Important: This documentation is about an older version. It's relevant only to the release noted, many of the features and functions have been updated or replaced. Please view the current version.
Explore
Grafana’s dashboard UI is all about building dashboards for visualization. Explore strips away all the dashboard and panel options so that you can focus on the query. Iterate until you have a working query and then think about building a dashboard.
Explore is only available in Grafana 6.0 and above.
For infrastructure monitoring and incident response, you no longer need to switch to other tools to debug what went wrong. Explore allows you to dig deeper into your metrics and logs to find the cause. Grafana’s new logging data source, Loki is tightly integrated into Explore and allows you to correlate metrics and logs by viewing them side-by-side. This creates a new debugging workflow where you can:
- Receive an alert
- Drill down and examine metrics
- Drill down again and search logs related to the metric and time interval (and in the future, distributed traces).
If you just want to explore your data and do not want to create a dashboard, then Explore makes this much easier. If your data source supports graph and table data, then Explore shows the results both as a graph and a table. This allows you to see trends in the data and more details at the same time.
Start exploring
Note: By default, users with the Viewer role cannot edit and do not have access to Explore. Refer to Organization roles for more information about what each role has access to.
There is an Explore icon on the menu bar to the left. This opens an empty Explore tab.

If you want to start with an existing query in a panel, choose the Explore option from the Panel menu. This opens an Explore tab with the query from the panel and allows you to tweak or iterate in the query outside of your dashboard.

Choose your data source from the dropdown in the top left. Prometheus has a custom Explore implementation, the other data sources use their standard query editor.
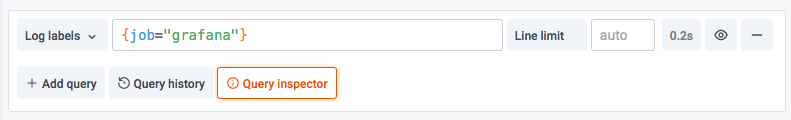
The query field is where you can write your query and explore your data. There are three buttons beside the query field, a clear button (X), an add query button (+) and the remove query button (-). Just like the normal query editor, you can add and remove multiple queries.
Split and compare
The split view feature is an easy way to compare graphs and tables side-by-side or to look at related data together on one page. Click the split button to duplicate the current query and split the page into two side-by-side queries. It is possible to select another data source for the new query which for example, allows you to compare the same query for two different servers or to compare the staging environment to the production environment.

In split view, timepickers for both panels can be linked (if you change one, the other gets changed as well) by clicking on one of the time-sync buttons attached to the timepickers. Linking of timepickers helps with keeping the start and the end times of the split view queries in sync and it will ensure that you’re looking at the same time interval in both split panels.
You can close the newly created query by clicking on the Close Split button.
Query history
Query history is a list of queries that you have used in Explore. The history is local to your browser and is not shared with others. To open and interact with your history, click the Query history button in Explore.
View query history
Query history lets you view the history of your querying. For each individual query, you can:
- Run a query.
- Create and/or edit a comment.
- Copy a query to the clipboard.
- Copy a URL link with the query to the clipboard.
- Star a query.
Manage favorite queries
All queries that have been starred in the Query history tab are displayed in the Starred. This allows you to access your favorite queries faster and to reuse these queries without typing them from scratch.
Sort query history
By default, query history shows you the most recent queries. You can sort your history by date or by data source name in ascending or descending order.
- Click the Sort queries by field.
- Select one of the following options:
- Newest first
- Oldest first
- Data source A-Z
- Data source Z-A
Note: If you are in split mode, then the chosen sorting mode applies only to the active panel.
Filter query history
Filter query history in Query history and Starred tab by data source name:
- Click the Filter queries for specific data source(s) field.
- Select the data source for which you would like to filter your history. You can select multiple data sources.
In Query history tab it is also possible to filter queries by date using the slider:
- Use vertical slider to filter queries by date.
- By dragging top handle, adjust start date.
- By dragging top handle, adjust end date.
Note: If you are in split mode, filters are applied only to your currently active panel.
Search in query history
You can search in your history across queries and your comments. Search is possible for queries in the Query history tab and Starred tab.
- Click the Search queries field.
- Type the term you are searching for into search field.
Query history settings
You can customize the query history in the Settings tab. Options are described in the table below.
Note: Query history settings are global, and applied to both panels in split mode.
Prometheus-specific Features
The first version of Explore features a custom querying experience for Prometheus. When a query is executed, it actually executes two queries, a normal Prometheus query for the graph and an Instant Query for the table. An Instant Query returns the last value for each time series which shows a good summary of the data shown in the graph.
Metrics explorer
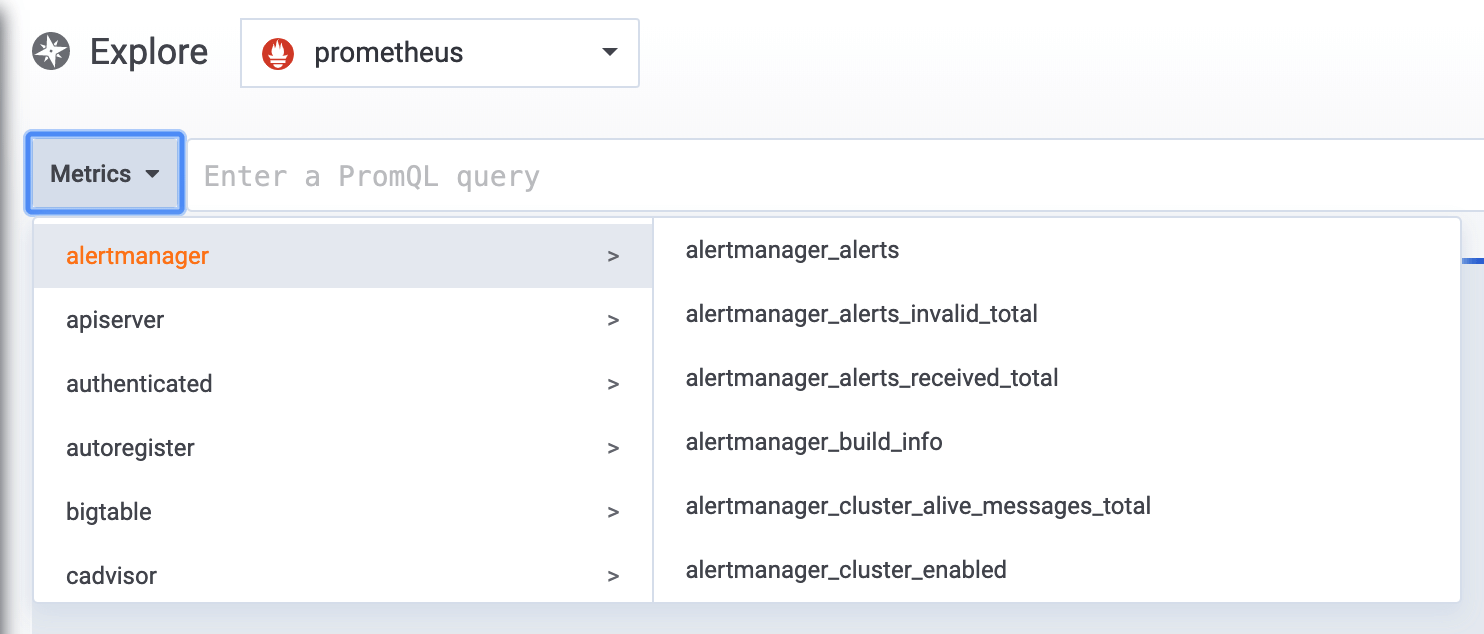
On the left side of the query field, click Metrics to open the Metric Explorer. This shows a hierarchical menu with metrics grouped by their prefix. For example, all Alertmanager metrics are grouped under the alertmanager prefix. This is a good starting point if you just want to explore which metrics are available.
Query field
The Query field supports autocomplete for metric names, function and works mostly the same way as the standard Prometheus query editor. Press the enter key to execute a query.
The autocomplete menu can be triggered by pressing Ctrl+Space. The Autocomplete menu contains a new History section with a list of recently executed queries.
Suggestions can appear under the query field - click on them to update your query with the suggested change.
- For counters (monotonically increasing metrics), a rate function will be suggested.
- For buckets, a histogram function will be suggested.
- For recording rules, possible to expand the rules.
Table filters
Click on the filter button in a labels column in the Table panel to add filters to the query expression. This works with multiple queries too - the filter will be added for all the queries.
Logs integration
Along with metrics, Explore allows you to investigate your logs with the following data sources:
Visualization options
You can customize how logs are displayed and select which columns are shown.
Time
Shows or hides the time column. This is the timestamp associated with the log line as reported from the data source.
Unique labels
Shows or hides the unique labels column that includes only non-common labels. All common labels are displayed above.
Wrap lines
Set this to True if you want the display to use line wrapping. If set to False, it will result in horizontal scrolling.
Deduping
Log data can be very repetitive and Explore can help by hiding duplicate log lines. There are a few different deduplication algorithms that you can use:
- Exact - Exact matches are done on the whole line except for date fields.
- Numbers - Matches on the line after stripping out numbers such as durations, IP addresses, and so on.
- Signature - The most aggressive deduping, this strips all letters and numbers and matches on the remaining whitespace and punctuation.
Flip results order
You can change the order of received logs from the default descending order (newest first) to ascending order (oldest first).
Labels and parsed fields
Each log row has an extendable area with its labels and parsed fields, for more robust interaction. For all labels we have added the ability to filter for (positive filter) and filter out (negative filter) selected labels. Each field or label also has a stats icon to display ad-hoc statistics in relation to all displayed logs.
Loki-specific features
As mentioned, one of the log integrations is for the new open source log aggregation system from Grafana Labs - Loki. Loki is designed to be very cost effective, as it does not index the contents of the logs, but rather a set of labels for each log stream. The logs from Loki are queried in a similar way to querying with label selectors in Prometheus. It uses labels to group log streams which can be made to match up with your Prometheus labels. Read more about Grafana Loki here or the Grafana Labs hosted variant: Grafana Cloud Logs.
See Loki’s data source documentation on how to query for log data.
Switch from metrics to logs
If you switch from a Prometheus query to a logs query (you can do a split first to have your metrics and logs side by side) then it will keep the labels from your query that exist in the logs and use those to query the log streams. For example, the following Prometheus query:
grafana_alerting_active_alerts{job="grafana"}
after switching to the Logs data source, the query changes to:
{job="grafana"}
This will return a chunk of logs in the selected time range that can be grepped/text searched.
Live tailing
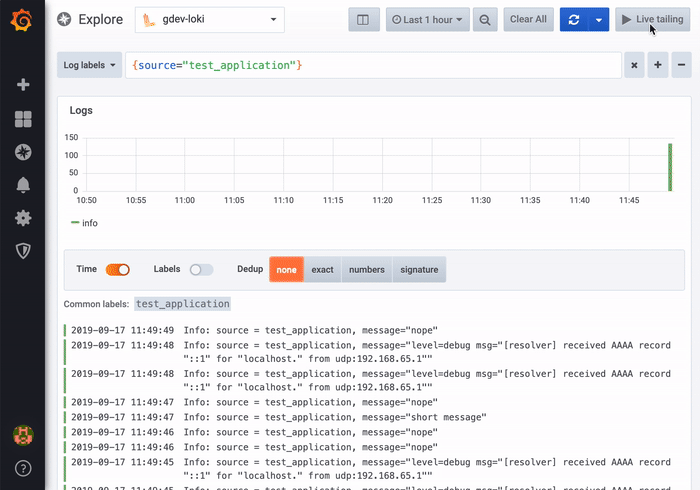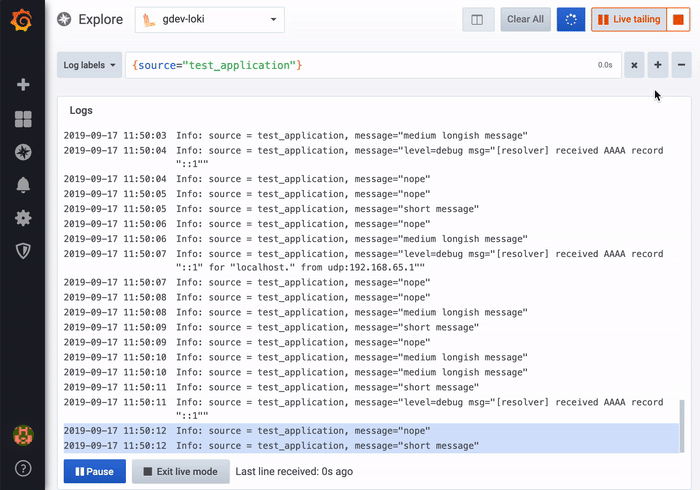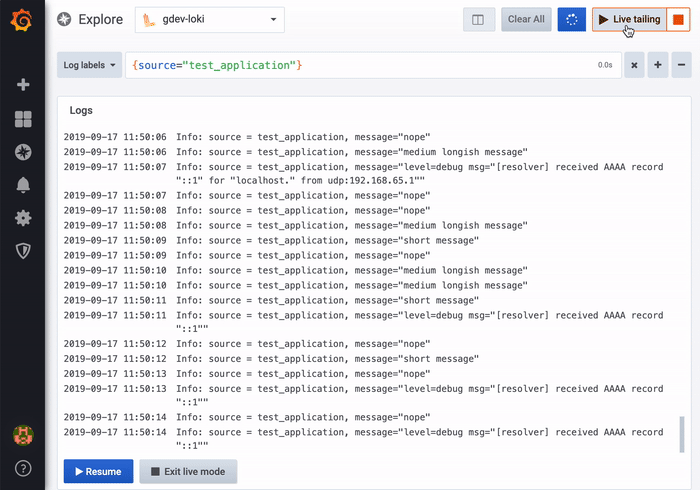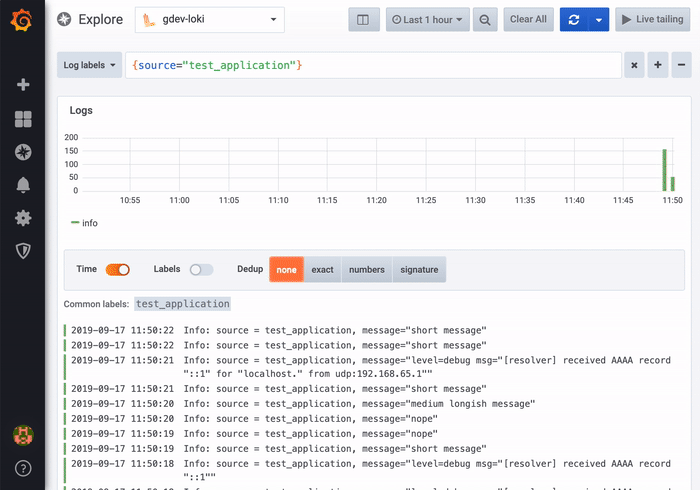
Use the Live tailing feature to see real-time logs on supported data sources.
Click the Live button in the Explore toolbar to switch to Live tail view.
While in Live tail view new logs will come from the bottom of the screen and will have fading contrasting background so you can keep track of what is new. Click the Pause button or scroll the logs view to pause the Live tailing and explore previous logs without interruption. Click Resume button to resume the Live tailing or click Stop button to exit Live tailing and go back to standard Explore view.
Tracing integration
Only available in Grafana v7.0+.
You can visualize traces from tracing data sources in explore. Data sources currently supported:
For information about how to use the query editor see documentation for specific data source.

Header
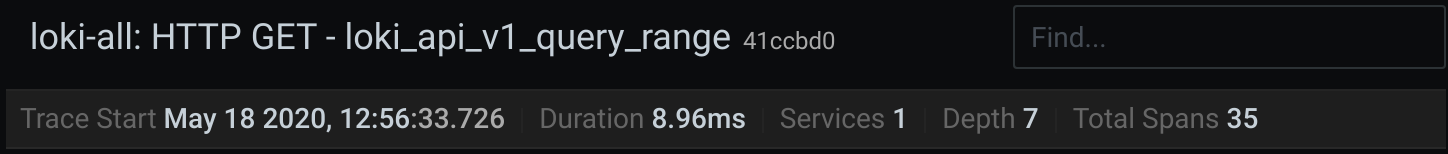
- Header title: Shows the name of the root span and trace ID.
- Search: Highlights spans containing the searched text.
- Metadata: Various metadata about the trace.
Minimap
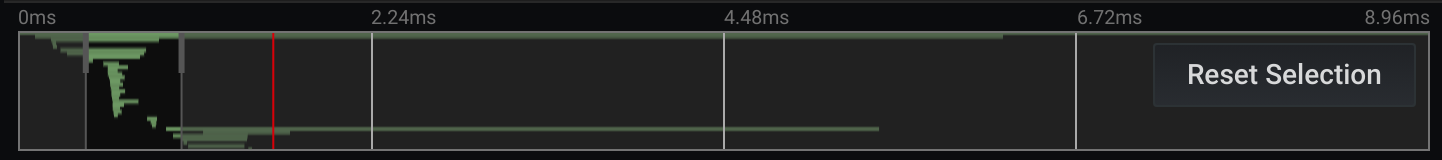
Shows condensed view or the trace timeline. Drag your mouse over the minimap to zoom into smaller time range. Zooming will also update the main timeline, so it is easy to see shorter spans. Hovering over the minimap, when zoomed, will show Reset Selection button which resets the zoom.
Timeline
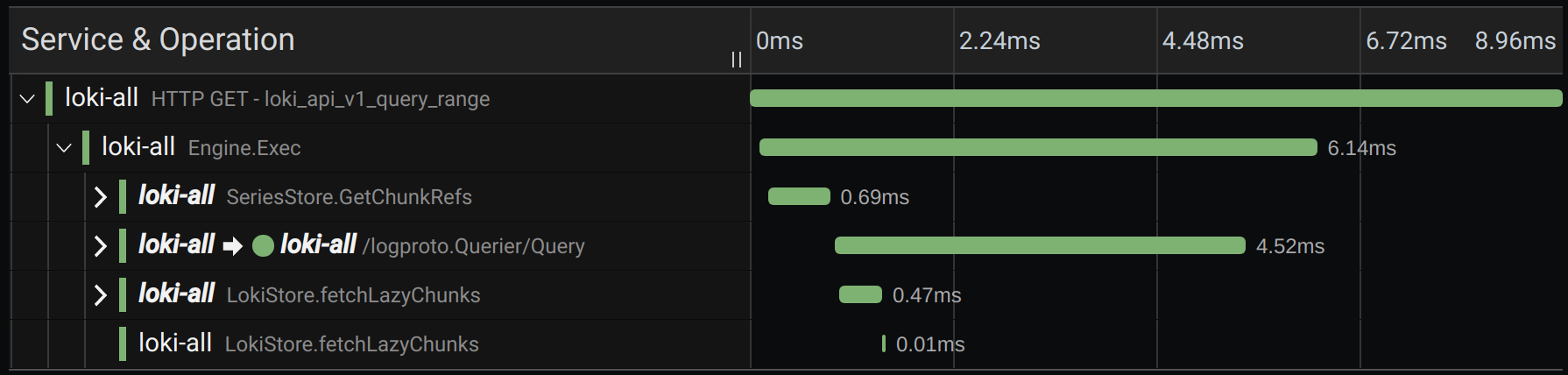
Shows list of spans within the trace. Each span row consists of these components:
- Expand children button: Expands or collapses all the children spans of selected span.
- Service name: Name of the service logged the span.
- Operation name: Name of the operation that this span represents.
- Span duration bar: Visual representation of the operation duration within the trace.
Clicking anywhere on the span row shows span details.
Span details
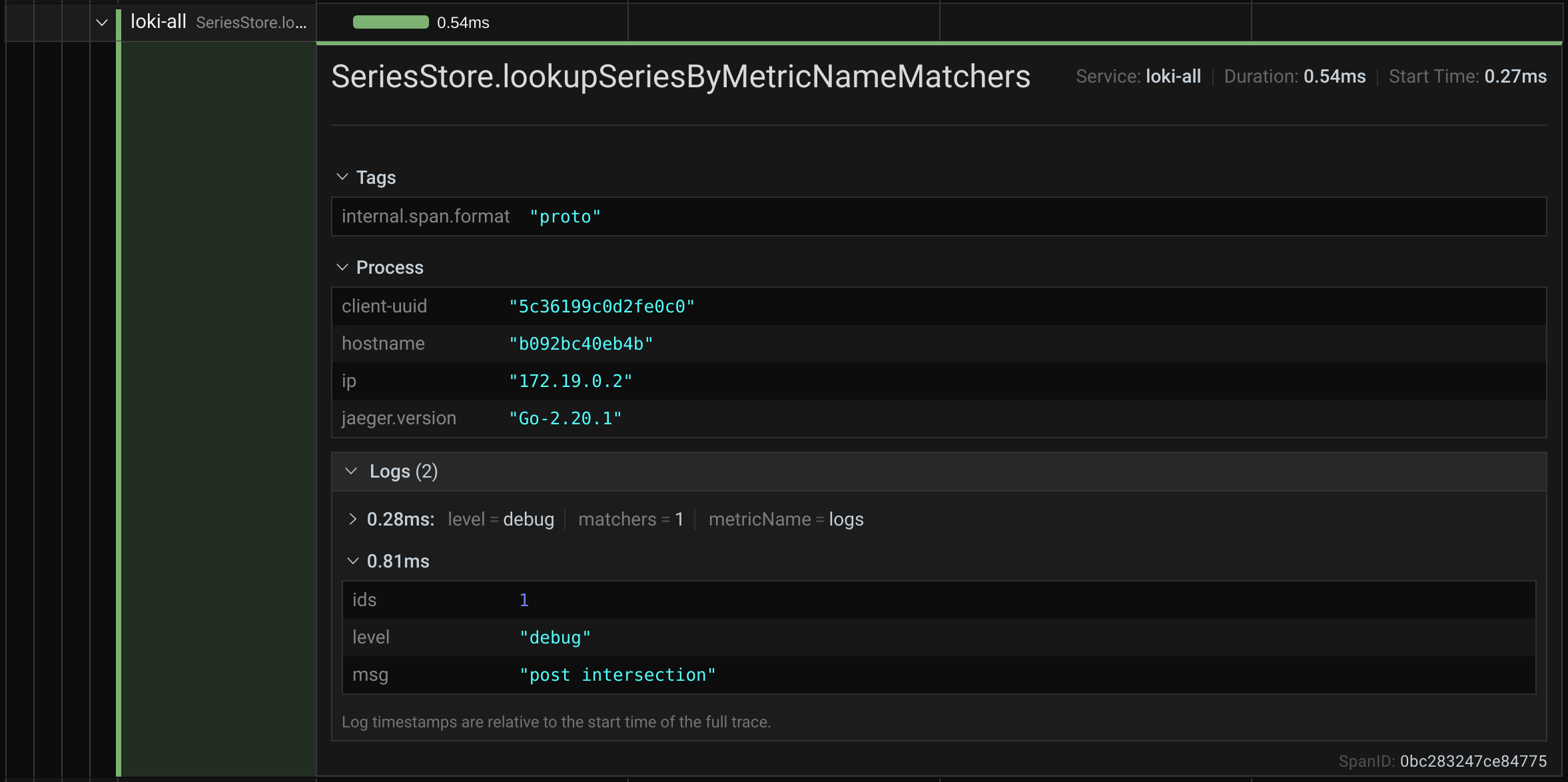
- Operation name
- Span metadata
- Tags: Any tags associated with this span.
- Process metadata: Metadata about the process that logged this span.
- Logs: List of logs logged by this span and associated key values. In case of Zipkin logs section shows Zipkin annotations.
Navigating between Explore and a dashboard
To help accelerate workflows that involve regularly switching from Explore to a dashboard and vice-versa, we’ve added the ability to return to the origin dashboard after navigating to Explore from the panel’s dropdown.

After you’ve navigated to Explore, you should notice a “Back” button in the Explore toolbar.

Simply clicking the button will return you to the origin dashboard, or, if you’d like to bring changes you make in Explore back to the dashboard, simply click the arrow next to the button to reveal a “Return to panel with changes” menu item.

Query inspector
To help with debugging queries, Explore allows you to investigate query requests and responses, as well as query statistics, via the Query inspector. This functionality is similar to the panel inspector Stats tab and Query tab.