Important: This documentation is about an older version. It's relevant only to the release noted, many of the features and functions have been updated or replaced. Please view the current version.
What’s new in Grafana v9.0
As tradition goes, GrafanaCon — our yearly community event for Grafana open source users — is also where we launch the latest software release of Grafana. Keeping up with tradition, we are excited to be announcing Grafana v9.0: a release that elevates Grafana’s ease of use, discovery of data through new and improved visualizations and a default Grafana Alerting experience.
A big focus for Grafana is making observability and data visualization and analytics easier and more accessible for everyone. For popular data sources like Prometheus and Loki, writing and understanding queries can be hard. This is why we are excited to announce that Grafana 9 comes with new visual query builders for both these data sources. These visual query builders will lower the barrier of entry and they help anyone to compose, understand and learn how the underlying query languages.
The release also includes a brand-new powerful and fast heatmap visualization, a more accessible navigation menu, improvements to dashboard search, advanced security and authentication features, and more.
We’ve summarized what’s new in the release here. If you’d like all the details you can check out the complete changelog.
Prometheus query builder
Prometheus queries are not the easiest to write or understand. The PromQL query language is very complex and advanced. Even relatively simple queries are hard to compose and read for new users. This is why we are introducing a new UI query builder that allows anyone to compose and learn how Prometheus queries work.
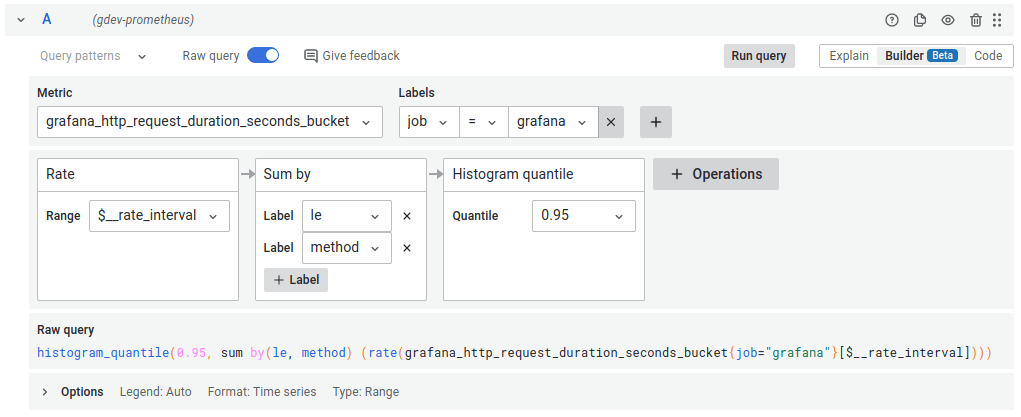
Metric and label filters
This new query builder allows you to easily search and select a metric as well as building label filters. You can start either the selecting a metric or a label filter as they both act as filters on each other. The metric selector allow you to search on multiple parts of the metric name at the same time, just separate each search string with a whitespace.
Operations
All functions, aggregations and binary operations are added via the + Operation button. Operations are presented in the order they are executed, not in the inverted order they are written in the text query. This makes queries a lot easier to read and reason about as you now clearly see what function parameter is going to which function as well as information about parameter names and function documentation integrated into the builder.
Range vector
The query builder will automatically manage and add the range selector. It will be shown as a parameter to the operations that require a range vector (rate, delta, increase, etc).
Binary operations
Simple binary operations like multiplication or division by a scalar are represented via simple operation boxes like other functions. The builder also supports binary operations on nested query expressions.
Switch between code and builder
You can switch between the text edit mode (Code) and the UI builder mode while having your text changes preserved as the visual builder model is derived from the text query using a full featured PromQL query parser.
Loki query builder
Loki also has complex and powerful query language in LogQL. In many ways it’s more complex and has more syntax to remember than PromQL. Luckily the new query builder we are introducing in Grafana v 9.0 will help you write and understand Loki queries without knowing any of the syntax. Take a look at this example log query.
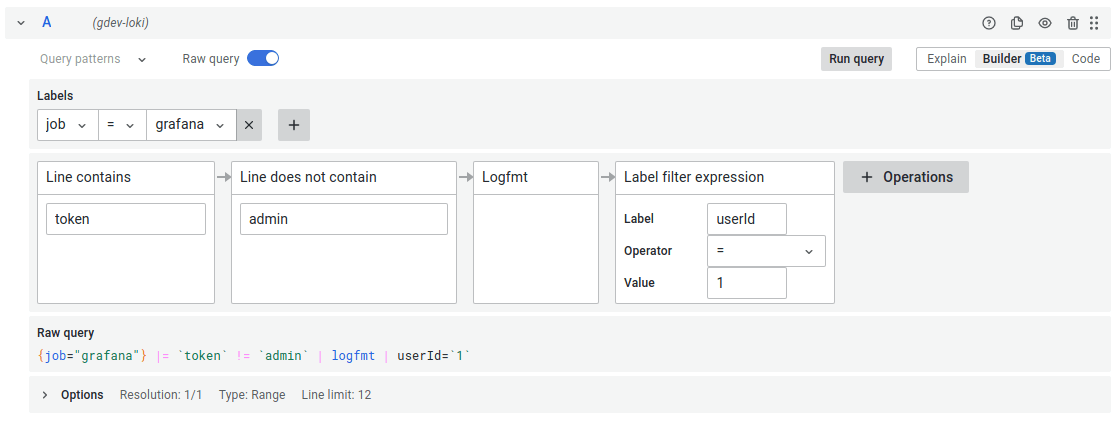
In the query builder you can add and edit label filters, line filters, parsers and functions. The image above shows a log query but you can also do metric queries.

The Loki query builder supports all the features listed for the prometheus query builder above, including support for nested binary operations, explain mode and switching between text editor and builder while preserving changes.
New heatmap panel
We are replacing the old heatmap panel with a new modern panel that is using the new panel option architecture.
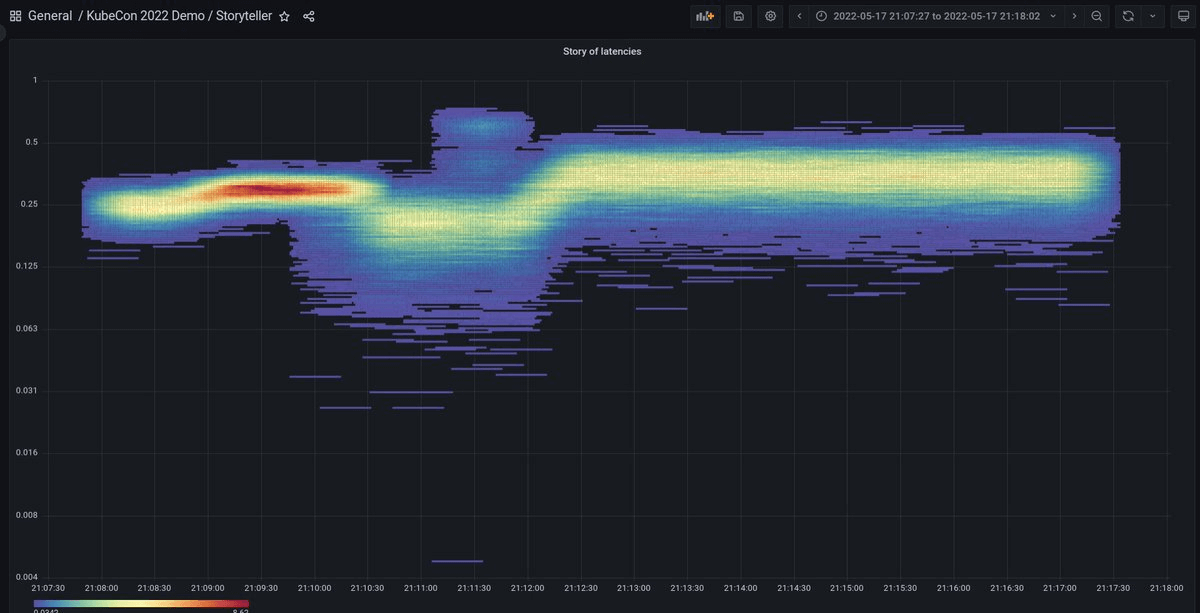
New new heatmap panel has a number enhancements compared to the old version.
- Multiple orders of magnitude faster
- Supports showing exemplars (traces) overlay
- Supports Prometheus sparse histograms
- Supports changing number of colors steps
- For unbucketed data, it performs smarter auto bucket sizing
- Supports filtering out bucket values close to but not exactly zero
The new heatmap by default assumes that the data is pre-bucketed. So if your query returns time series each series is seen as separate bucket (y axis tick). The panel is so much faster than the old one so it can render many time series with thousands of data points each without issue.

Grafana Alerting is the default in Grafana 9
Grafana Alerting is now on by default if you upgrade from an earlier version of Grafana. If you have been using legacy alerting in an earlier version of Grafana and you upgrade to Grafana 9 your alert rules will be automatically migrated and the legacy alerting interface will be replaced by the Grafana Alerting interface.
Grafana Alerting, called unified alerting in Grafana 8, has been available since June, 2021 now provides feature parity with legacy alerting and many additional benefits. To find out more on the process to revert back to legacy alerts if needed, click here. Note that if you do revert back (by setting the Grafana config flag GF_UNIFIED_ALERTING_ENABLED to false), that we expect to remove legacy alerting in the next major Grafana release, Grafana 10.
Alert state history for Grafana managed alerts
Alert state history for Grafana managed alerts indicates the cause of the state. Alert rules can be configured to use the “Alerting” or “OK” states when rule evaluations result in Error or NoData conditions. This change tracks the difference between, for example, Alerting, Alerting (NoData), and Alerting (Error). This change also updates the UI to handle the new serialized states: filtering, sorting, and coloring.
Images in notifications for Grafana managed alerts
Grafana Alerting now provides the ability to capture an image for Grafana managed alerts and deliver it via a notification. This is configurable via the contact points tab of Grafana Alerting . This functionality was available in legacy dashboard alerting, but was missing in Grafana Alerting. It requires the alert to be related to a specific dashboard panel using the “Dashboard UID” and “Panel ID” annotations.
Envelope encryption is generally available and enabled by default
Grafana now uses envelope encryption to encrypt secrets in the database. Envelope encryption adds a layer of indirection to the encryption process. Instead of encrypting all secrets in the database with a single key, Grafana uses a set of keys called data encryption keys (DEKs) to encrypt them. These data encryption keys are themselves encrypted with a single key encryption key (KEK). This allows you to rotate your KEK and quickly re-encrypt your DEKs in case a key is compromised. In Grafana Enterprise, you can also store your KEK in an external key management service (KMS) like AWS KMS or Azure Key Vault, for extra security. Learn more about envelope encryption in the database encryption documentation.
Dashboard previews (opt-in beta)
The dashboard previews initially came to life during our internal Grafana Labs Hackathon, and are now ready for an opt-in beta release. The previews provide an overview of all available dashboards and help you quickly find the right dashboard when the dashboard names aren’t enough.
Refer to the Dashboard previews topic for instructions on how to enable the feature and current limitations.
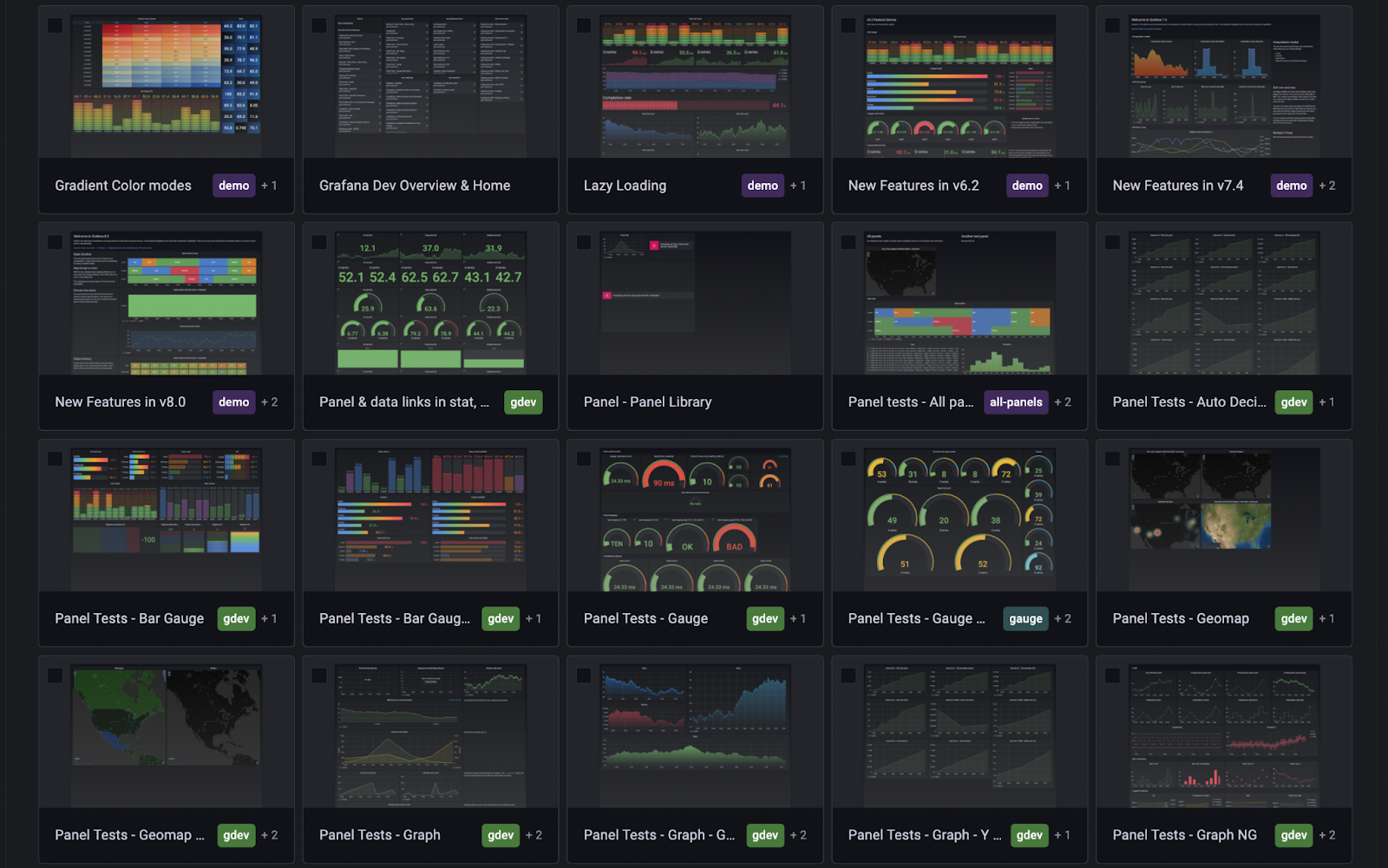
Panel title search (opt-in beta)
Grafana 9 has a feature toggle panelTitleSearch. When enabled, it tells Grafana to use a new search engine. Instead of using SQL queries, the new search uses an in-memory full-text index. That provides a better search experience and additionally allows searching through panel titles.
Expanding the navigation bar
You can expand the navigation bar for a better overview of Grafana’s features and installed integrations. This is the first improvement to Grafana’s navigation, with more to come in future releases.
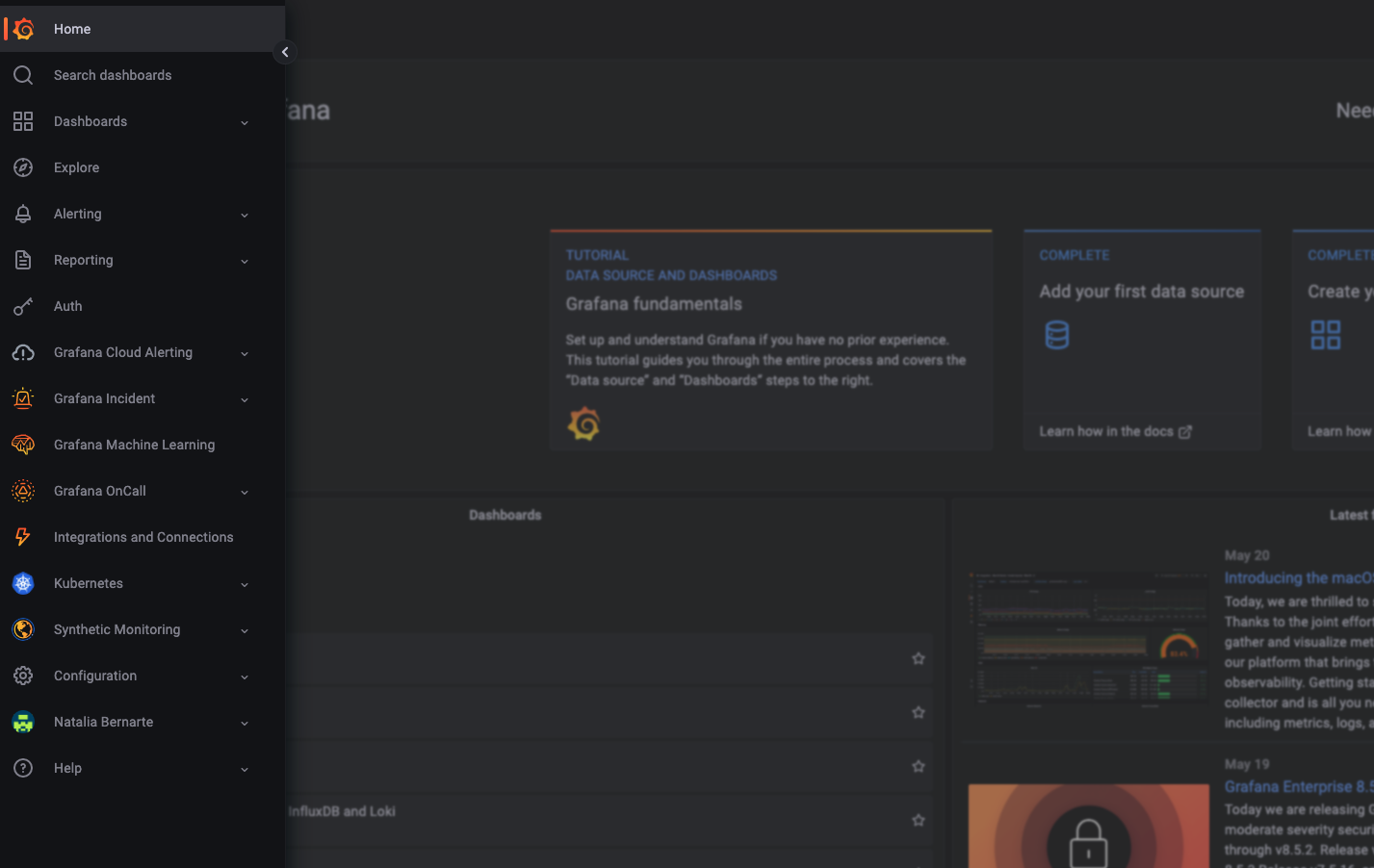
Starred dashboards in the navigation bar
As part of the upcoming improvements to Grafana’s navigation, you can now directly access your starred dashboards from the navigation bar. This is currently an opt-in feature that can be accessed by enabling the savedItems feature flag.
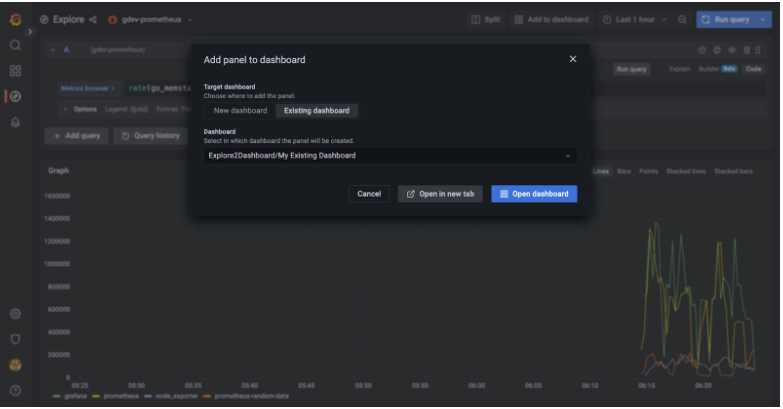
Explore to Dashboard
It is now possible to create panels and/or dashboards directly from Explore. When clicking on the “Add to dashboard” button in the Explore toolbar users can now create a panel in a new dashboard or in an existing one. The generated panel contains all the pane’s queries and a default visualization automatically picked from the current results shown in Explore. Dashboards are not automatically saved so that users can go through the current save flow. Optionally, dashboards can be opened in a new tab to preserve Explore’s state.
Command palette
Using cmd+k (macOS) or ctrl+k (Linux/Windows), users can pull up a palette of commands that allow easier navigation and other tasks.
List of errors with trace IDs
In order to support debugging issues in Grafana, error alerts that appear in Grafana include a trace ID, and these alerts can be accessed under your Profile. This is currently an opt-in feature that can be accessed by enabling two feature flags:
tracing- enables the tracing id in error messagespersistNotifications- enables the alerts page under Profile
Query History migration
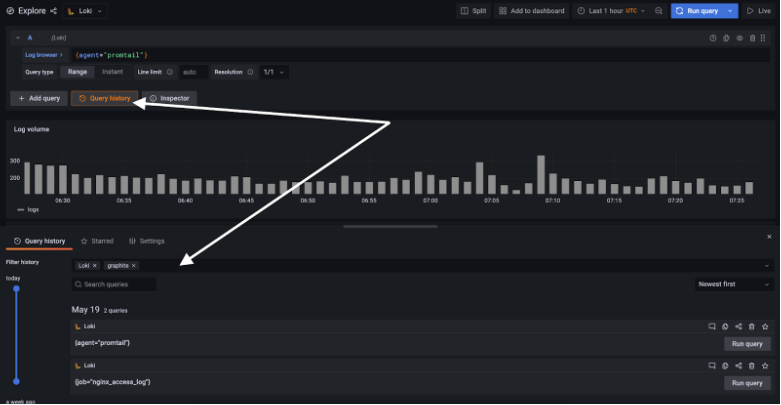
Query history is a panel that keeps track of all queries that are run in Explore. So far the history was saved in browser local storage causing some problems, for example running out of storage space or not being able to use the same query history in different browsers. Not anymore! We’re migrating all entries from browser local storage to the database. Migration will happen behind the senses when query history panel is opened. This feature can be disabled using config entry query_history in custom.ini.
Enterprise
Access control
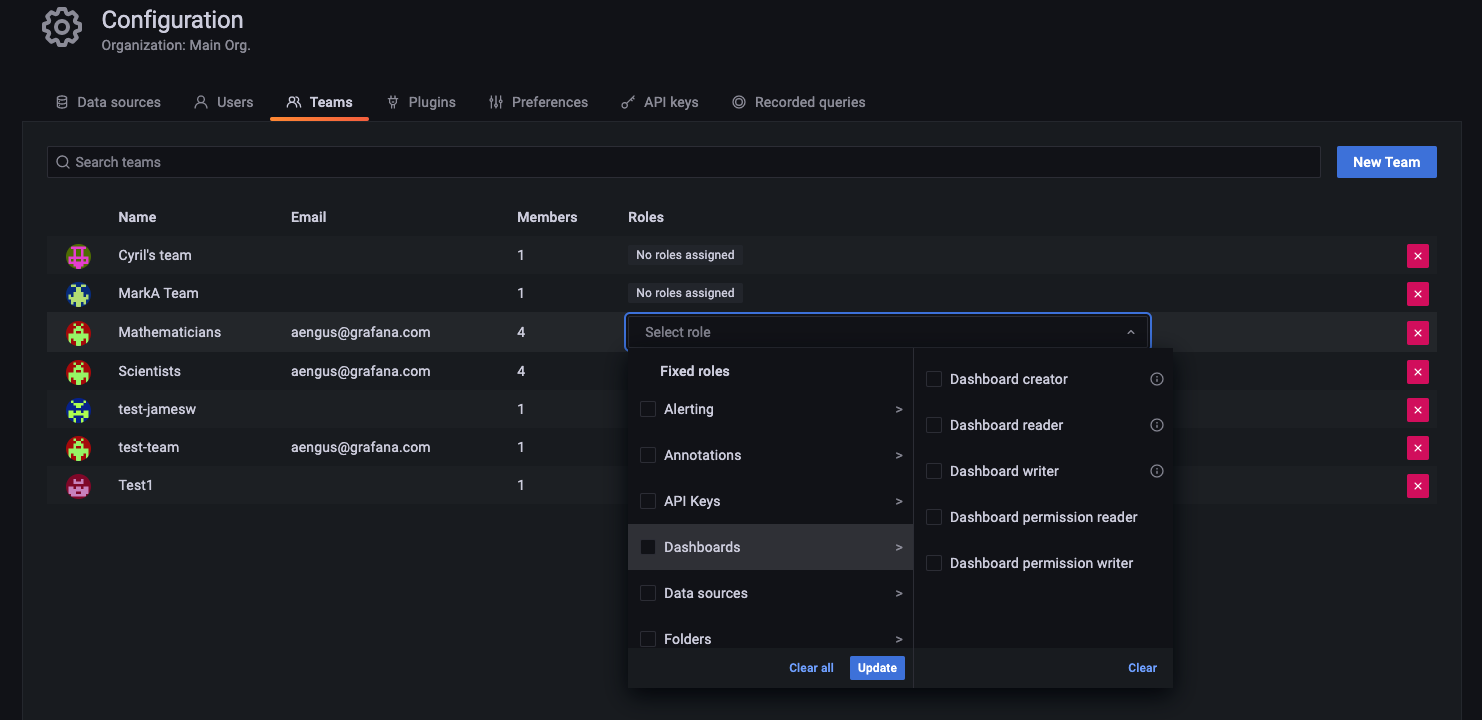
RBAC is generally available
Fine-grained access control is now called role-based access control, or RBAC. It is now enabled by default in Grafana Enterprise and Grafana Cloud Advanced, so you can create and define custom roles like Annotations Writer, Users Viewer, and Dashboard Permissions Writer for users, teams, or service accounts. Learn more about RBAC in the docs.
Reporting
Add multiple dashboards to a single report
If you have information spread across several dashboards that you’d like to send out to a group of recipients periodically, you can now add multiple dashboards to a single report and send it all in one email. Learn more about Reporting in the Reporting docs.
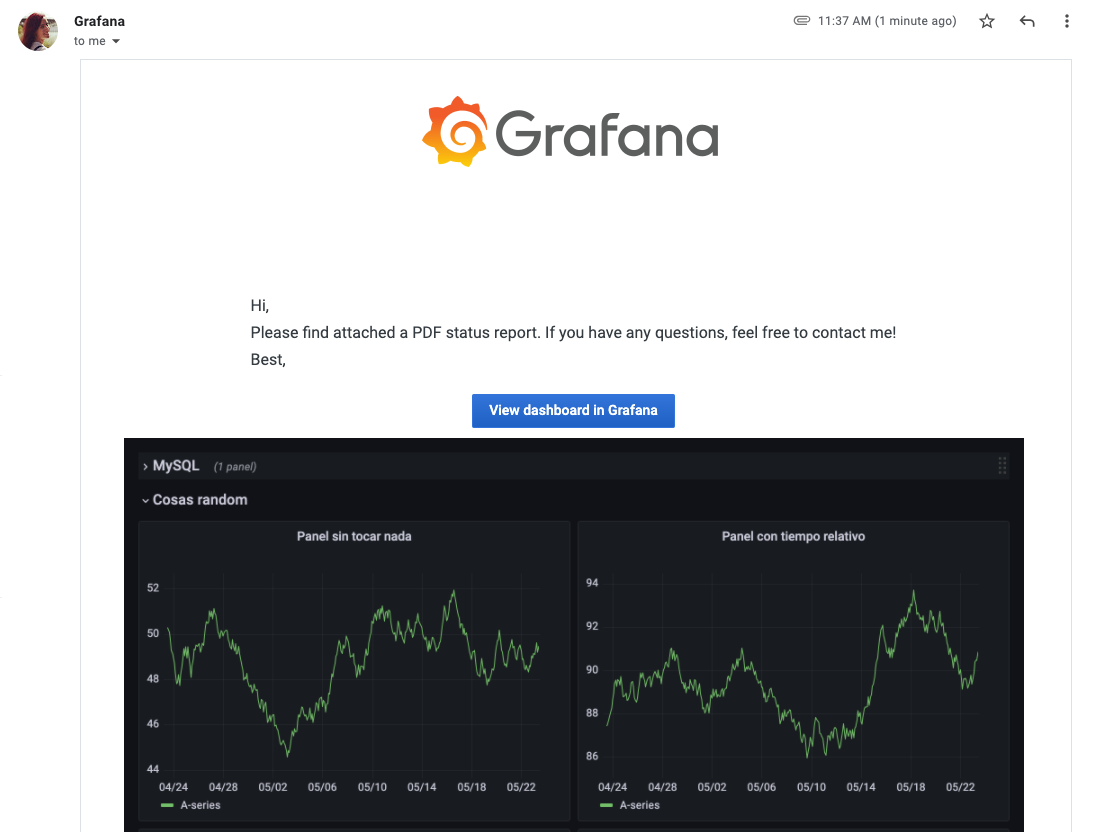
Embed an image of a dashboard in a report
Reporting is all about convenience - getting info to eyeballs as quickly as possible. Now you can embed an image of a dashboard directly within a report email, so your recipients can see it right when they open the message instead of opening an attached PDF. This is especially handy for SLOs, financial results, or other at-a-glance data. Learn more about Reporting in the Reporting docs.
Breaking changes
This is a partial list of notable breaking changes. For the complete list, see our Release Notes.
Role-based access control: changes for general release
Fine-grained access control is now called “Role-based access control”. As part of the Grafana 9.0 release, the service is generally available, and there are several breaking changes:
- Built-in roles are now called basic roles. They now consist of permissions, not roles.
- The Terraform builtin_role_assignment resource is going away.
- Grafana provisioning has a new schema. Please refer to the documentation for more information.
- Basic roles no longer support permission inheritance. Previously, when permissions of a Viewer basic role were modified, it was propagated to the Editor and Admin basic roles. With the Grafana 9.0 release, this is not the case anymore.
- Several role-based access control actions have been renamed. All the database entries that use legacy action names will be migrated to use the new names, but provisioning files and scripts will have to be updated by the user. This change also means that if Grafana is downgraded from 9.0 to a lower version, some role-based access control permissions will not be resolved correctly.
Loki: logs data format changed
In the Loki data source, the data format used to represent Loki logs-data has been changed to a more efficient format. (NOTE: this change applies to logs data only, it does not apply to numeric data) The logs are represented by a single dataframe with a “labels” field added, instead of separate dataframes for every label combination. Displaying logs data in explore, or in a dashboard using the logs panel will continue to work without changes. But, when displaying logs data in other dashboard panels, for example in a table visualization, changes will be visible, and configurations might need to be adjusted. For example, if the “Labels to fields” transformation was used, it has to be replaced with an “Extract fields” transformation, where the “labels” field is chosen as the source.
Loki: NaN values representation changed in numeric data
In the Loki data source, when grafana receives numeric data from Loki, it may contain NaN (not a number) values. For consistency and performance reasons we changed how we represent such values in Grafana. In previous versions, the behavior was different between alerting queries and other queries (like dashboard queries or explore queries). Alerting queries kept NaN values unchanged, but other queries converted these values to “null”. Starting with grafana 9.0.0, we will always keep these values unchanged. In other words, queries in dashboards and explore will behave the same as alerting queries in this regard.
Elasticsearch: Support for versions after their end of life was removed
Support for Elasticsearch versions that are after their end of life ( based on https://www.elastic.co/support/eol ) was removed. This means that versions older than Elasticseach 7.10.0 will not be supported in Grafana 9.0.0.
Elasticsearch: Support for browser access mode removed
In the Elasticsearch data source, browser access mode was deprecated in grafana 7.4.0 and removed in 9.0.0. If you used this mode, please switch to server access mode on the data source configuration page.
Prometheus: NaN values representation changed in numeric data
In the Prometheus data source, when grafana receives numeric data from Prometheus, it may contain NaN (not a number) values. For consistency and performance reasons we changed how we represent such values in Grafana. In previous versions, the behavior was different between alerting queries and other queries (like dashboard queries or explore queries). Alerting queries kept NaN values unchanged, but other queries converted these values to “null”. Starting with grafana 9.0.0, we will always keep NaN values unchanged for all queries.
Transformations: Allow more complex regex expressions in rename by regex
The rename by regex transformation has been improved to allow global patterns of the form /<stringToReplace>/g. Depending on the regex match used, this may cause some transformations to behave slightly differently. You can guarantee the same behavior as before by wrapping the match string in forward slashes (/), for example, (.*) would become /(.*)/. (Github Issue #48179)
Clock Panel
We have updated clock panel to version 2.0.0 to make it compatible with Grafana 9. The previous version 1.3.1 will cause the Grafana 9 to crash when being used in a dashboard, we encourage you to update the panel before migrating to Grafana 9.
Polystat Panel
We have updated polystat panel to version 1.2.10 to make it compatible with Grafana 9. The previous versions 1.2.8 and below will render empty in Grafana 9. We encourage you to update the panel before or immediately after migrating to Grafana 9.
Plugins: Most relevant breaking changes
getColorForThemewas removed, usetheme.visualization.getColorByNameinstead PR #49519TextDisplayOptionswas removed, useVizTextDisplayOptionsinstead PR #49705- We have changed the internals of
backendSrv.fetch()to throw an error when the response is an incorrect JSON. Make sure to handle possible errors on the callsite where usingbackendSrv.fetch()(or any otherbackendSrvmethods) PR #47493 - We have removed the deprecated
getFormStylesfunction from grafana-ui. UseGrafanaTheme2and theuseStyles2hook instead PR #49945 - We have removed the deprecated
/api/tsdb/querymetrics endpoint. Use/api/ds/queryinstead PR #49916
You can find the complete list of breaking changes in the links below. Please check them out for more details and see if there is anything affecting your plugin
- https://grafana.com/docs/grafana/next/release-notes/release-notes-9-0-0-beta1/
- https://grafana.com/docs/grafana/next/release-notes/release-notes-9-0-0-beta2/
- https://grafana.com/docs/grafana/next/release-notes/release-notes-9-0-0-beta3/
- https://grafana.com/docs/grafana/next/release-notes/release-notes-9-0-0
Envelope encryption enabled by default
Grafana v8.5 added a new kind of encryption called “envelope encryption” for secrets stored in the Grafana database, such as data source credentials, alerting notification channel credentials, oauth tokens, etc., behind a feature toggle named envelopeEncryption.
In v9.0, the envelopeEncryption feature toggle is replaced in favor of disableEnvelopeEncryption, and Grafana uses the envelope encryption mechanism by default.
Therefore, any secret created or updated in Grafana v9.0 won’t be decryptable by any previous Grafana version, unless the Grafana version is at least v8.5 and the feature toggle envelopeEncryption is enabled. If not properly configured, this can cause issues in high availability setups, progressive rollouts, or any situation that involves rolling back to a previous Grafana version.
We strongly recommend that you enable envelopeEncryption for older versions to deploy envelope encryption. You can alternatively configure the disableEnvelopeEncryption feature toggle before upgrading to v9.0; however, this feature toggle might be removed in a future Grafana release.
For more details, and workarounds for potential issues, refer to the documentation.
A note on Grafana Enterprise licensing
When we release Grafana 9.0 on June 14th, Grafana will no longer enforce viewers and editor-admins differently. That means that regardless of whether your Grafana Enterprise license is tiered or combined, instead of seeing this on the Stats & Licensing page:
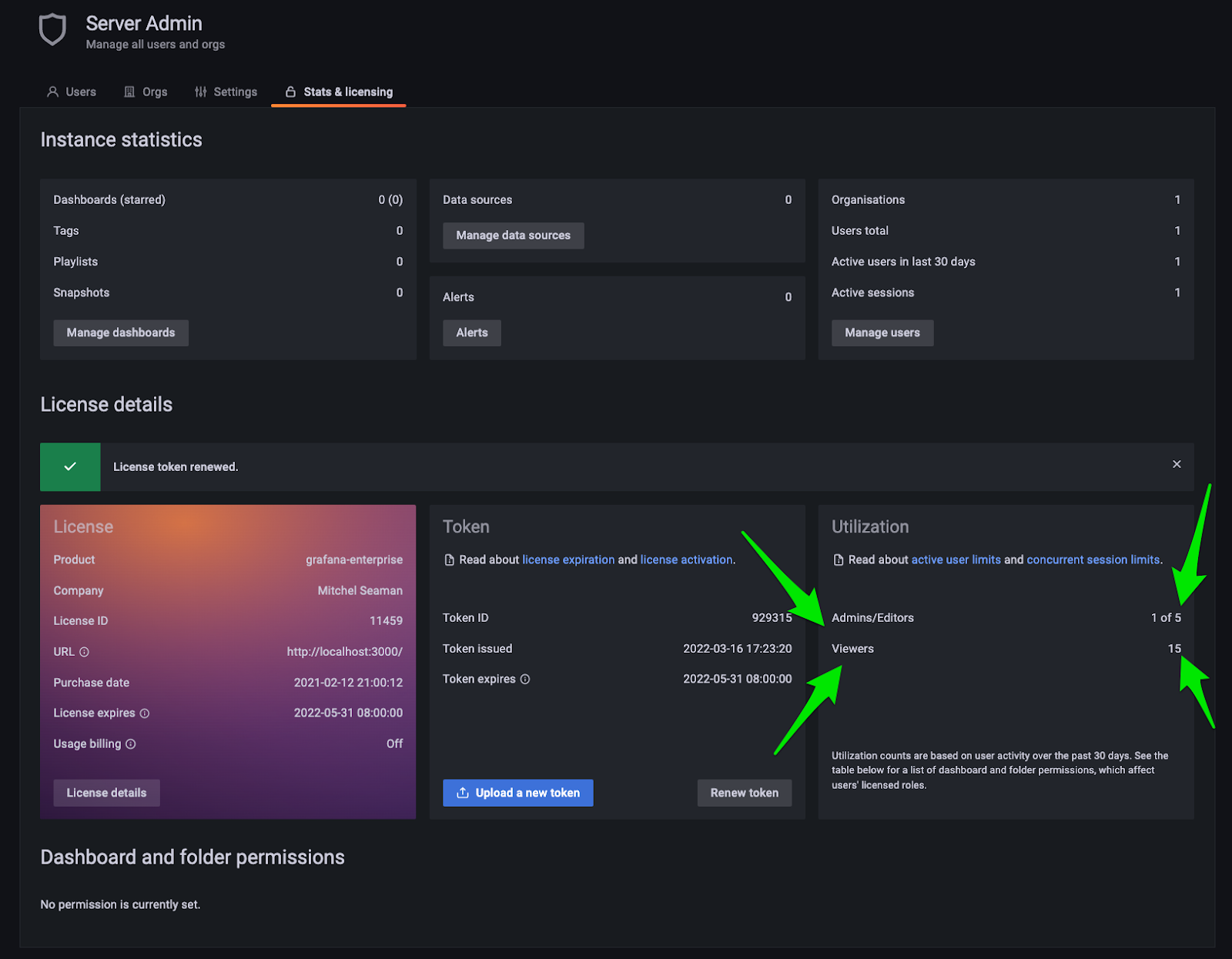
You will see this:
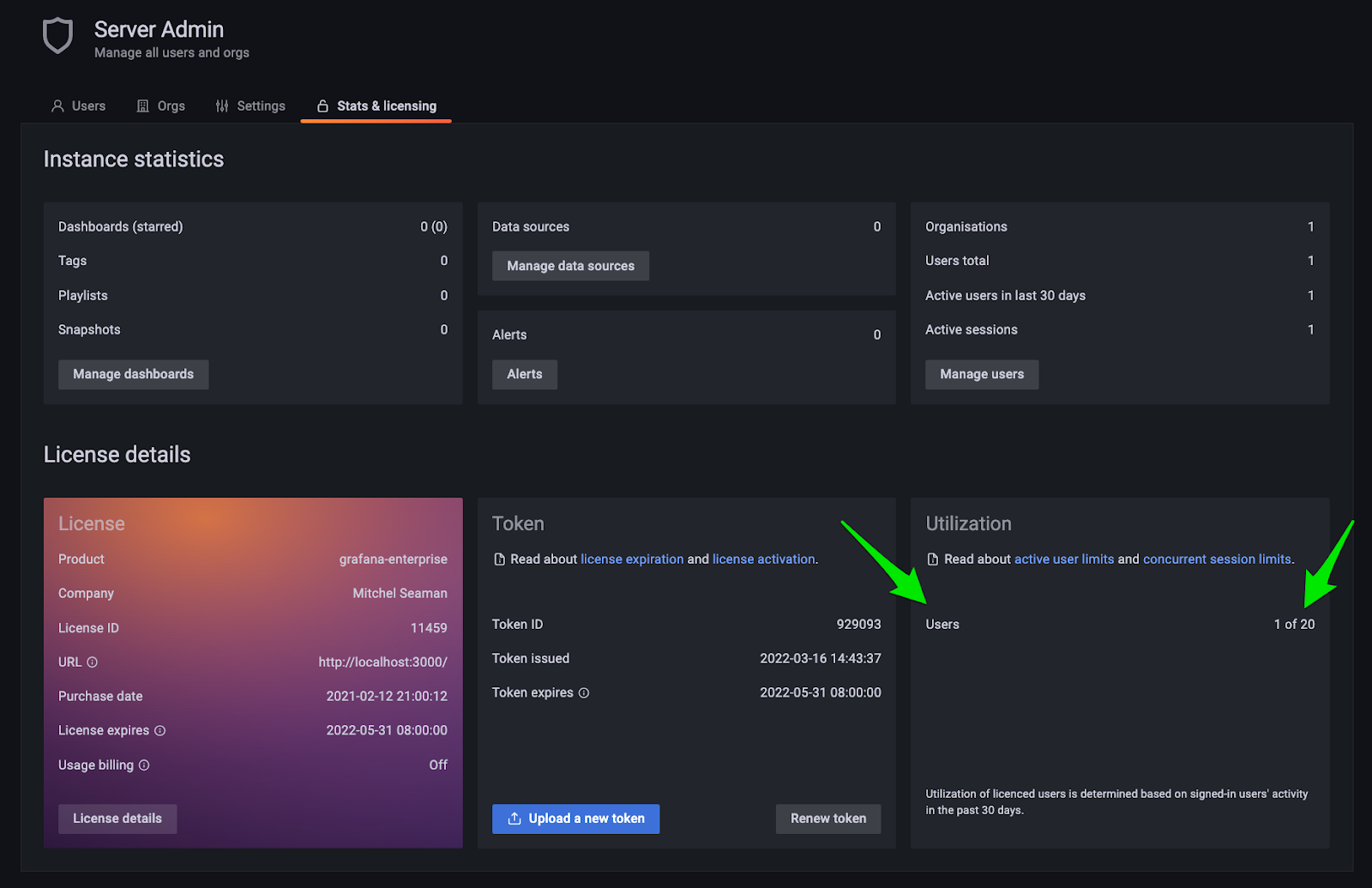
It also means that Grafana will count all users the same, regardless of their role, including org roles (Viewer, Editor, Admin) and fine-grained roles (Dashboard Editor, Reports Editor, etc.). You won’t see a separate warning banner or see users locked out if you hit your limit of viewers or editor-admins, only your total combined limit of active users.
For example, if you have a license for 10 active admins and 100 active viewers in your Grafana Enterprise license, then starting in v9.0 you will have a limit of 110 active users, and it doesn’t matter what roles those users have, they will all be counted and enforced the same.
This is a more permissive policy than before.



