Important: This documentation is about an older version. It's relevant only to the release noted, many of the features and functions have been updated or replaced. Please view the current version.
User-configurable overrides
User-configurable overrides in Tempo let you change overrides for your tenant using an API. Instead of modifying a file or Kubernetes configmap, you (and other services relying on Tempo) can use this API to modify the overrides directly.
Architecture
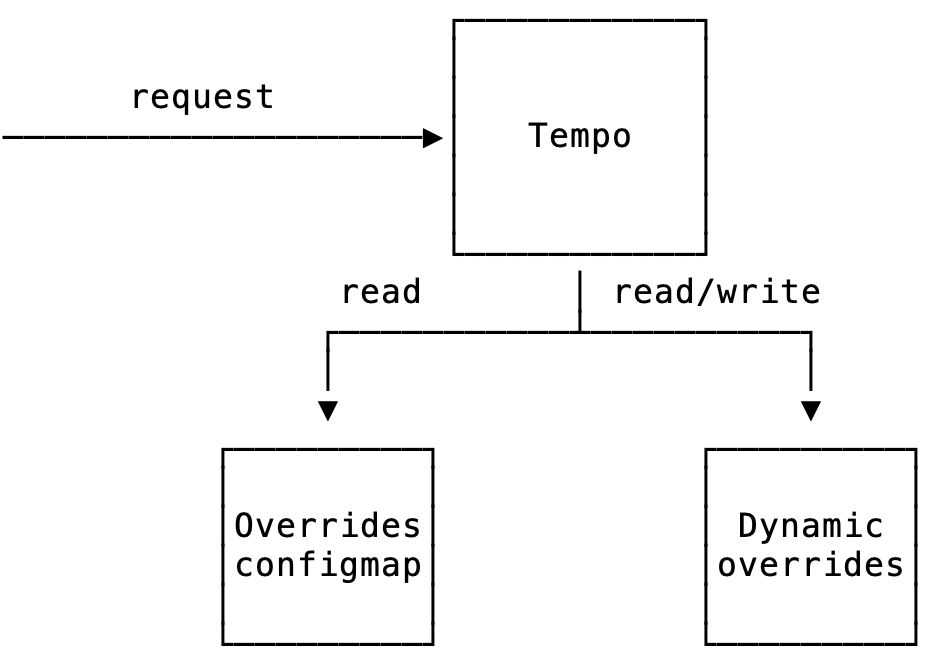
User-configurable overrides are stored in an object store bucket managed by Tempo.
Note
We recommend using a different bucket for overrides and traces storage, but they can share a bucket if needed. When sharing a bucket, make sure any lifecycle rules are scoped correctly to not remove data of user-configurable overrides module.
Overrides of every tenant are stored at /{tenant name}/overrides.json:
overrides/
├── 1/
│ └── overrides.json
└── 2/
└── overrides.jsonTempo regularly polls this bucket and keeps a copy of the limits in-memory. When requesting the overrides for a tenant, the overrides module:
- Checks this override is set in the user-configurable overrides, if so return that value
- Checks if this override is set in the runtime config (configmap), if so return that value
- Returns the default value
Supported fields
User-configurable overrides are designed to be a subset of the runtime overrides. Refer to [Overrides]/docs/tempo/v2.4.x/configuration/#overrides for information about all overrides. When a field is set in both the user-configurable overrides and the runtime overrides, the value from the user-configurable overrides will take priority.
Note
processorsis an exception: Tempo will merge values from both user-configurable overrides and runtime overrides into a single list.
[forwarders: <list of strings>]
metrics_generator:
[processors: <list of strings>]
[collection_interval: <duration>]
[disable_collection: <bool> | default = false]
processor:
service_graphs:
[histogram_buckets: <list of float>]
[dimensions: <list of string>]
[peer_attributes: <list of string>]
[enable_client_server_prefix: <bool>]
span_metrics:
[histogram_buckets: <list of float>]
[dimensions: <list of string>]
[intrinsic_dimensions: <map string to bool>]
[filter_policies: [
[
include/exclude:
match_type: <string> # options: strict, regexp
attributes:
- key: <string>
value: <any>
]
]
[enable_target_info: <bool>]
[target_info_excluded_dimensions: <list of string>]API
All API requests are handled on the /api/overrides endpoint. The module supports GET, POST, PATCH, and DELETE requests.
This endpoint is tenant-specific. If Tempo is run in multitenant mode, all requests should have an appropriate X-Scope-OrgID header.
If the tenant is run in distributed mode, only the query-frontend will accept API requests.
Operations
GET /api/overrides
Returns the current overrides and it’s version.
Query-parameters:
scope: whether to return overrides from the API onlyapior merge it with the runtime overridesmerged. Defaults toapi.
Example:
$ curl -X GET -v -H "X-Scope-OrgID: 3" http://localhost:3100/tempo/api/overrides\?scope=merged`POST /api/overrides
Update the overrides with the given payload. Note this will overwrite any existing overrides.
Example:
curl -X POST -v -H "X-Scope-OrgID: 3" -H "If-Match: 1697726795401423" http://localhost:3100/api/overrides --data "{}"PATCH /api/overrides
Update the existing overrides by patching it with the payload. It follows the JSON merge patch protocol (RFC 7386).
Example:
curl -X PUT -v -H "X-Scope-OrgID: 3" -H "If-Match: 1697726795401423" http://localhost:3100/api/overrides --data "{\"forwarders\":null}"DELETE /api/overrides
Delete the existing overrides.
Example:
curl -X DELETE -H "X-Scope-OrgID: 3" -H "If-Match: 1697726795401423" http://localhost:3100/api/overridesVersioning
To handle concurrent read and write operations, overrides are stored with a version in the backend. Whenever the overrides are returned, the response will have an Etag header with the current version.
$ curl -v http://localhost:3100/api/overrides
...
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Type: application/json
< Etag: 1697726795401423
< Date: Wed, 07 Feb 2024 17:49:04 GMT
< Content-Length: 118
...Requests that modify or delete overrides need to pass the current version using the If-Match header:
$ curl -X POST -H "If-Match: 1697726795401423" http://localhost:3100/api/overrides --data "..."This example uses uses overrides in the overrides.json file with the location in pwd:
$ curl -X POST -H "X-Scope-OrgID: 3" -H "If-Match: 1697726795401423" http://localhost:3100/api/overrides --data @overrides.jsonIf the version does not match the version in the backend, the request is rejected with HTTP error 412.
Conflicting runtime overrides check
Overrides set through the user-configurable overrides take priority over runtime overrides. This can lead to misleading scenarios because a value set in the runtime overrides is not actively being used.
To warn users about preexisting runtime overrides, there is an optional check for conflicting runtime overrides. If enabled requests are rejected if:
- There are no user-configurable overrides yet for this tenant.
- There are runtime overrides set that contain overrides present in the user-configurable overrides.
The check can be enabled in the configuration:
overrides:
user_configurable_overrides:
api:
check_for_conflicting_runtime_overrides: trueYou can bypass this check by setting the query parameter skip-conflicting-overrides-check=true:
$ curl -X POST -H "If-Match: 1697726795401423" http://localhost:3100/api/overrides?skip-conflicting-overrides-check=true --data "..."

