Important: This documentation is about an older version. It's relevant only to the release noted, many of the features and functions have been updated or replaced. Please view the current version.
Loki Canary
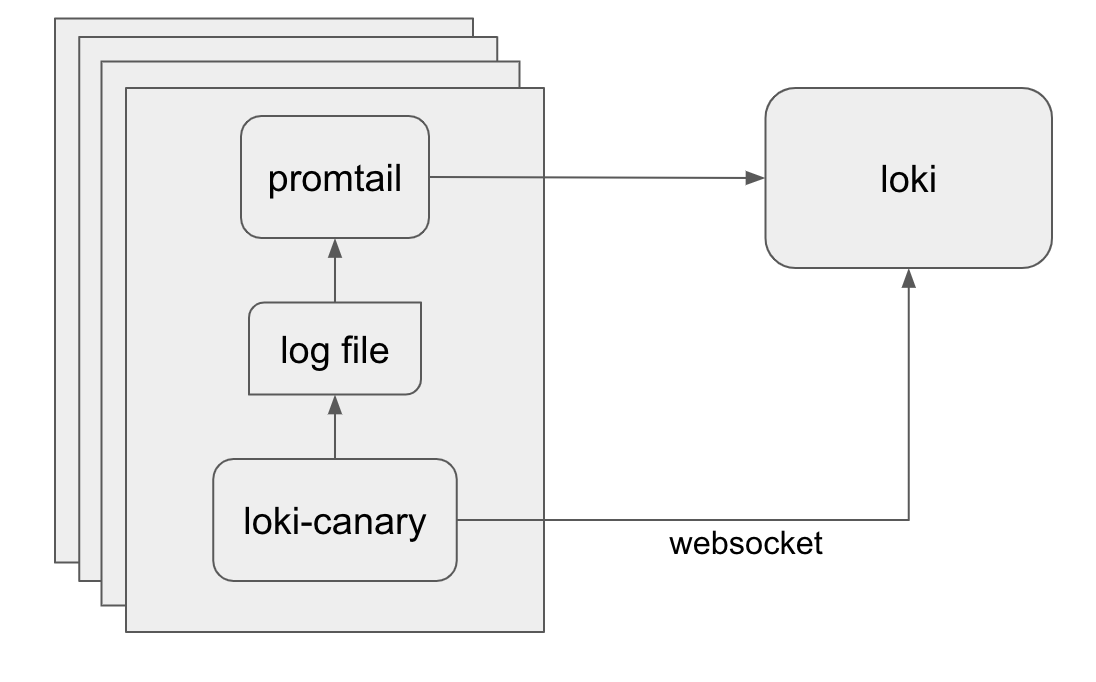
Loki Canary is a standalone app that audits the log-capturing performance of a Grafana Loki cluster.
This component emits and periodically queries for logs, making sure that Loki is ingesting logs without any data loss.
When something is wrong with Loki, the Canary often provides the first indication.
Loki Canary generates artificial log lines. These log lines are sent to the Loki cluster. Loki Canary communicates with the Loki cluster to capture metrics about the artificial log lines, such that Loki Canary forms information about the performance of the Loki cluster. The information is available as Prometheus time series metrics.
Loki Canary writes a log to a file and stores the timestamp in an internal array. The contents look something like this:
1557935669096040040 pppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppppThe relevant part of the log entry is the timestamp; the ps are just filler
bytes to make the size of the log configurable.
An agent (like Grafana Alloy) should be configured to read the log file and ship it to Loki.
Meanwhile, Loki Canary will open a WebSocket connection to Loki and will tail the logs it creates. When a log is received on the WebSocket, the timestamp in the log message is compared to the internal array.
If the received log is:
- The next in the array to be received, it is removed from the array and the
(current time - log timestamp) is recorded in the
response_latencyhistogram. This is the expected behavior for well behaving logs. - Not the next in the array to be received, it is removed from the array, the
response time is recorded in the
response_latencyhistogram, and theout_of_order_entriescounter is incremented. - Not in the array at all, it is checked against a separate list of received
logs to either increment the
duplicate_entriescounter or theunexpected_entriescounter.
In the background, Loki Canary also runs a timer which iterates through all of
the entries in the internal array. If any of the entries are older than the
duration specified by the -wait flag (defaulting to 60s), they are removed
from the array and the websocket_missing_entries counter is incremented. An
additional query is then made directly to Loki for any missing entries to
determine if they are truly missing or only missing from the WebSocket. If
missing entries are not found in the direct query, the missing_entries counter
is incremented.
Additional Queries
Spot Check
Starting with version 1.6.0, the canary will spot check certain results over time to make sure they are present in Loki, this is helpful for testing the transition of inmemory logs in the ingester to the store to make sure nothing is lost.
-spot-check-interval and -spot-check-max are used to tune this feature,
-spot-check-interval will pull a log entry from the stream at this interval
and save it in a separate list up to -spot-check-max.
Every -spot-check-query-rate, Loki will be queried for each entry in this list and
loki_canary_spot_check_entries_total will be incremented, if a result
is missing loki_canary_spot_check_missing_entries_total will be incremented.
The defaults of 15m for spot-check-interval and 4h for spot-check-max
means that after 4 hours of running the canary will have a list of 16 entries
it will query every minute (default spot-check-query-rate interval is 1m),
so be aware of the query load this can put on Loki if you have a lot of canaries.
NOTE: if you are using out-of-order-percentage to test ingestion of out-of-order
log lines be sure not to set the two out of order time range flags too far in the past.
The defaults are already enough to test this functionality properly, and setting them
too far in the past can cause issues with the spot check test.
When using out-of-order-percentage you also need to make use of pipeline stages
in your Promtail configuration in order to set the timestamps correctly as the logs are pushed
to Loki. The client/promtail/pipelines docs have examples of how to do this.
Metric Test
Loki Canary will run a metric query count_over_time to
verify that the rate of logs being stored in Loki corresponds to the rate they are being
created by Loki Canary.
-metric-test-interval and -metric-test-range are used to tune this feature, but
by default every 15m the canary will run a count_over_time instant-query to Loki
for a range of 24h.
If the canary has not run for -metric-test-range (24h) the query range is adjusted
to the amount of time the canary has been running such that the rate can be calculated
since the canary was started.
The canary calculates what the expected count of logs would be for the range
(also adjusting this based on canary runtime) and compares the expected result with
the actual result returned from Loki. The difference is stored as the value in
the gauge loki_canary_metric_test_deviation
It’s expected that there will be some deviation, the method of creating an expected calculation based on the query rate compared to actual query data is imperfect and will lead to a deviation of a few log entries.
It’s not expected for there to be a deviation of more than 3-4 log entries.
Control
Loki Canary responds to two endpoints to allow dynamic suspending/resuming of the
canary process. This can be useful if you’d like to quickly disable or reenable the
canary. To stop or start the canary issue an HTTP GET request against the /suspend or
/resume endpoints.
Installation
Binary
Loki Canary is provided as a pre-compiled binary as part of the Loki Releases on GitHub.
Docker
Loki Canary is also provided as a Docker container image:
# change tag to the most recent release
$ docker pull grafana/loki-canary:2.9.2Kubernetes
To run on Kubernetes, you can do something simple like:
kubectl run loki-canary --generator=run-pod/v1 --image=grafana/loki-canary:latest --restart=Never --image-pull-policy=IfNotPresent --labels=name=loki-canary -- -addr=loki:3100
Or you can do something more complex like deploy it as a DaemonSet, there is a
Tanka setup for this in the production folder, you can import it using
jsonnet-bundler:
jb install github.com/grafana/loki-canary/production/ksonnet/loki-canaryThen in your Tanka environment’s main.jsonnet you’ll want something like
this:
local loki_canary = import 'loki-canary/loki-canary.libsonnet';
loki_canary {
loki_canary_args+:: {
addr: "loki:3100",
port: 80,
labelname: "instance",
interval: "100ms",
size: 1024,
wait: "3m",
},
_config+:: {
namespace: "default",
}
}Examples
Standalone Pod Implementation of loki-canary
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
labels:
app: loki-canary
name: loki-canary
name: loki-canary
spec:
containers:
- args:
- -addr=loki:3100
image: grafana/loki-canary:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: loki-canary
resources: {}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: loki-canary
labels:
app: loki-canary
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: loki-canary
ports:
- name: metrics
protocol: TCP
port: 3500
targetPort: 3500DaemonSet Implementation of loki-canary
---
kind: DaemonSet
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
metadata:
labels:
app: loki-canary
name: loki-canary
name: loki-canary
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: loki-canary
labels:
app: loki-canary
spec:
containers:
- args:
- -addr=loki:3100
image: grafana/loki-canary:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: loki-canary
resources: {}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: loki-canary
labels:
app: loki-canary
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: loki-canary
ports:
- name: metrics
protocol: TCP
port: 3500
targetPort: 3500From Source
If the other options are not sufficient for your use case, you can compile
loki-canary yourself:
Clone the source tree.
$ git clone https://github.com/grafana/lokiBuild the binary.
$ make loki-canaryOptional: Build the container image.
$ make loki-canary-image
Configuration
The address of Loki must be passed in with the -addr flag or by setting the
environment variable LOKI_ADDRESS, and if your Loki server uses TLS, -tls=true
must also be provided. Note that using TLS will cause the WebSocket connection
to use wss:// instead of ws://.
The -labelname and -labelvalue flags should also be provided, as these are
used by Loki Canary to filter the log stream to only process logs for the
current instance of the canary. Ensure that the values provided to the flags are
unique to each instance of Loki Canary. Grafana Labs’ Tanka config
accomplishes this by passing in the Pod name as the label value.
If Loki Canary reports a high number of unexpected_entries, Loki Canary may
not be waiting long enough and the value for the -wait flag should be
increased to a larger value than 60s.
Be aware of the relationship between pruneinterval and the interval.
For example, with an interval of 10ms (100 logs per second) and a prune interval
of 60s, you will write 6000 logs per minute. If those logs were not received
over the WebSocket, the canary will attempt to query Loki directly to see if
they are completely lost. However the query return is limited to 1000
results so you will not be able to return all the logs even if they did make it
to Loki.
Likewise, if you lower the pruneinterval you risk causing a denial of
service attack as all your canaries attempt to query for missing logs at
whatever your pruneinterval is defined at.
All options:
-addr string
The Loki server URL:Port, e.g. loki:3100. Loki address can also be set using the environment variable LOKI_ADDRESS.
-buckets int
Number of buckets in the response_latency histogram (default 10)
-ca-file string
Client certificate authority for optional use with TLS connection to Loki
-cert-file string
Client PEM encoded X.509 certificate for optional use with TLS connection to Loki
-insecure
Allow insecure TLS connections
-interval duration
Duration between log entries (default 1s)
-key-file string
Client PEM encoded X.509 key for optional use with TLS connection to Loki
-labelname string
The label name for this instance of loki-canary to use in the log selector (default "name")
-labelvalue string
The unique label value for this instance of loki-canary to use in the log selector (default "loki-canary")
-max-wait duration
Duration to keep querying Loki for missing websocket entries before reporting them missing (default 5m0s)
-metric-test-interval duration
The interval the metric test query should be run (default 1h0m0s)
-metric-test-range duration
The range value [24h] used in the metric test instant-query. Note: this value is truncated to the running time of the canary until this value is reached (default 24h0m0s)
-out-of-order-max duration
Maximum amount of time to go back for out of order entries (in seconds). (default 1m0s)
-out-of-order-min duration
Minimum amount of time to go back for out of order entries (in seconds). (default 30s)
-out-of-order-percentage int
Percentage (0-100) of log entries that should be sent out of order.
-pass string
Loki password. This credential should have both read and write permissions to Loki endpoints
-port int
Port which loki-canary should expose metrics (default 3500)
-pruneinterval duration
Frequency to check sent vs received logs, also the frequency which queries for missing logs will be dispatched to loki (default 1m0s)
-push
Push the logs directly to given Loki address
-query-timeout duration
How long to wait for a query response from Loki (default 10s)
-size int
Size in bytes of each log line (default 100)
-spot-check-initial-wait duration
How long should the spot check query wait before starting to check for entries (default 10s)
-spot-check-interval duration
Interval that a single result will be kept from sent entries and spot-checked against Loki, e.g. 15min default one entry every 15 min will be saved and then queried again every 15min until spot-check-max is reached (default 15m0s)
-spot-check-max duration
How far back to check a spot check entry before dropping it (default 4h0m0s)
-spot-check-query-rate duration
Interval that the canary will query Loki for the current list of all spot check entries (default 1m0s)
-streamname string
The stream name for this instance of loki-canary to use in the log selector (default "stream")
-streamvalue string
The unique stream value for this instance of loki-canary to use in the log selector (default "stdout")
-tenant-id string
Tenant ID to be set in X-Scope-OrgID header.
-tls
Does the loki connection use TLS?
-user string
Loki username.
-version
Print this builds version information
-wait duration
Duration to wait for log entries on websocket before querying loki for them (default 1m0s)
-write-max-backoff duration
Maximum backoff time between retries (default 5m0s)
-write-max-retries int
Maximum number of retries when push a log entry (default 10)
-write-min-backoff duration
Initial backoff time before first retry (default 500ms)
-write-timeout duration
How long to wait write response from Loki (default 10s)


