local-executionruns k6 locally and streams the results to the cloud.k6 cloud run, on the other hand, uploads your script to the cloud solution and runs the test on the cloud infrastructure. In this case you’ll only see status updates in your CLI.
In all cases you’ll be able to see your test results at k6 Cloud or Grafana Cloud.
Caution
Data storage and processing are primary cloud costs, so
k6 cloud run --local-executionwill consume VUH or test runs from your subscription.
Instructions
(Optional) - Log in to the cloud
Assuming you have installed k6, the first step is to log in to the cloud service.
With the
k6 cloud logincommand, you can set up your API token on the k6 machine to authenticate against the cloud service and a default stack to use.Copy your token from k6 Cloud or Grafana Cloud k6. For Grafana Cloud k6, you should also set up a default stack by passing it either as a full URL (e.g. https://my-team.grafana.net) or just a slug (e.g. my-team):
k6 cloud login --token <YOUR_API_TOKEN> --stack <YOUR_STACK_SLUG>Run the tests and upload the results
Now, k6 will authenticate you against the cloud service, and you can use the
--local-executionoption to send the k6 results to the cloud as:k6 cloud run --local-execution script.jsAlternatively, you could skip the
k6 cloud logincommand when passing your API token and stack ID (available in your settings, along with your API token) to thek6 cloud runcommand as:K6_CLOUD_TOKEN=<YOUR_API_TOKEN> K6_CLOUD_STACK_ID=<YOUR_STACK_ID> k6 cloud run --local-execution script.jsAfter running the command, the console shows a URL. Copy this URL and paste it in your browser’s address bar to visualize the test results.
execution: local output: cloud (https://acmecorp.grafana.net/a/k6-app/runs/123456) script: script.js
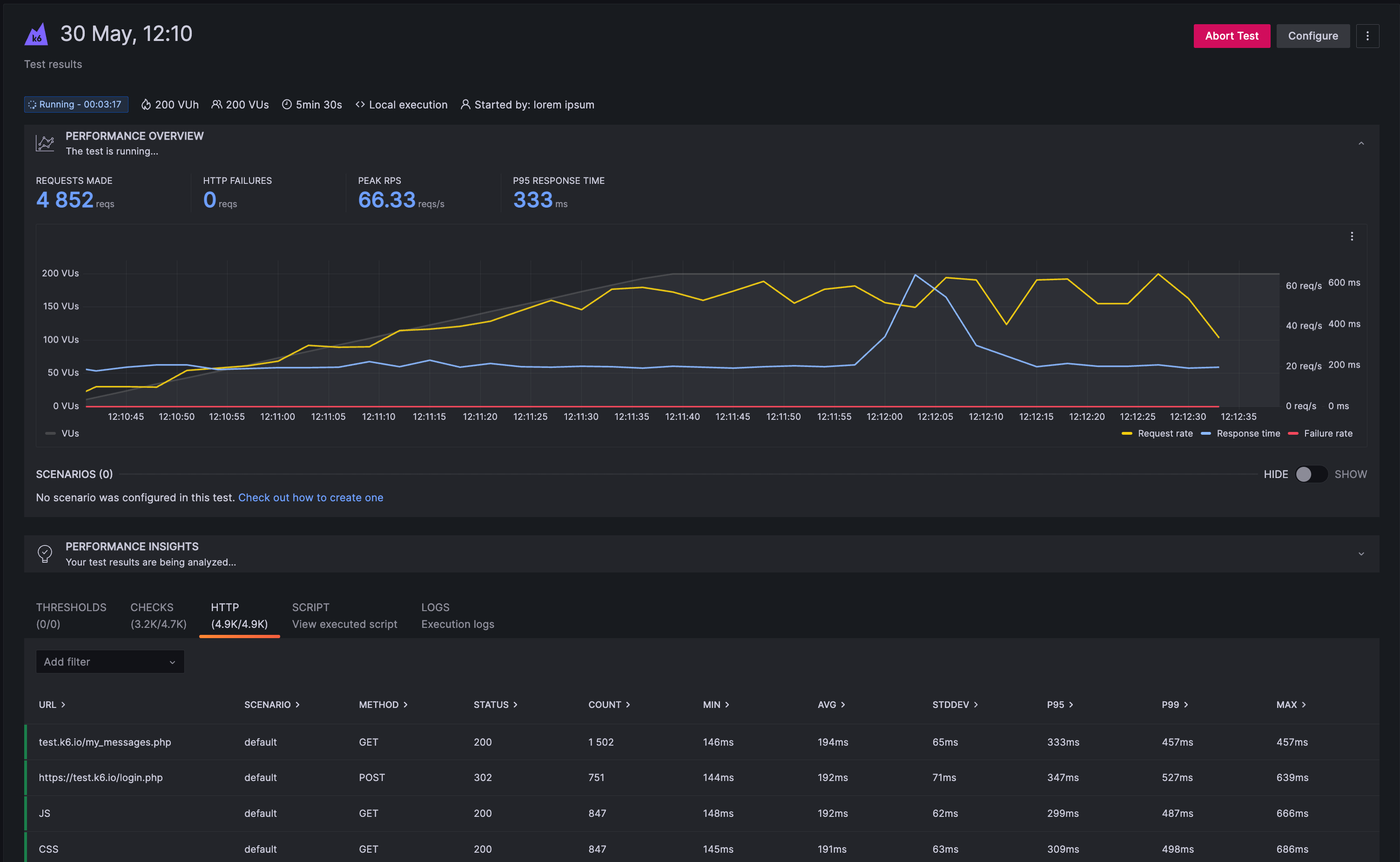
When you send the results to the k6 Cloud with k6 cloud run --local-execution, data will be
continuously streamed to the cloud. While this happens the state of the test run
will be marked as Running. A test run that ran its course will be marked
Finished. The run state has nothing to do with the test passing any
thresholds, only that the test itself is operating correctly.
If you deliberately abort your test (e.g. by pressing Ctrl-C), your test will
end up as Aborted by User. You can still look and analyze the test data you
streamed so far. The test will just have run shorter than originally planned.
Another possibility would be if you lose network connection with the cloud service
while your test is running. In that case the cloud service will patiently wait for
you to reconnect. In the meanwhile your test’s run state will continue to
appear as Running on the web app.
If no reconnection happens, the cloud service will time out after two minutes of no
data, setting the run state to Timed out. You can still analyze a timed out
test but you’ll of course only have access to as much data as was streamed
before the network issue.
Caution
The
k6 cloud run --local-execution script.jscommand uploads the test archive k6 produces from your test script and resources to Grafana Cloud.This behavior can be deactivated by adding the
--no-archive-uploadoption to your command:k6 cloud run --local-execution --no-archive-upload script.js.


