Important: This documentation is about an older version. It's relevant only to the release noted, many of the features and functions have been updated or replaced. Please view the current version.
Bar chart
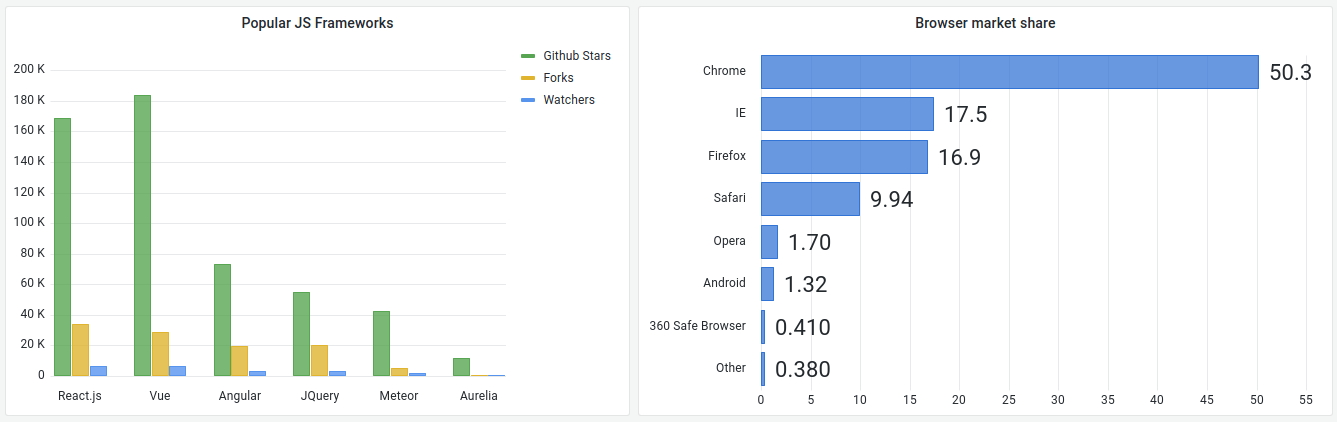
Bar charts allow you to graph categorical data.
Give it a try using Grafana Play
With Grafana Play, you can explore and see how it works, learning from practical examples to accelerate your development. This feature can be seen on Grafana Bar Charts and Pie Charts.
Supported data formats
Only one data frame is supported and it must have at least one string field that will be used as the category for an X or Y axis and one or more numerical fields.
Example:
| Browser | Market share |
|---|---|
| Chrome | 50 |
| IE | 17.5 |
If you have more than one numerical field the visualization will show grouped bars.
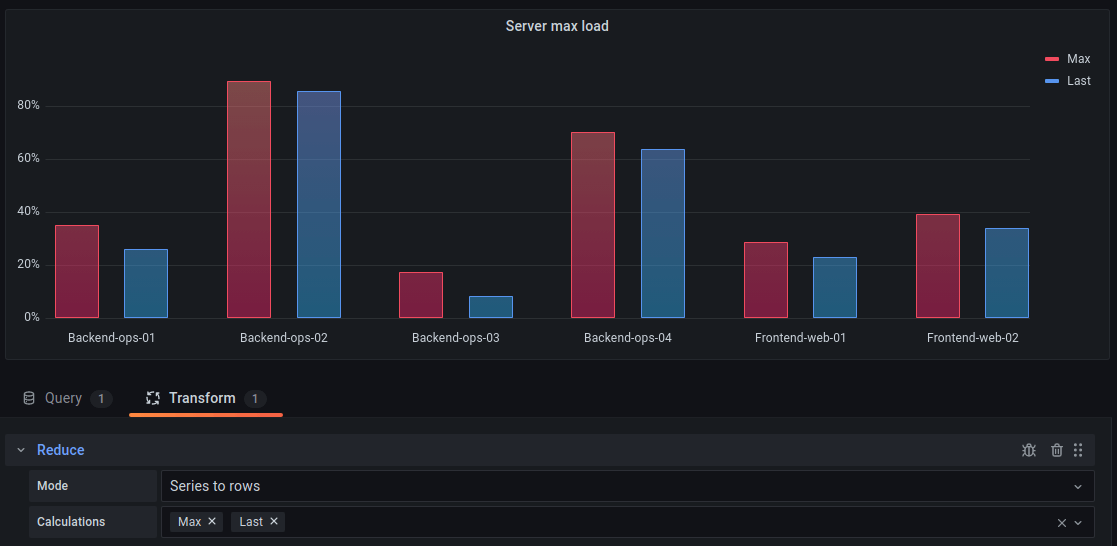
Visualizing time series or multiple result sets
If you have multiple time series or tables you first need to join them using a join or reduce transform. For example if you have multiple time series and you want to compare their last and max value add the Reduce transform and specify Max and Last as options under Calculations.
Panel options
In the Panel options section of the panel editor pane, you set basic options like the panel title and description. You can also configure repeating panels in this section. To learn more, refer to Configure panel options.
Bar chart options
Use these options to refine your visualization.
Orientation
- Auto - Grafana decides the bar orientation based on what the panel dimensions.
- Horizontal - Will make the X axis the category axis.
- Vertical - Will make the Y axis the category axis.
Rotate x-axis tick labels
When the graph is vertically oriented, this setting rotates the labels under the bars. This setting is useful when bar chart labels are long and overlap.
X-axis tick label maximum length
Sets the maximum length of bar chart labels. Labels longer than the maximum length are truncated, and appended with ....
Bar labels minimum spacing
Sets the minimum spacing between bar labels.
Show values
This controls whether values are shown on top or to the left of bars.
- Auto Values will be shown if there is space
- Always Always show values.
- Never Never show values.
Stacking
Controls bar chart stacking.
- Off: Bars will not be stacked.
- Normal: Bars will be stacked on each other.
- Percent: Bars will be stacked on each other, and the height of each bar is the percentage of the total height of the stack.
Group width
Controls the width of groups. 1 = max with, 0 = min width.
Bar width
Controls the width of bars. 1 = Max width, 0 = Min width.
Bar radius
Controls the radius of the bars.
- 0 = Minimum radius
- 0.5 = Maximum radius
Highlight full area on cover
Controls if the entire surrounding area of the bar is highlighted when you hover over the bar.
Line width
Controls line width of the bars.
Fill opacity
Controls the fill opacity bars.
Gradient mode
Set the mode of the gradient fill. Fill gradient is based on the line color. To change the color, use the standard color scheme field option.
Gradient appearance is influenced by the Fill opacity setting.
None
No gradient fill. This is the default setting.
Opacity
Transparency of the gradient is calculated based on the values on the y-axis. Opacity of the fill is increasing with the values on the Y-axis.
Hue
Gradient color is generated based on the hue of the line color.
Scheme gradient mode
The Gradient mode option located under the Graph styles has a mode named Scheme. When you enable Scheme, the bar receives a gradient color defined from the selected Color scheme.
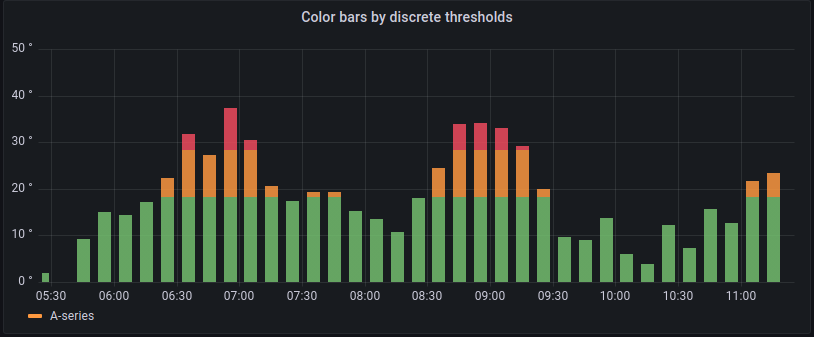
From thresholds
If the Color scheme is set to From thresholds (by value) and Gradient mode is set to Scheme, then the bar color changes as they cross the defined thresholds.
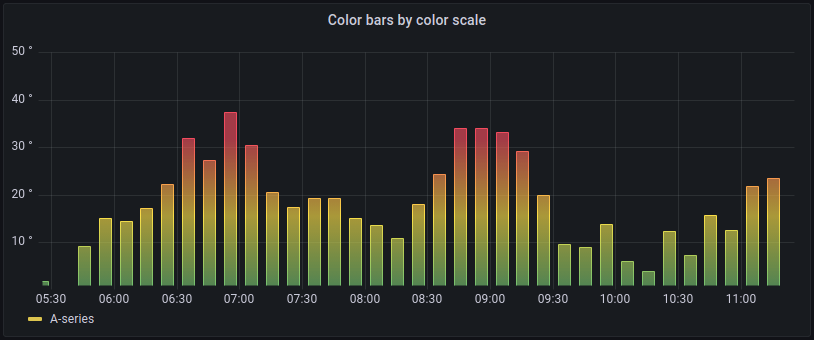
Gradient color schemes
The following image shows a bar chart with the Green-Yellow-Red (by value) color scheme option selected.
Tooltip options
Tooltip options control the information overlay that appears when you hover over data points in the visualization.
Tooltip mode
When you hover your cursor over the visualization, Grafana can display tooltips. Choose how tooltips behave.
- Single - The hover tooltip shows only a single series, the one that you are hovering over on the visualization.
- All - The hover tooltip shows all series in the visualization. Grafana highlights the series that you are hovering over in bold in the series list in the tooltip.
- Hidden - Do not display the tooltip when you interact with the visualization.
Use an override to hide individual series from the tooltip.
Values sort order
When you set the Tooltip mode to All, the Values sort order option is displayed. This option controls the order in which values are listed in a tooltip. Choose from the following:
- None - Grafana automatically sorts the values displayed in a tooltip.
- Ascending - Values in the tooltip are listed from smallest to largest.
- Descending - Values in the tooltip are listed from largest to smallest.
Max height
Set the maximum height of the tooltip box. The default is 600 pixels.
Legend options
Legend options control the series names and statistics that appear under or to the right of the graph. For more information about the legend, refer to Configure a legend.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Visibility | Toggle the switch to turn the legend on or off. |
| Mode | Use these settings to define how the legend appears in your visualization. List displays the legend as a list. This is a default display mode of the legend. Table displays the legend as a table. |
| Placement | Choose where to display the legend. Bottom - Below the graph. Right - To the right of the graph. |
| Width | Control how wide the legend is when placed on the right side of the visualization. This option is only displayed if you set the legend placement to Right. |
| Values | Choose which of the standard calculations to show in the legend. You can have more than one. |
Text size
Enter a Value to change the size of the text on your bar chart.
Axis
Use the following field settings to refine how your axes display.
Some field options will not affect the visualization until you click outside of the field option box you are editing or press Enter.
Placement
Select the placement of the Y-axis.
Auto
Grafana automatically assigns Y-axis to the series. When there are two or more series with different units, then Grafana assigns the left axis to the first unit and right to the following units.
Left
Display all Y-axes on the left side.
Right
Display all Y-axes on the right side.
Hidden
Hide all axes.
To selectively hide axes, Add a field override that targets specific fields.
Label
Set a Y-axis text label.
If you have more than one Y-axis, then you can give assign different labels with an override.
Width
Set a fixed width of the axis. By default, Grafana dynamically calculates the width of an axis.
By setting the width of the axis, data whose axes types are different can share the same display proportions. This makes it easier to compare more than one graph’s worth of data because the axes are not shifted or stretched within visual proximity of each other.
Soft min and soft max
Set a Soft min or soft max option for better control of Y-axis limits. By default, Grafana sets the range for the Y-axis automatically based on the dataset.
Soft min and soft max settings can prevent blips from turning into mountains when the data is mostly flat, and hard min or max derived from standard min and max field options can prevent intermittent spikes from flattening useful detail by clipping the spikes past a defined point.
You can set standard min/max options to define hard limits of the Y-axis. For more information, refer to Standard options definitions.
Display multiple y-axes
In some cases, you may want to display multiple y-axes. For example, if you have a dataset showing both temperature and humidity over time, you may want to show two y-axes with different units for these two series.
You can do this by adding field overrides. Follow the steps as many times as required to add as many y-axes as you need.
Standard options
Standard options in the panel editor pane let you change how field data is displayed in your visualizations. When you set a standard option, the change is applied to all fields or series. For more granular control over the display of fields, refer to Configure overrides.
You can customize the following standard options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Unit | Choose which unit a field should use. |
| Min/Max | Set the minimum and maximum values used in percentage threshold calculations or leave these field empty for them to be calculated automatically. |
| Field min/max | Enable Field min/max to have Grafana calculate the min or max of each field individually, based on the minimum or maximum value of the field. |
| Decimals | Specify the number of decimals Grafana includes in the rendered value. |
| Display name | Set the display title of all fields. You can use variables in the field title. |
| Color scheme | Set single or multiple colors for your entire visualization. |
| No value | Enter what Grafana should display if the field value is empty or null. The default value is a hyphen (-). |
To learn more, refer to Configure standard options.
Data links
Data links allow you to link to other panels, dashboards, and external resources while maintaining the context of the source panel. You can create links that include the series name or even the value under the cursor.
For each data link, set the following options:
- Title
- URL
- Open in new tab
To learn more, refer to Configure data links.
Thresholds
A threshold is a value or limit you set for a metric that’s reflected visually when it’s met or exceeded. Thresholds are one way you can conditionally style and color your visualizations based on query results.
Set the following options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Value | Set the value for each threshold. |
| Thresholds mode | Choose from Absolute and Percentage. |
| Show thresholds | Choose from a variety of display options including not displaying thresholds at all. |
To learn more, refer to Configure thresholds.
Value mappings
Value mapping is a technique you can use to change how data appears in a visualization.
For each value mapping, set the following options:
- Condition - Choose what’s mapped to the display text and (optionally) color:
- Value - Specific values
- Range - Numerical ranges
- Regex - Regular expressions
- Special - Special values like
Null,NaN(not a number), or boolean values liketrueandfalse
- Display text
- Color (Optional)
- Icon (Canvas only)
To learn more, refer to Configure value mappings.
Field overrides
Overrides allow you to customize visualization settings for specific fields or series. When you add an override rule, it targets a particular set of fields and lets you define multiple options for how that field is displayed.
Choose from one the following override options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Fields with name | Select a field from the list of all available fields. |
| Field with name matching regex | Specify fields to override with a regular expression. |
| Fields with type | Select fields by type, such as string, numeric, or time. |
| Fields returned by query | Select all fields returned by a specific query, such as A, B, or C. |
| Fields with values | Select all fields returned by your defined reducer condition, such as Min, Max, Count, Total. |
To learn more, refer to Configure field overrides.



