Zipkin data source
Grafana ships with built-in support for Zipkin, an open source, distributed tracing system. This topic explains configuration and queries specific to the Zipkin data source.
For instructions on how to add a data source to Grafana, refer to the administration documentation. Only users with the organization administrator role can add data sources. Administrators can also configure the data source via YAML with Grafana’s provisioning system.
Once you’ve added the Zipkin data source, you can configure it so that your Grafana instance’s users can create queries in its query editor when they build dashboards and use Explore.
You can also upload a JSON trace file, link to a trace ID from logs, and link to a trace ID from metrics.
Configure the data source
To configure basic settings for the data source, complete the following steps:
Click Connections in the left-side menu.
Under Your connections, click Data sources.
Enter
Zipkinin the search bar.Select Zipkin.
The Settings tab of the data source is displayed.
Set the data source’s basic configuration options:
Name Description Name Sets the name you use to refer to the data source in panels and queries. Default Defines whether this data source is pre-selected for new panels. URL Sets the URL of the Zipkin instance, such as http://localhost:9411.Basic Auth Enables basic authentication for the Zipkin data source. User Defines the user name for basic authentication. Password Defines the password for basic authentication.
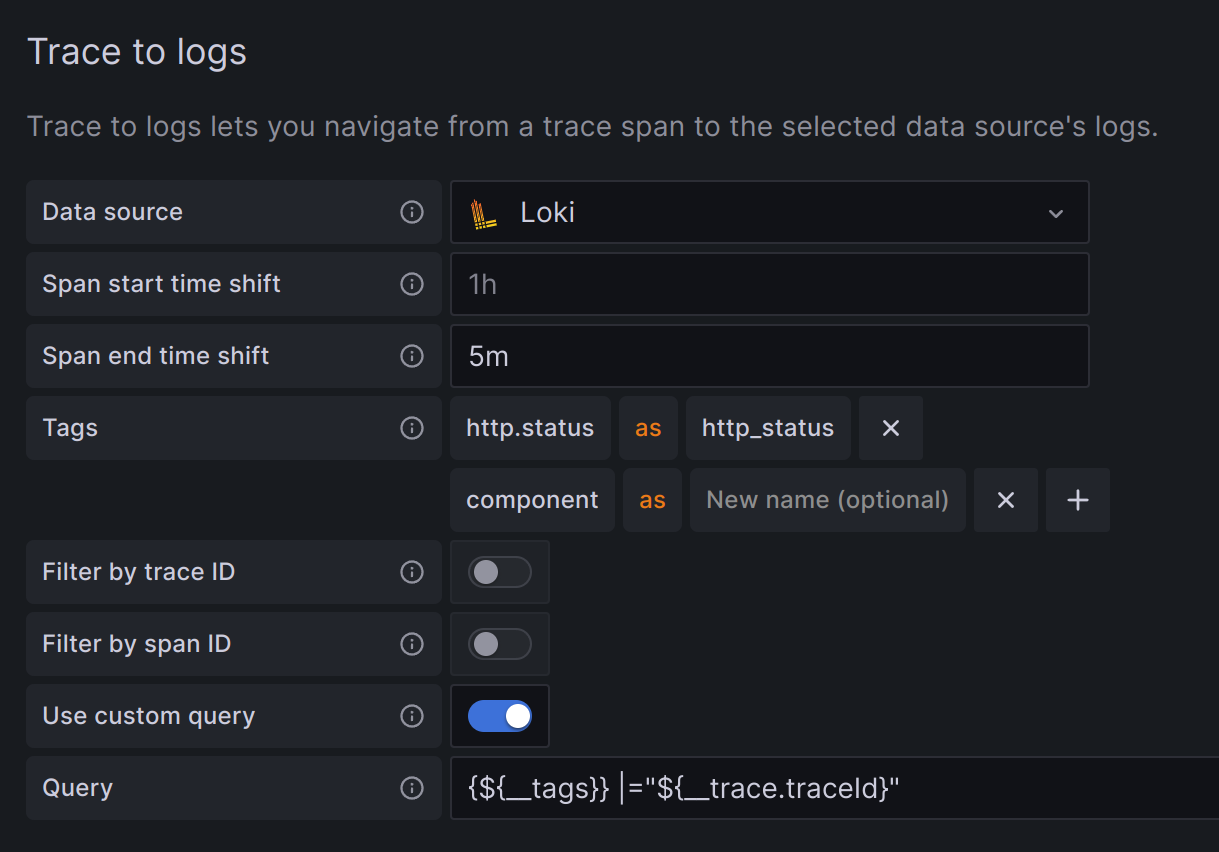
Trace to logs
Note
If you use Grafana Cloud, open a support ticket in the Cloud Portal to access this feature.
The Trace to logs setting configures the trace to logs feature that is available when you integrate Grafana with Zipkin.
There are two ways to configure the trace to logs feature:
- Use a simplified configuration with default query, or
- Configure a custom query where you can use a template language to interpolate variables from the trace or span.
Use a simple configuration
Select the target data source from the drop-down list.
You can also click Open advanced data source picker to see more options, including adding a data source.
Set start and end time shift. As the logs timestamps may not exactly match the timestamps of the spans in trace it may be necessary to search in larger or shifted time range to find the desired logs.
Select which tags to use in the logs query. The tags you configure must be present in the spans attributes or resources for a trace to logs span link to appear. You can optionally configure a new name for the tag. This is useful if the tag has dots in the name and the target data source does not allow using dots in labels. In that case, you can for example remap
http.statustohttp_status.Optionally, switch on the Filter by trace ID and/or Filter by span ID setting to further filter the logs if your logs consistently contain trace or span IDs.
Configure a custom query
Select the target data source from the drop-down list.
You can also click Open advanced data source picker to see more options, including adding a data source.
Set start and end time shift. Since the logs timestamps may not exactly match the timestamps of the spans in the trace, you may need to widen or shift the time range to find the desired logs.
Optionally, select tags to map. These tags can be used in the custom query with
${__tags}variable. This variable will interpolate the mapped tags as list in an appropriate syntax for the data source and will only include the tags that were present in the span omitting those that weren’t present. You can optionally configure a new name for the tag. This is useful when the tag has dots in the name and the target data source does not allow using dots in labels. For example, you can remaphttp.statustohttp_status. If you don’t map any tags here, you can still use any tag in the query like thismethod="${__span.tags.method}".Skip Filter by trace ID and Filter by span ID settings as these cannot be used with a custom query.
Switch on Use custom query.
Specify a custom query to be used to query the logs. You can use various variables to make that query relevant for current span. The link will only be shown only if all the variables are interpolated with non-empty values to prevent creating an invalid query.
Variables that can be used in a custom query
To use a variable you need to wrap it in ${}. For example ${__span.name}.
| Variable name | Description |
|---|---|
| __tags | This variable uses the tag mapping from the UI to create a label matcher string in the specific data source syntax. The variable only uses tags that are present in the span. The link is still created even if only one of those tags is present in the span. You can use this if all tags are not required for the query to be useful. |
| __span.spanId | The ID of the span. |
| __span.traceId | The ID of the trace. |
| __span.duration | The duration of the span. |
| __span.name | Name of the span. |
| __span.tags | Namespace for the tags in the span. To access a specific tag named version, you would use ${__span.tags.version}. In case the tag contains dot, you have to access it as ${__span.tags["http.status"]}. |
| __trace.traceId | The ID of the trace. |
| __trace.duration | The duration of the trace. |
| __trace.name | The name of the trace. |
The following table describes the ways in which you can configure your trace to logs settings:
| Setting name | Description |
|---|---|
| Data source | Defines the target data source. You can select only Loki or Splunk logs data sources. |
| Span start time shift | Shifts the start time for the logs query, based on the span’s start time. You can use time units, such as 5s, 1m, 3h. To extend the time to the past, use a negative value. Default: 0. |
| Span end time shift | Shifts the end time for the logs query, based on the span’s end time. You can use time units. Default: 0. |
| Tags | Defines the tags to use in the logs query. Default: cluster, hostname, namespace, pod, service.name, service.namespace. You can change the tag name for example to remove dots from the name if they are not allowed in the target data source. For example, map http.status to http_status. |
| Filter by trace ID | Toggles whether to append the trace ID to the logs query. |
| Filter by span ID | Toggles whether to append the span ID to the logs query. |
| Use custom query | Toggles use of custom query with interpolation. |
| Query | Input to write custom query. Use variable interpolation to customize it with variables from span. |
Trace to metrics
The Trace to metrics setting configures the trace to metrics feature available when integrating Grafana with Zipkin.
To configure trace to metrics:
Select the target data source from the drop-down list.
You can also click Open advanced data source picker to see more options, including adding a data source.
Create any desired linked queries.
| Setting name | Description |
|---|---|
| Data source | Defines the target data source. |
| Tags | Defines the tags used in linked queries. The key sets the span attribute name, and the optional value sets the corresponding metric label name. For example, you can map k8s.pod to pod. To interpolate these tags into queries, use the $__tags keyword. |
Each linked query consists of:
- Link Label: (Optional) Descriptive label for the linked query.
- Query: The query ran when navigating from a trace to the metrics data source.
Interpolate tags using the
$__tagskeyword. For example, when you configure the queryrequests_total{$__tags}with the tagsk8s.pod=podandcluster, the result looks likerequests_total{pod="nginx-554b9", cluster="us-east-1"}.
Node Graph
The Node Graph setting enables the Node Graph visualization, which is disabled by default.
Once enabled, Grafana displays the Node Graph after loading the trace view.
Span bar
The Span bar setting helps you display additional information in the span bar row.
You can choose one of three options:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| None | Adds nothing to the span bar row. |
| Duration | (Default) Displays the span duration on the span bar row. |
| Tag | Displays the span tag on the span bar row. You must also specify which tag key to use to get the tag value, such as component. |
Provision the data source
You can define and configure the data source in YAML files as part of Grafana’s provisioning system. For more information about provisioning and available configuration options, refer to Provisioning Grafana.
Provisioning example
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: Zipkin
type: zipkin
uid: EbPG8fYoz
url: http://localhost:16686
access: proxy
basicAuth: true
basicAuthUser: my_user
readOnly: true
isDefault: false
jsonData:
tracesToLogsV2:
# Field with an internal link pointing to a logs data source in Grafana.
# datasourceUid value must match the uid value of the logs data source.
datasourceUid: 'loki'
spanStartTimeShift: '1h'
spanEndTimeShift: '-1h'
tags: ['job', 'instance', 'pod', 'namespace']
filterByTraceID: false
filterBySpanID: false
customQuery: true
query: 'method="$${__span.tags.method}"'
tracesToMetrics:
datasourceUid: 'prom'
spanStartTimeShift: '1h'
spanEndTimeShift: '-1h'
tags: [{ key: 'service.name', value: 'service' }, { key: 'job' }]
queries:
- name: 'Sample query'
query: 'sum(rate(traces_spanmetrics_latency_bucket{$$__tags}[5m]))'
nodeGraph:
enabled: true
traceQuery:
timeShiftEnabled: true
spanStartTimeShift: '1h'
spanEndTimeShift: '-1h'
spanBar:
type: 'None'
secureJsonData:
basicAuthPassword: my_passwordQuery the data source
You can query and display traces from Zipkin via Explore
This topic explains configuration and queries specific to the Zipkin data source. For general documentation on querying data sources in Grafana, see Query and transform data.
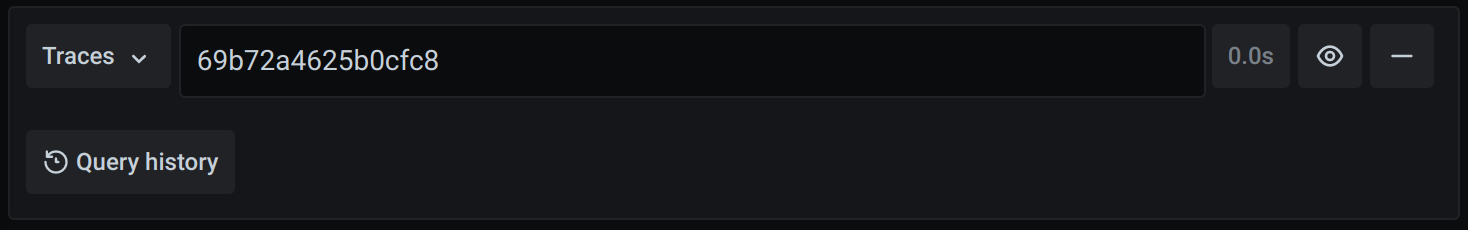
Query by trace ID
To query a particular trace:
- Select the TraceID query type.
- Enter the trace’s ID into the Trace ID field.
Query by trace selector
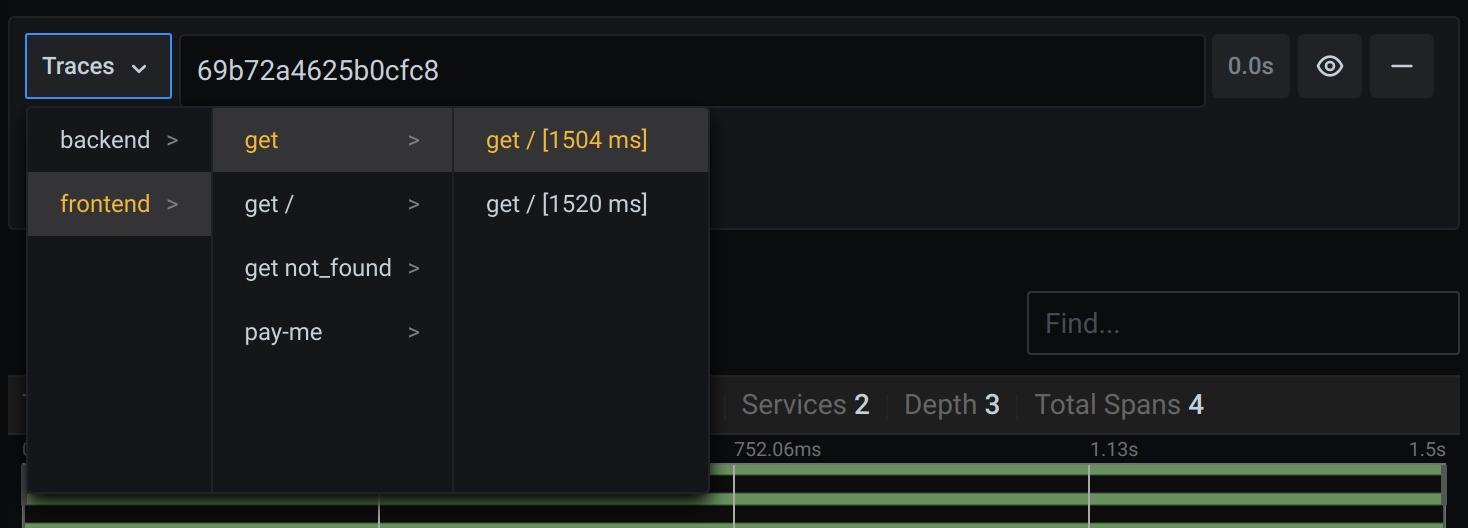
To select a particular trace from all traces logged in the time range you have selected in Explore, you can also query by trace selector. The trace selector has three levels of nesting:
- The service you’re interested in.
- Particular operation, part of the selected service
- Specific trace in which the selected operation occurred, represented by the root operation name and trace duration
View data mapping in the trace UI
You can view Zipkin annotations in the trace view as logs with annotation value displayed under the annotation key.
Upload a JSON trace file
You can upload a JSON file that contains a single trace and visualize it. If the file has multiple traces, Grafana visualizes its first trace.
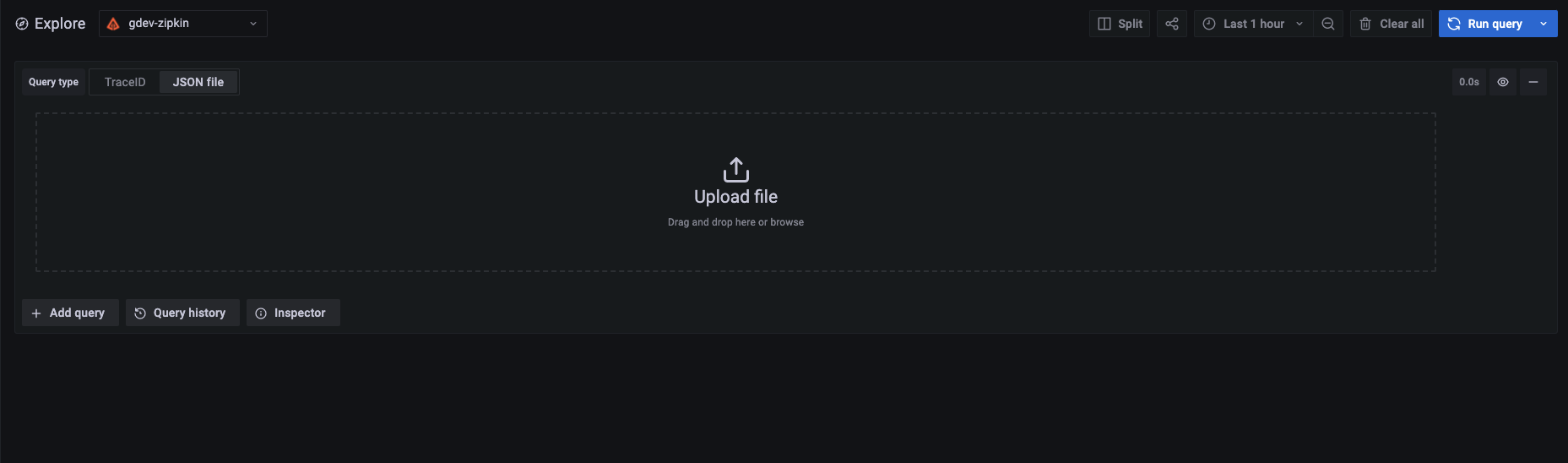
Trace JSON example
[
{
"traceId": "efe9cb8857f68c8f",
"parentId": "efe9cb8857f68c8f",
"id": "8608dc6ce5cafe8e",
"kind": "SERVER",
"name": "get /api",
"timestamp": 1627975249601797,
"duration": 23457,
"localEndpoint": { "serviceName": "backend", "ipv4": "127.0.0.1", "port": 9000 },
"tags": {
"http.method": "GET",
"http.path": "/api",
"jaxrs.resource.class": "Resource",
"jaxrs.resource.method": "printDate"
},
"shared": true
}
]Span Filters
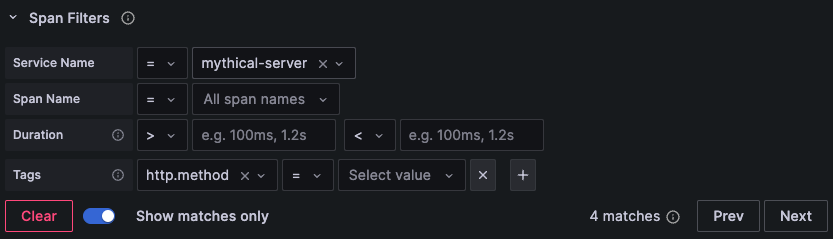
Using span filters, you can filter your spans in the trace timeline viewer. The more filters you add, the more specific are the filtered spans.
You can add one or more of the following filters:
- Service name
- Span name
- Duration
- Tags (which include tags, process tags, and log fields)
To only show the spans you have matched, you can press the Show matches only toggle.
Link to a trace ID from logs
You can link to Zipkin traces from logs in Loki, Elasticsearch, Splunk, and other logs data sources by configuring an internal link.
To configure this feature, see the Derived fields section of the Loki data source docs or the Data links section of the Elasticsearch or Splunk data source docs.
Link to a trace ID from metrics
You can link to Zipkin traces from metrics in Prometheus data sources by configuring an exemplar.
To configure this feature, see the introduction to exemplars documentation.