Important: This documentation is about an older version. It's relevant only to the release noted, many of the features and functions have been updated or replaced. Please view the current version.
Provisioning RBAC with Terraform
Note
Available in Grafana Enterprise and Grafana Cloud.
You can create, change or remove Custom roles and create or remove basic and custom role assignments, by using Terraform’s Grafana provider.
Before you begin
Ensure you have the grafana/grafana Terraform provider 1.29.0 or higher.
Ensure you are using Grafana 9.2 or higher.
Create a Service Account Token for provisioning
We recommend using service account tokens for provisioning. Service accounts support fine grained permissions, which allows you to easily authenticate and use the minimum set of permissions needed to provision your RBAC infrastructure.
To create a service account token for provisioning, complete the following steps.
- Create a new service account for your CI pipeline.
- Assign permissions to service account:
- You will need roles “Role reader”, “Role writer” and roles including any permissions that will be provisioned. For example, to create or assign a role that allows creating users, a service account needs permissions to create users.
- Alternatively, you can assign “Admin” basic role to the service account.
- Create a new service account token for use in Terraform.
Alternatively, you can use basic authentication. To view all the supported authentication formats, see here.
Configure the Terraform provider
RBAC support is included as part of the Grafana Terraform provider.
The following is an example you can use to configure the Terraform provider.
terraform {
required_providers {
grafana = {
source = "grafana/grafana"
version = ">= 1.29.0"
}
}
}
provider "grafana" {
url = <YOUR_GRAFANA_URL>
auth = <YOUR_GRAFANA_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_TOKEN>
}Provision custom roles
The following example shows how to provision a custom role with some permissions.
- Copy this code block into a .tf file on your local machine.
resource "grafana_role" "my_new_role" {
name = "my_new_role"
description = "My test role"
version = 1
uid = "newroleuid"
global = true
permissions {
action = "org.users:add"
scope = "users:*"
}
permissions {
action = "org.users:write"
scope = "users:*"
}
permissions {
action = "org.users:read"
scope = "users:*"
}
permissions {
action = "teams:create"
}
permissions {
action = "teams:read"
scope = "teams:*"
}
permissions {
action = "teams:write"
scope = "teams:*"
}
}- Run the command
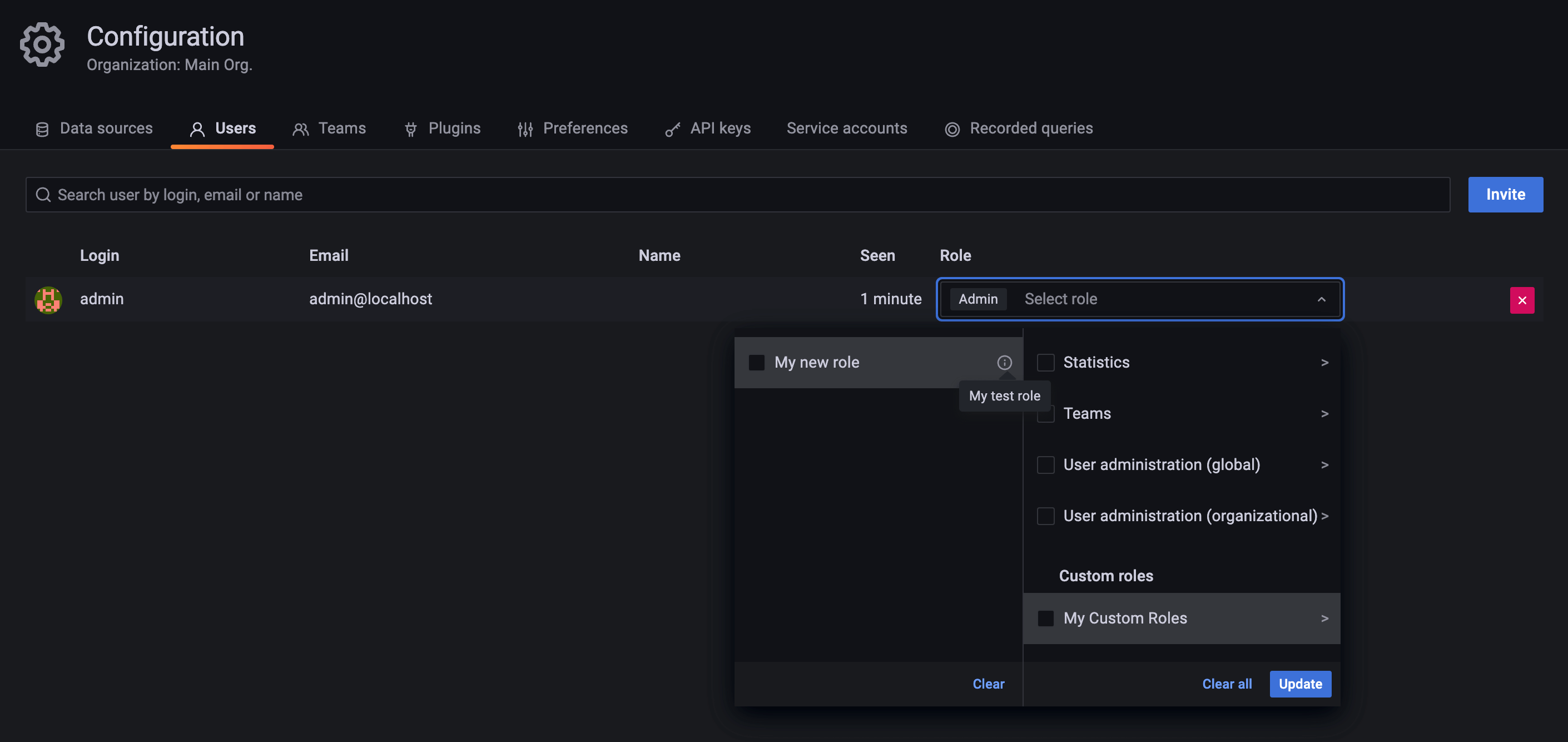
terraform apply. - Go to Grafana’s UI and check that the new role appears in the role picker:
![Role Picker]()
Provision role assignments
The following example shows how to provision role assignments. In this example a team, user and service account are provisioned, and the custom role from the previous example is assigned to them.
- Extend the configuration file from the previous example with the following:
resource "grafana_team" "test_team" {
name = "terraform_test_team"
}
resource "grafana_user" "test_user" {
email = "terraform_user@test.com"
login = "terraform_test_user"
password = <TEST_PASSWORD>
}
resource "grafana_service_account" "test_sa" {
name = "terraform_test_sa"
role = "Viewer"
}
resource "grafana_role_assignment" "my_new_role_assignment" {
role_uid = grafana_role.my_new_role.uid
users = [grafana_user.test_user.id]
teams = [grafana_team.test_team.id]
service_accounts = [grafana_service_account.test_sa.id]
}Substitute
<TEST_PASSWORD>with a test password for your test user.Run the command
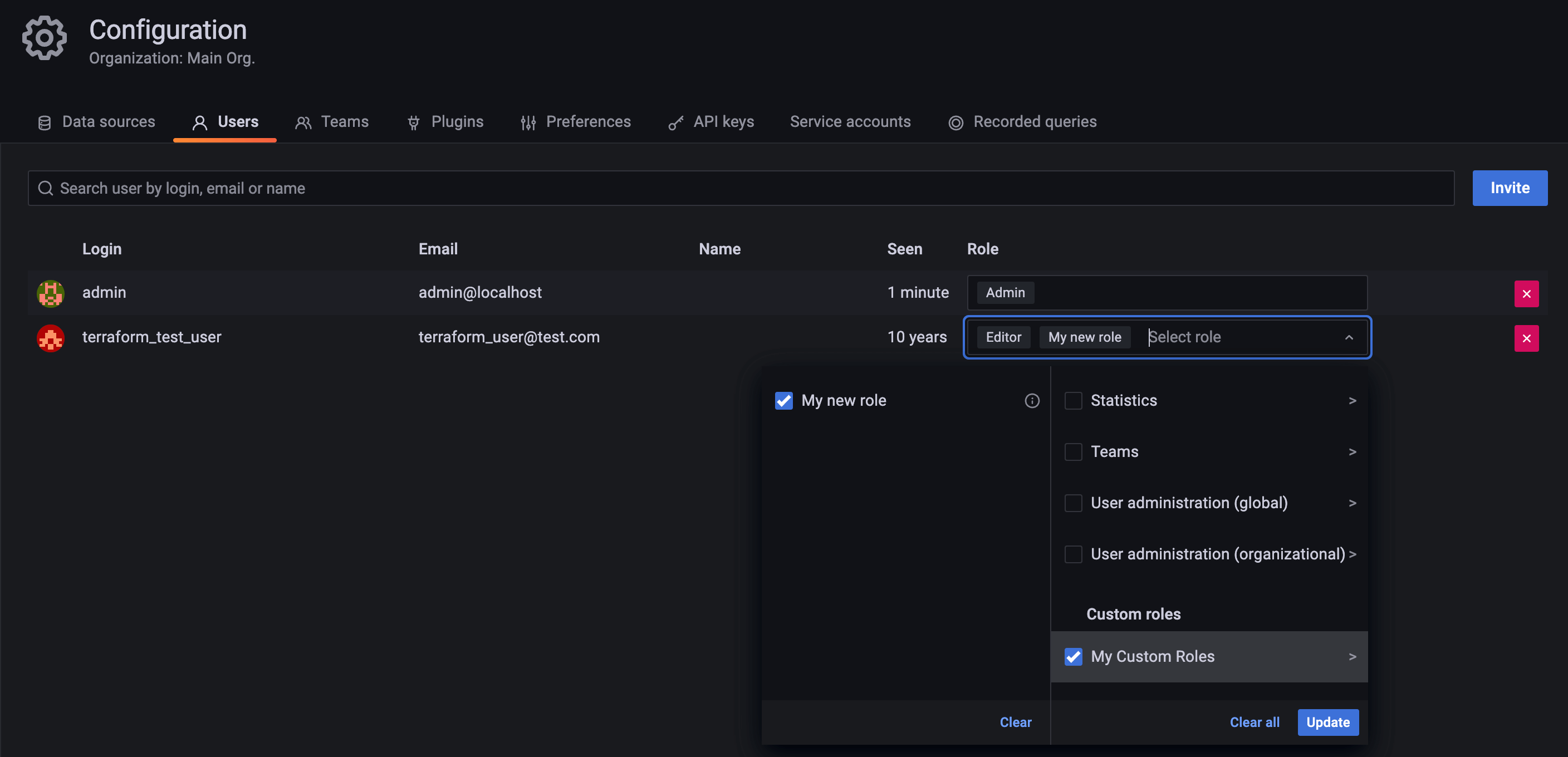
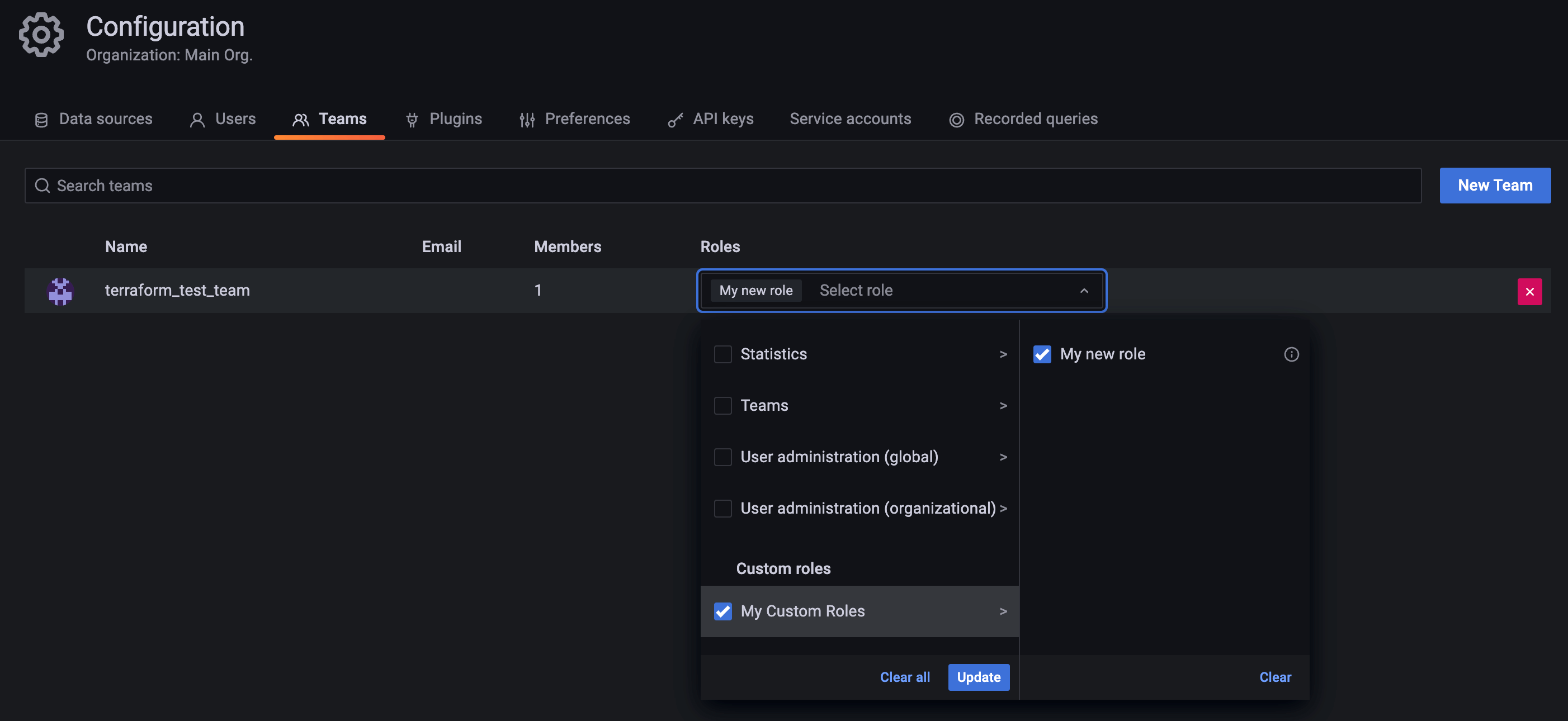
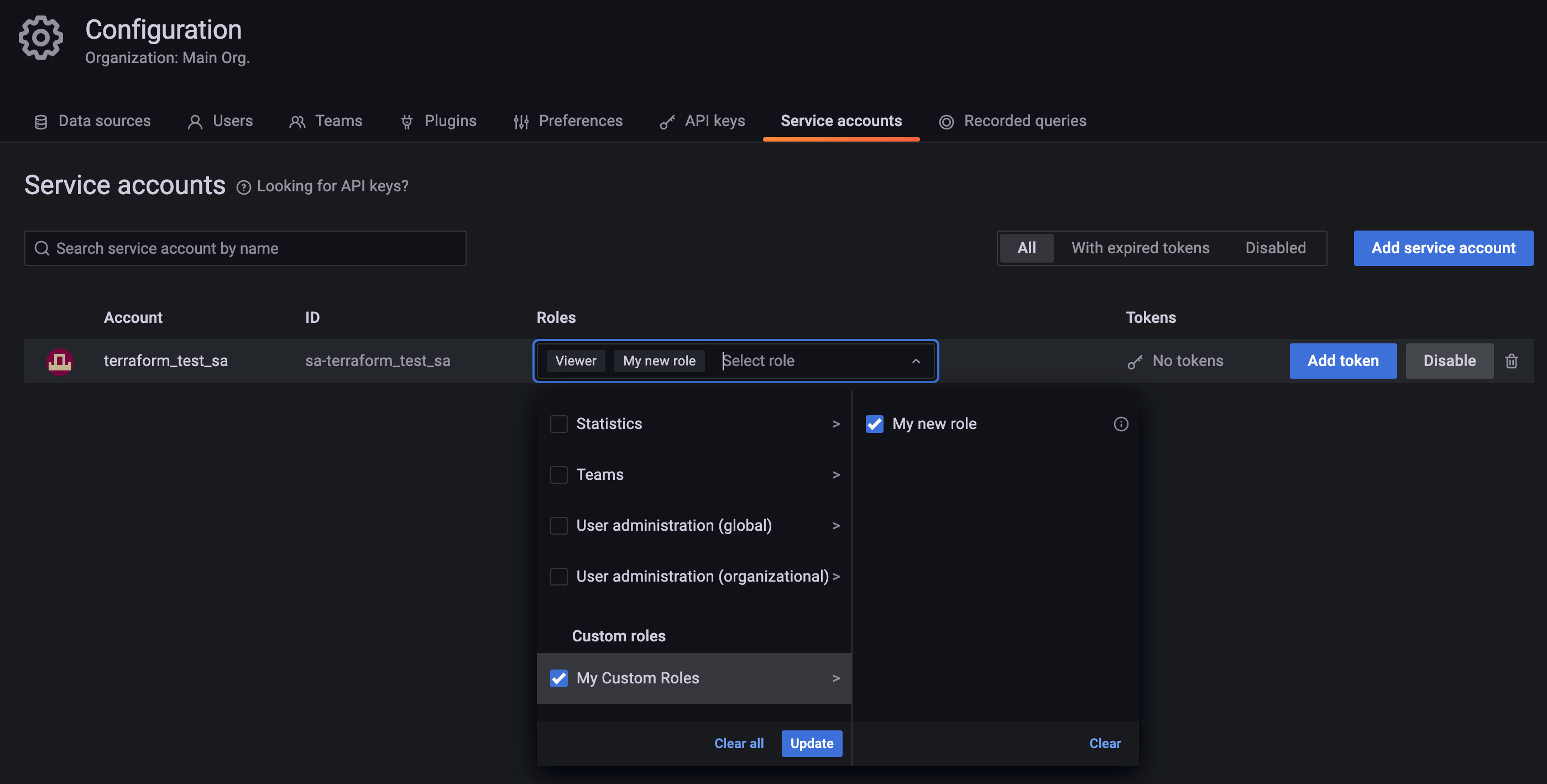
terraform apply.Go to Grafana’s UI and check that a user, team and service account have been created, and that the role has been assigned to them:
![User Role Assignment]()
![Team Role Assignment]()
![Service Account Role Assignment]()
Note that instead of using a provisioned role, you can also look up the uid of an already existing fixed or custom role and use that instead.
You can use the
API endpoint for listing roles to look up role uids.
Similarly, you can look up and use ids of users, teams and service accounts that have not been provisioned to assign roles to them.