Integrate your source code on GitHub with Pyroscope profiling data
The Grafana Pyroscope source code integration offers seamless integration between your GitHub code repositories and Grafana. Using this app, you can map your code directly within Grafana and visualize resource performance line by line. With these powerful capabilities, you can gain deep insights into your code’s execution and identify performance bottlenecks.
Every profile type works with the integration for code written in Go, Java, and Python.
For information on profile types and the profiles available with Go, Java, and Python, refer to Profiling types and their uses.

How it works
The Pyroscope source code integration uses labels configured in the application being profiled to associate profiles with source code. The integration is available for Go, Java, and Python applications.
The Pyroscope source code integration uses three labels, service_repository, service_git_ref, and service_root_path, to add commit information, repository link, and an enhanced source code preview to the Function Details screen.
Note
The source code mapping is only available to people who have access to the source code in GitHub.
Before you begin
To use the Pyroscope source code integration with GitHub, you need an application that emits profiling data, a GitHub account, and a Grafana instance with a Grafana Pyroscope backend.
Application with profiling data requirements
Warning
- Applications in other languages aren’t supported
- A Go application which is profiled by Grafana Alloy
pyroscope.scrape,pyroscope.ebpf(Alloy v1.11.0+), or using the Go Push SDK. - A Java application which is profiled by Grafana Alloy
pyroscope.java,pyroscope.ebpf(Alloy v1.11.0+), or using the Java SDK. For Java applications, a committed.pyroscope.yamlfile is required to map package names to source code locations (refer to Advanced source code mapping with.pyroscope.yaml). - A Python application which is profiled by Grafana Alloy
pyroscope.ebpf(Alloy v1.11.0+) or using the Python SDK.
Your application provides the following labels (tags):
service_git_refpoints to the Git commit or reference from which the binary was builtservice_repositoryis the GitHub repository that hosts the source codeservice_root_path(Optional) is the path where the code lives inside the repository
To activate this integration, add at least the two mandatory labels when
sending profiles: service_repository and service_git_ref. Set them to the
full repository GitHub URL and the current git ref
respectively.
For example, using the Go SDK you can set these labels as tags in the configuration:
pyroscope.Start(pyroscope.Config{
Tags: map[string]string{
"service_git_ref": "<GIT_REF>",
"service_repository": "https://github.com/<YOUR_ORG>/<YOUR_REPOSITORY>",
"service_root_path": "<PATH_TO_SERVICE_ROOT>", // optional
},
// Other configuration
})You can also override these values directly in the UI by clicking the edit button next to the repository information in the Function Details panel. This is useful for testing new configurations before deploying label changes, or for quickly setting up source code viewing during an incident.
![]()
GitHub requirements
- A GitHub account
- Source code hosted on GitHub
Note
Data from your GitHub repository may be limited if your GitHub organization or repository restricts third-party applications. For example, the organization may need to add this app to an allowlist to access organizational resources. Contact your organization administrator for assistance. Refer to Requesting a GitHub App from your organization owner.
Grafana Cloud requirements
- A Grafana Cloud account
- A Grafana instance with a configured Pyroscope data source. Refer to Configure Pyroscope data source for information.
Enable the Pyroscope source code integration
To enable this capability, click Drilldown > Profiles in the sidebar menu and then press the Settings ⚙ button in the top right corner.
Select the toggle for Enable function details to activate. The toggle appears blue with a check mark.
Note
The Profiles Drilldown app plugin proxies requests to the Pyroscope server through the data source proxy. This means you need to allow the data source proxy to also forward the
pyroscope_git_sessioncookie. This can be done by addingpyroscope_git_sessionunder Additional settings > Advanced HTTP settings > Allowed cookies in the Pyroscope data source settings page.
Authorize access to GitHub
You can authorize with GitHub using the Connect to GitHub in the Function Details panel.
- From within Single view with a configured Pyroscope app plugin.
- Select Pyroscope service. For this example, select
cpu_profile. - Click in the flame graph on a function you want to explore. Select Function details.
- On Function Details, locate the Repository field and select Connect to <GITHUB REPOSITORY>, where
<GITHUB REPOSITORY>is replaced with the repository name where the files reside. In this case, it’s connecting to thegrafana/pyroscoperepository. - If prompted, log in to GitHub.
- After Grafana connects to your GitHub account, review the permissions and select Authorize Grafana Pyroscope.
Note
Organization owners may disallow third-party apps for the entire organization or specific organization resources, like repositories. If this is the case, you won’t be able authorize the Grafana Pyroscope source code integration to view source code or commit information for the protected resources.
Modify or remove the Pyroscope source code integration from your GitHub account
The Pyroscope source code integration for GitHub uses a GitHub app called “Grafana Pyroscope” to connect to GitHub. This application authorizes Grafana Cloud to access source code and commit information.
After authorizing the app, your GitHub account, GitHub > Settings > Applications lists the Grafana Pyroscope app.
You can change the repositories the Pyroscope source code integration can access on the Applications page.
You can use also remove the app’s permissions by selecting Revoke. Revoking the permissions disables the integration in your Grafana Cloud account.
For more information about GitHub applications:
How your GitHub code shows up in profile data queries
After authorizing the Pyroscope Grafana source code integration, you see more details in the Function Details from flame graphs in Profiles Drilldown.
- Open a browser to your Pyroscope instance.
- Sign in to your account, if prompted.
- After the Grafana instance loads, select Drilldown.
- Next, select Profiles > Single view from the left-side menu.
- Optional: Select a Service and Profile.
- Click in the flame graph and select Function details from the pop-up menu.
Function Details
The Function Details section provides information about the function you selected from the flame graph.
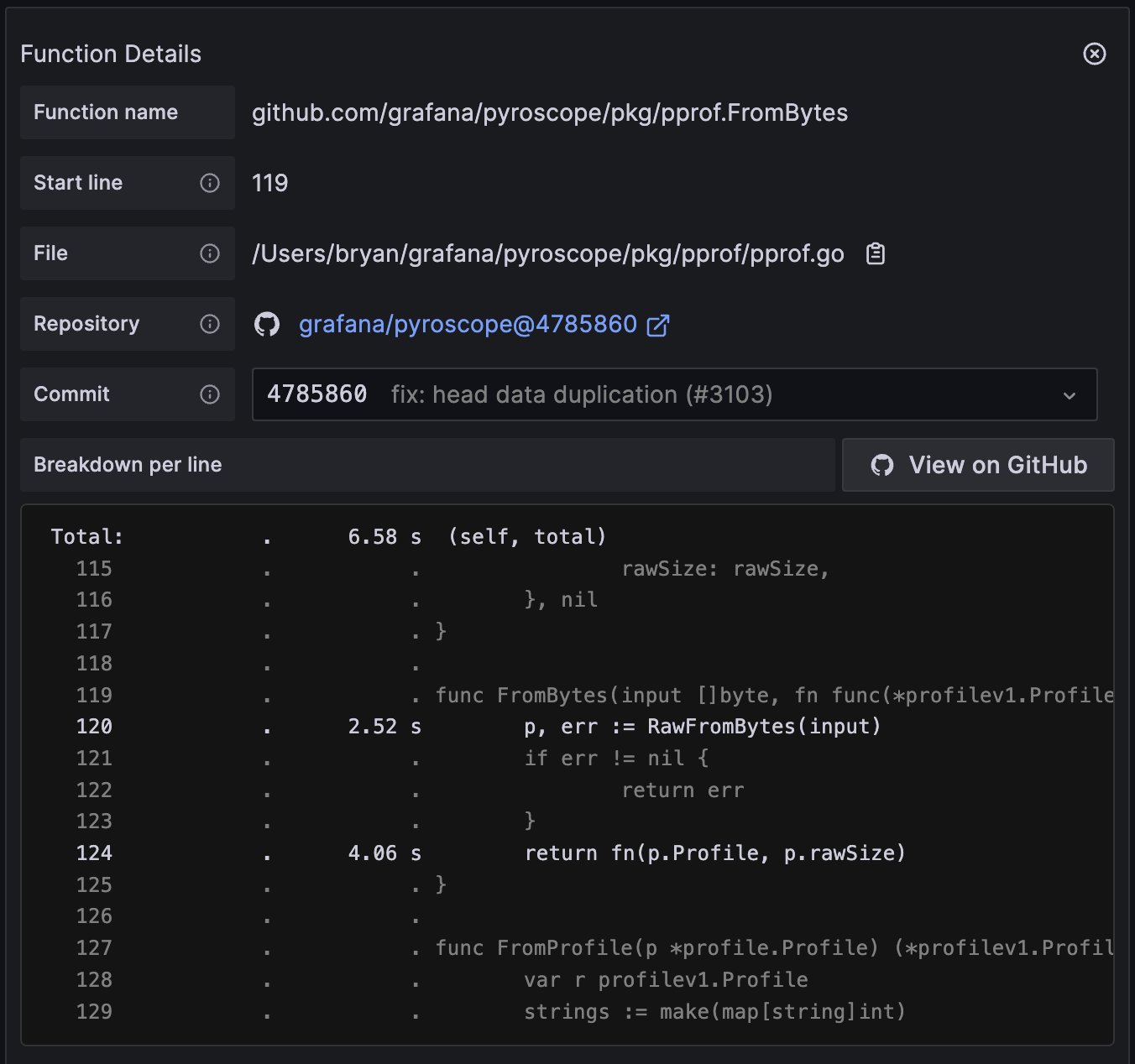
The table explains the main fields in the table. The values for some of the fields, such as Self and Total, change depending whether a profile uses time or memory amount. Refer to Understand Self versus Total metrics in profiling with Pyroscope for more information.
Advanced source code mapping with .pyroscope.yaml
For more complex applications with multiple dependencies and external libraries, you can configure custom source code mappings using a .pyroscope.yaml configuration file in your repository. This feature enables Pyroscope to resolve and display source code from:
- Multiple GitHub repositories (for example, third-party dependencies)
- Different versions and branches of dependencies
- Standard library code (Go, Java)
- Vendor directories and local paths
How source code mapping works
When you click on a function in the flame graph, Pyroscope performs the following steps to retrieve the source code:
- Load configuration: Pyroscope checks for a
.pyroscope.yamlfile in your service’s root path. This is determined by labels on the profiling data as mentioned in How this works. - Match file location: If a configuration file exists, the system matches the path or function name from the profiling data against the configured mappings using a longest-prefix-match algorithm.
- Resolve matched source location: If a mapping matches, Pyroscope determines whether to fetch code from:
- A local path within your repository
- An external GitHub repository at a specific version
- Automatic mapping: If no configuration file exists or no mappings matched, the system tries to find the related source code using heuristics:
- Go: Detect standard library functions and
go.moddependencies - All languages: Resolve using the path relative to the service root
- Go: Detect standard library functions and
- Fetch and display: The source code is retrieved and displayed in the Function Details panel with line-by-line profiling data
Supported languages
The source code integration in Grafana Pyroscope supports the following languages:
- Go: Full support including standard library, Go modules, and vendor directories. Works automatically without configuration, but can be customized with
.pyroscope.yaml. - Python: Full support including standard library and installed packages. Works automatically without configuration, but can be customized with
.pyroscope.yaml. - Java: Requires a
.pyroscope.yamlfile with explicit mappings for application code and dependencies.
Note
While Go and Python work automatically, you can use a
.pyroscope.yamlfile to customize source mappings for any language.
Configuration file format
Create a .pyroscope.yaml file in the root of your repository (or in the path specified by service_root_path if configured) with the following structure:
version: v1 # Config format version (currently only v1 is supported)
source_code:
mappings: # Array of source-to-repository mappings
- path: # Match files by path prefix (optional if function_name is specified)
- prefix: path/to/match
- prefix: another/path
function_name: # Match by function name prefix (optional if path is specified)
- prefix: function/prefix
language: go # Required: "go", "java", or "python"
source: # Define where to fetch the source code
local:
path: src/main/java # Path relative to the location of the .pyroscope.yaml file
# OR
github:
owner: organization # GitHub repository owner
repo: repository # GitHub repository name
ref: v1.0.0 # Branch, tag, or commit SHA
path: src # Path within the external repositoryConfiguration rules
- Each mapping must specify either a
localorgithubsource (not both) - Multiple
pathorfunction_nameprefixes can be specified per mapping (they are combined with OR logic) - Mappings are evaluated using longest-prefix-match (more specific mappings take precedence)
- If no mapping matches, Pyroscope falls back to language-specific default behavior (automatic resolution for Go; Java requires explicit mappings)
Example: Go standard library mapping
Map the Go standard library to a specific Go version:
version: v1
source_code:
mappings:
- path:
- prefix: $GOROOT/src
language: go
source:
github:
owner: golang
repo: go
ref: go1.24.10
path: srcThis configuration ensures that when you view standard library functions like fmt.Println or net/http.Server, Pyroscope fetches the source code from the golang/go repository at version 1.24.10.
Example: Java application with dependencies
Configure mappings for a Java Spring application:
version: v1
source_code:
mappings:
# Local application code
- function_name:
- prefix: org/example/myapp
language: java
source:
local:
path: src/main/java
# JDK standard library
- function_name:
- prefix: java
- prefix: javax
language: java
source:
github:
owner: openjdk
repo: jdk
ref: jdk-17+0
path: src/java.base/share/classes
# Spring Framework dependencies
- function_name:
- prefix: org/springframework/web/servlet
language: java
source:
github:
owner: spring-projects
repo: spring-framework
ref: v5.3.20
path: spring-webmvc/src/main/java
- function_name:
- prefix: org/springframework/web
- prefix: org/springframework/http
language: java
source:
github:
owner: spring-projects
repo: spring-framework
ref: v5.3.20
path: spring-web/src/main/javaThis configuration demonstrates:
- Longest-prefix matching:
org/springframework/web/servletmatches the more specific mapping, whileorg/springframework/web/clientmatches the less specific one - Multiple prefixes: HTTP and web packages from Spring are grouped together
- Mixed sources: Local application code and external dependencies
Example: Go application with vendor dependencies
Map vendor dependencies and modules:
version: v1
source_code:
mappings:
# Vendor directory (for dependencies copied into your repo)
- path:
- prefix: vendor/
language: go
source:
local:
path: vendor
# External dependency at specific version
- path:
- prefix: github.com/prometheus/client_golang
language: go
source:
github:
owner: prometheus
repo: client_golang
ref: v1.19.0
path: ''Example: Python application with dependencies
Map Python application code and external dependencies:
version: v1
source_code:
mappings:
# Local application code
- path:
- prefix: /app/src
language: python
source:
local:
path: src
# Python standard library
- path:
- prefix: /usr/lib/python3.12
- prefix: /usr/local/lib/python3.12
language: python
source:
github:
owner: python
repo: cpython
ref: v3.12.0
path: Lib
# External package (requests)
- path:
- prefix: /usr/local/lib/python3.12/site-packages/requests
language: python
source:
github:
owner: psf
repo: requests
ref: v2.31.0
path: src/requestsThis configuration demonstrates:
- Local application code: Maps your application’s source directory
- Standard library: Maps Python standard library paths to the CPython repository
- External packages: Maps third-party packages to their GitHub repositories
Language-specific behavior
Go
For Go applications, Pyroscope provides intelligent fallback behavior even without a .pyroscope.yaml file:
- Standard library: Automatically detected and mapped to the appropriate
golang/gorepository version - Go modules: Parsed from
go.modin your repository, with automatic version resolution - Vanity URLs: Resolved to canonical repositories (for example,
gopkg.in,google.golang.org) - Vendor directories: Files in
vendor/are searched relative to repository root
The system extracts Go version information from paths like /usr/local/go/go1.24.10/src/fmt/print.go.
Java
Java applications require explicit mappings in .pyroscope.yaml:
- Function name conversion: Java function names like
org/example/App$Inner.methodare automatically converted toorg/example/App.java - No fallback: Unlike Go and Python, Java files cannot be resolved without configuration
- Inner classes: Automatically handled (inner class markers are stripped)
Python
For Python applications, Pyroscope provides intelligent fallback behavior similar to Go:
- Standard library: Automatically detected and mapped to the appropriate
python/cpythonrepository version - Installed packages: Resolved from virtual environments or system packages
- Paths: Direct paths are used when available from profiling data
The system extracts Python version information from paths to map to the correct CPython repository version.
Troubleshooting
No source code displayed
- Verify the
.pyroscope.yamlfile is in your service’s configured root path and that the root path is configured as expected - Check that the
pathorfunction_nameprefixes match your profiling data - For Java applications, ensure all dependencies have mappings configured
- Confirm GitHub OAuth authorization is active and hasn’t expired
Wrong version displayed
- Check the
reffield in your mapping points to the correct branch, tag, or commit - For Go standard library, verify the Go version in your mapping matches your application’s Go version
- Use explicit commit SHA identifiers for reproducibility
Mapping precedence issues
Pyroscope uses longest-prefix-match. If a more specific mapping isn’t being used:
- Verify the prefix exactly matches the beginning of the path or function name
- Check that more specific mappings are listed in the configuration (order doesn’t matter, but clarity helps)
- Test with exact prefixes from your profiling data



