Push spans with HTTP
Sometimes using a tracing system is intimidating because it seems like you need complex application instrumentation or a span ingestion pipeline in order to push spans. This guide aims to show an extremely basic technique for pushing spans with HTTP/JSON from a Bash script using the OpenTelemetry receiver.
Before you begin
This procedure uses an example Docker Compose setup to run Tempo, so you don’t need an existing installation. The Docker image also includes a Grafana container which lets you visualize traces.
To use this procedure, you need to have Docker and docker compose installed.
Start Tempo using the quick start
Use the instructions in the Quick start for Tempo documentation to start a local instance of Tempo and Grafana.
Push spans with OTLP
Now that Tempo is running and listening on port 4318 for OTLP spans, let’s push a span to it using curl.
Before you can use this example, you need to update the start and end time as instructed.
Note that the startTimeUnixNano field is in nanoseconds and can be obtained by any tool that provides the epoch date in nanoseconds (for example, under Linux, date +%s%N). The endTimeUnixNano field is also in nanoseconds, where 100000000 nanoseconds is 100 milliseconds.
Copy and paste the curl command into a text editor.
Replace
startTimeUnixNanoandendTimeUnixNanowith current values for the last 24 hours to allow you to search for them using a 24 hour relative time range. You can get this in seconds and milliseconds from the following link. Multiple the milliseconds value by 1,000,000 to turn it into nanoseconds. You can do this from a bash terminal with:echo $((<epochTimeMilliseconds> * 1000000))Copy the updated curl command to a terminal window and run it.
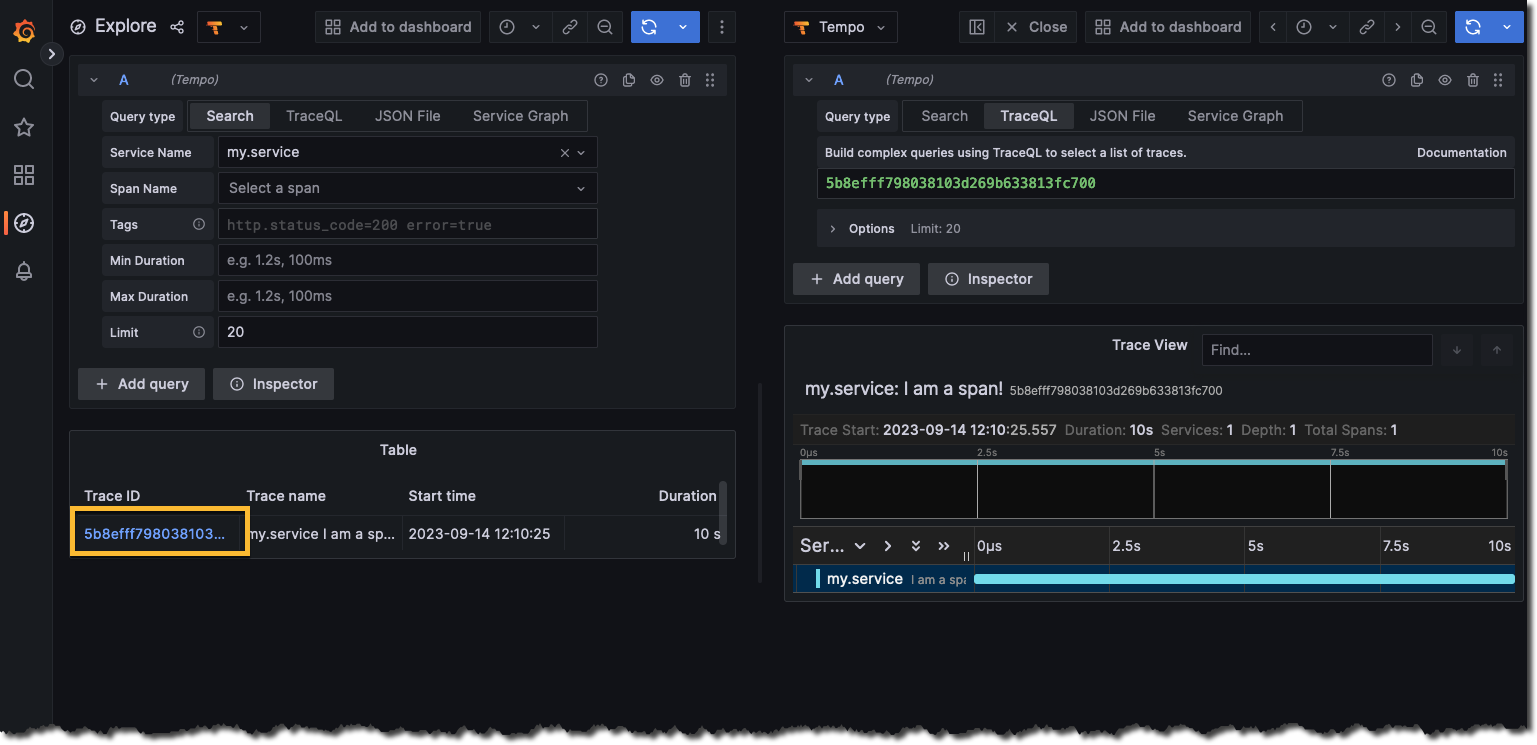
View the trace in Grafana:
- Open a browser window to http://localhost:3000.
- Open the Explorer page and select the Tempo data source.
- Select the Search query type.
- Select Run query to list available traces.
- Select the trace ID (yellow box) to view details about the trace and its spans.
Retrieve traces
The easiest way to get the trace is to execute a simple curl command to Tempo. The returned format is OTLP.
Replace the trace ID in the
curlcommand with the trace ID that was generated from the push. This information is in the data that’s sent with thecurl. You could use Grafana’s Explorer page to find this, as shown in the previous section.curl http://localhost:3200/api/v2/traces/5b8efff798038103d269b633813fc700 {"trace": {"resourceSpans":[{"resource":{"attributes":[{"key":"service.name","value":{"stringValue":"my.service"}}]},"scopeSpans":[{"scope":{"name":"my.library","version":"1.0.0"},"spans":[{"traceId":"W47/95gDgQPSabYzgT/HAA==","spanId":"7uGbfsPBsQA=","name":"I am a span!","kind":"SPAN_KIND_SERVER","startTimeUnixNano":"1689969302000000000","endTimeUnixNano":"1689970000000000000","attributes":[{"key":"my.span.attr","value":{"stringValue":"some value"}}],"status":{}}]}]}]}}Copy and paste the updated
curlcommand into a terminal window.
Use TraceQL to search for a trace
Alternatively, you can also use TraceQL to search for the trace that was pushed. You can search by using the unique trace attributes that were set:
curl -G -s http://localhost:3200/api/search --data-urlencode 'q={ .service.name = "my.service" }'
{"traces":[{"traceID":"5b8efff798038103d269b633813fc700","rootServiceName":"my.service","rootTraceName":"I am a span!","startTimeUnixNano":"1694718625557000000","durationMs":10000,"spanSet":{"spans":[{"spanID":"eee19b7ec3c1b100","startTimeUnixNano":"1694718625557000000","durationNanos":"10000000000","attributes":[{"key":"service.name","value":{"stringValue":"my.service"}}]}],"matched":1},"spanSets":[{"spans":[{"spanID":"eee19b7ec3c1b100","startTimeUnixNano":"1694718625557000000","durationNanos":"10000000000","attributes":[{"key":"service.name","value":{"stringValue":"my.service"}}]}],"matched":1}]}],"metrics":{"inspectedBytes":"292781","completedJobs":1,"totalJobs":1}}To format this in a more human-readable output, consider using a tool such as jq, which lets you to run the same curl command and pipe it to jq to format the block. For example:
curl -G -s http://localhost:3200/api/search --data-urlencode 'q={ .service.name = "my.service" }' | jqSpans from everything
Tracing isn’t limited to enterprise languages with complex frameworks. As you can see, it’s easy to store and track events from your js, python or bash scripts. You can use Tempo and distributed tracing today to trace CI pipelines, long running bash processes, python data processing flows, or anything else you can think of.
Happy tracing!



