OpenLDAP integration for Grafana Cloud
OpenLDAP is an open-source implementation of the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), providing robust and scalable directory services. It facilitates the storage, search, and retrieval of directory information, commonly used in identity management and authentication services. This integration with Grafana Cloud enables users to oversee an OpenLDAP environment with observation metrics such as connections, waiters, directory entries, operations, threads, and logs dashboard.
This integration supports OpenLDAP 2.4.5+ and uses a Grafana forked Prometheus Exporter.
This integration includes 4 useful alerts and 2 pre-built dashboards to help monitor and visualize OpenLDAP metrics and logs.
Before you begin
In order for the integration to properly collect metrics and logs within OpenLDAP users must enable the monitoring configurations for metrics, configure slapd stats logs, and set up a Prometheus Exporter.
Important Note: Throughout this document, several placeholders are used that you need to replace with your specific values:
yourpasswordshould be replaced with the actual admin password you intend to use.yourdomainshould be replaced with your domain details (e.g.,dc=example,dc=com).
Enabling monitor module
To effectively collect metrics from OpenLDAP, it’s essential to configure the monitoring module, create a monitor user, and establish a monitor database. This setup involves several key steps, each critical to ensuring that OpenLDAP’s monitoring capabilities are fully functional.
Enabling Monitor Module for OpenLDAP
To effectively collect metrics from OpenLDAP, it’s essential to configure the monitoring module, create a monitor user, and establish a monitor database. This setup involves several key steps, each critical to ensuring that OpenLDAP’s monitoring capabilities are fully functional.
1. Generate a Hashed Password
Generate a hashed password for the admin and monitor users. Use the slappasswd command with a specified password to create a secure hash:
# Generate a hashed password
slappasswd -s yourpassword > /tmp/hashed_password.txt
HASHED_PASSWORD=$(cat /tmp/hashed_password.txt)2. Configure the LDAP Admin User
With the hashed password, configure the LDAP admin user by applying modifications to the LDAP configuration:
# Set up the LDAP admin user with the hashed password
echo "dn: olcDatabase={1}mdb,cn=config\nchangetype: modify\nreplace: olcRootDN\nolcRootDN: cn=admin,dc=yourdomain\n-\nreplace: olcRootPW\nolcRootPW: $HASHED_PASSWORD" > /tmp/set_admin_pw.ldif
ldapmodify -Y EXTERNAL -H ldapi:/// -f /tmp/set_admin_pw.ldif3. Load the Monitoring Module
Activate the monitoring module by modifying the LDAP configuration to include the module:
# Enable the monitoring module in OpenLDAP
echo "dn: cn=module{0},cn=config\nchangetype: modify\nadd: olcModuleLoad\nolcModuleLoad: back_monitor" > /tmp/module_monitor.ldif
ldapmodify -Y EXTERNAL -H ldapi:/// -f /tmp/module_monitor.ldif4. Set Up the Monitor User
Configure the monitor user with the hashed password using the following commands:
# Set up the monitor user with the hashed password
echo "dn: cn=monitor,dc=yourdomain\nobjectClass: simpleSecurityObject\nobjectClass: organizationalRole\ncn: monitor\ndescription: LDAP monitor\nuserPassword: $HASHED_PASSWORD" > /tmp/cn_monitor.ldif
ldapadd -x -D "cn=admin,dc=yourdomain" -w yourpassword -f /tmp/cn_monitor.ldif5. Establish the Monitor Database
Finally, create the monitor database by defining its configuration with appropriate access controls:
# Setup the monitor database in OpenLDAP
echo "dn: olcDatabase={2}Monitor,cn=config\nobjectClass: olcDatabaseConfig\nobjectClass: olcMonitorConfig\nolcDatabase: {2}Monitor\nolcAccess: to dn.subtree=\"cn=Monitor\" by dn.base=\"cn=monitor,dc=yourdomain\" read by * none" > /tmp/database_monitor.ldif
ldapadd -Y EXTERNAL -H ldapi:/// -f /tmp/database_monitor.ldifThis setup can be achieved by following a monitor setup based on backend monitoring guide, monitoring as an admin.
By following these steps, OpenLDAP will be configured to provide valuable monitoring data, facilitating better management and oversight of LDAP services.
Enabling Logging for OpenLDAP
To collect comprehensive logs from OpenLDAP, including slapd stats logs, it’s essential to configure both the OpenLDAP logging settings and the system’s logging service (such as rsyslog). The following steps outline how to enable detailed logging capabilities.
1. Configure OpenLDAP for Detailed Logging
Enhance the log settings of OpenLDAP to capture statistics by modifying the LDAP configuration:
# Configure OpenLDAP for additional logging
echo "dn: cn=config
changeType: modify
replace: olcLogLevel
olcLogLevel: stats" > /tmp/slapdlog.ldif
ldapmodify -Y EXTERNAL -H ldapi:/// -f /tmp/slapdlog.ldif2. Set Up Rsyslog for OpenLDAP Logging
Configure rsyslog to specifically handle and format OpenLDAP logs, ensuring they are stored appropriately:
# Configure rsyslog for OpenLDAP logging
echo '$template slapdtmpl,"[%$DAY%-%$MONTH%-%$YEAR% %timegenerated:12:19:date-rfc3339%] %app-name% %syslogseverity-text% %msg%\\n"
local4.* /var/log/slapd.log;slapdtmpl' > /etc/rsyslog.d/10-slapd.conf
service rsyslog restartThese configuration steps will help in effectively logging important data for OpenLDAP.
Note: The configuration settings for logging are pre-applied when using the OpenLDAP helm chart.
For further guidance on setting up OpenLDAP logging, you may refer to this detailed logging tutorial.
Setting up the Prometheus Exporter for OpenLDAP
To effectively collect and monitor metrics from OpenLDAP, the Prometheus Exporter must be installed and configured. Here are the steps to ensure the exporter is properly set up and integrated with your OpenLDAP instance.
1. Install and Build the OpenLDAP Exporter
Clone the repository and build the Prometheus Exporter from the source:
# Clone the OpenLDAP Exporter repository
git clone https://github.com/grafana/openldap_exporter.git openldap_exporter
# Build the OpenLDAP Exporter
cd openldap_exporter/cmd/openldap_exporter
go build -buildvcs=false2. Configure and Start the Prometheus Exporter
Set up the Prometheus Exporter as a systemd service to ensure it starts with the system and restarts on failure:
# Create systemd service for the OpenLDAP Exporter
echo -e "[Unit]\nDescription=OpenLDAP Exporter\nAfter=network.target\n\n[Service]\nType=simple\nExecStart=$(pwd)/openldap_exporter/openldap_exporter --promAddr \":8080\" --ldapAddr \"ldap://localhost:389\" --ldapUser \"cn=monitor,dc=yourdomain\" --ldapPass \"yourpassword\" --interval \"10s\"\nRestart=on-failure\n\n[Install]\nWantedBy=multi-user.target" > /etc/systemd/system/openldap_exporter.service
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable openldap_exporter.service
systemctl start openldap_exporter.service3. Verify the Prometheus Exporter Setup
Once the exporter is running, validate that metrics are being correctly exposed by accessing the Prometheus metrics endpoint:
# Check Prometheus metrics
curl http://localhost:8080/metricsThese instructions ensure that the Prometheus Exporter is set up correctly to collect metrics from your OpenLDAP instance. For additional configuration options and details on the exporter’s capabilities, refer to the GitHub repository.
Install OpenLDAP integration for Grafana Cloud
- In your Grafana Cloud stack, click Connections in the left-hand menu.
- Find OpenLDAP and click its tile to open the integration.
- Review the prerequisites in the Configuration Details tab and set up Grafana Agent to send OpenLDAP metrics and logs to your Grafana Cloud instance.
- Click Install to add this integration’s pre-built dashboards and alerts to your Grafana Cloud instance, and you can start monitoring your OpenLDAP setup.
Configuration snippets for Grafana Alloy
Simple mode
These snippets are configured to scrape a single OpenLDAP instance with Grafana Alloy running locally.
Copy and Paste the following snippets into your Grafana Agent Flow river configuration file.
Logs snippets
linux
local.file_match "logs_integrations_integrations_openldap" {
path_targets = [{
__address__ = "localhost",
__path__ = "/var/log/slapd/*.log",
instance = "<your-instance-name>",
job = "integrations/openldap",
}]
}
loki.process "logs_integrations_integrations_openldap" {
forward_to = []
stage.multiline {
firstline = "^\\[\\d{2}-\\d{2}-\\d{4} \\d{2}:\\d{2}:\\d{2}\\]"
max_lines = 0
max_wait_time = "0s"
}
stage.regex {
expression = "^\\[\\d{2}-\\d{2}-\\d{4} \\d{2}:\\d{2}:\\d{2}\\] (?P<component>\\S+) (?P<level>\\w+)"
}
stage.labels {
values = {
component = null,
level = null,
}
}
}
loki.source.file "logs_integrations_integrations_openldap" {
targets = local.file_match.logs_integrations_integrations_openldap.targets
forward_to = [loki.write.grafana_cloud_loki.receiver]
}Advanced mode
The following snippets provide examples to guide you through the configuration process.
To instruct Grafana Alloy to scrape your OpenLDAP instance, copy and paste the snippets to your configuration file and follow subsequent instructions.
Advanced metrics snippets
prometheus.scrape "metrics_integrations_integrations_openldap" {
targets = [{
__address__ = "localhost:<your-host-ip>",
}]
forward_to = [prometheus.remote_write.metrics_service.receiver]
job_name = "integrations/openldap"
}This integration uses the prometheus.exporter.openldap component to collect metrics from an OpenLDAP instance.
The snippet must be configured with the following properties within the prometheus.scrape, targets section:
<your-instance-port>: The exporter port label used to collect metrics.
Advanced logs snippets
linux
local.file_match "logs_integrations_integrations_openldap" {
path_targets = [{
__address__ = "localhost",
__path__ = "/var/log/slapd/*.log",
instance = "<your-instance-name>",
job = "integrations/openldap",
}]
}
loki.process "logs_integrations_integrations_openldap" {
forward_to = []
stage.multiline {
firstline = "^\\[\\d{2}-\\d{2}-\\d{4} \\d{2}:\\d{2}:\\d{2}\\]"
max_lines = 0
max_wait_time = "0s"
}
stage.regex {
expression = "^\\[\\d{2}-\\d{2}-\\d{4} \\d{2}:\\d{2}:\\d{2}\\] (?P<component>\\S+) (?P<level>\\w+)"
}
stage.labels {
values = {
component = null,
level = null,
}
}
}
loki.source.file "logs_integrations_integrations_openldap" {
targets = local.file_match.logs_integrations_integrations_openldap.targets
forward_to = [loki.write.grafana_cloud_loki.receiver]
}To collect your OpenLDAP logs, you must use a local.file_match component to tag the file to be scraped, a loki.source.file component to prepare it for Loki ingestion and a loki.process component to process your logs with adequate labels and drop empty lines.
You can check the full array of options in each component documentation.
To show show logs and metrics signals correlated in your dashboards as a single pane of glass, ensure the following config changes are made:
<your-instance-name>: Must be set to a value that uniquely identifies your OpenLDAP instance.
Grafana Agent static configuration (deprecated)
The following section shows configuration for running Grafana Agent in static mode which is deprecated. You should use Grafana Alloy for all new deployments.
Before you begin with Grafana Agent static
In order for the integration to properly collect metrics and logs within OpenLDAP, users must enable the monitoring configurations for metrics, configure slapd stats logs, and set up a Prometheus Exporter.
Enabling monitor module
In order to collect metrics from OpenLDAP, a monitoring module, monitor user, and monitor database must be setup. This setup can be achieved by following a monitor setup based on the backend monitoring guide, monitoring as an admin or viewing an example sample app.
Enabling logging
In order to collect slapd stats logs, the production server logs and rsyslog must be enabled. This setup can be achieved by following this guide or by viewing an example sample app.
Note: These log settings are pre-applied when using a helm chart.
Setting up the Prometheus Exporter
In order to collect metrics from OpenLDAP, a Prometheus Exporter must be setup. Once the Prometheus Exporter is installed, set the target of your OpenLDAP instance with the monitor user and password setup such as:
./openldap_exporter --ldapAddr=ldap://localhost:389", "--ldapUser=cn=monitor,dc=example,dc=org" "--ldapPass=<monitor-user-password>"`This setup can be achieved by following this example sample app as a guide.
To validate that the Prometheus Exporter is setup correctly, the Prometheus metrics are accessible locally via curl:
curl http://localhost:8080/metricsInstall OpenLDAP integration
- In your Grafana Cloud stack, click Connections in the left-hand menu.
- Find OpenLDAP and click its tile to open the integration.
- Review the prerequisites in the Configuration Details tab and set up Grafana Agent to send OpenLDAP metrics and logs to your Grafana Cloud instance.
- Click Install to add this integration’s pre-built dashboards and alerts to your Grafana Cloud instance, and you can start monitoring your OpenLDAP setup.
Post-install configuration for the OpenLDAP integration
After enabling metric and logs, enable the integration by adding the suggested snippets to your configuration file.
joblabel values must match for metrics and logs scrape config in your agent configuration file.joblabel must be set tointegrations/openldap(already configured in the snippets).instancemust be set to a value that uniquely identifies your OpenLDAP instance.__path__is the slapd logs location which should be set to/var/logs/slapd.logsif logging is configured and enabled.
Configuration snippets for Grafana Agent
Below metrics.configs.scrape_configs, insert the following lines and change the URLs according to your environment:
- job_name: integrations/openldap
metrics_path: /metrics
static_configs:
- targets: ["<your-instance-name>:<your-instance-port>"]Below logs.configs.scrape_configs, insert the following lines according to your environment.
- job_name: integrations/openldap
static_configs:
- targets: [localhost]
labels:
job: integrations/openldap
__path__: /var/log/slapd/*.log
instance: '<your-instance-name>'
pipeline_stages:
- multiline:
firstline: '^\[\d{2}-\d{2}-\d{4} \d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}\]'
- regex:
expression: '^\[\d{2}-\d{2}-\d{4} \d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}\] (?P<component>\S+) (?P<level>\w+)'
- labels:
level:
component:Full example configuration for Grafana Agent
Refer to the following Grafana Agent configuration for a complete example that contains all the snippets used for the OpenLDAP integration. This example also includes metrics that are sent to monitor your Grafana Agent instance.
integrations:
prometheus_remote_write:
- basic_auth:
password: <your_prom_pass>
username: <your_prom_user>
url: <your_prom_url>
agent:
enabled: true
relabel_configs:
- action: replace
source_labels:
- agent_hostname
target_label: instance
- action: replace
target_label: job
replacement: "integrations/agent-check"
metric_relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: (prometheus_target_sync_length_seconds_sum|prometheus_target_scrapes_.*|prometheus_target_interval.*|prometheus_sd_discovered_targets|agent_build.*|agent_wal_samples_appended_total|process_start_time_seconds)
source_labels:
- __name__
# Add here any snippet that belongs to the `integrations` section.
# For a correct indentation, paste snippets copied from Grafana Cloud at the beginning of the line.
logs:
configs:
- clients:
- basic_auth:
password: <your_loki_pass>
username: <your_loki_user>
url: <your_loki_url>
name: integrations
positions:
filename: /tmp/positions.yaml
scrape_configs:
# Add here any snippet that belongs to the `logs.configs.scrape_configs` section.
# For a correct indentation, paste snippets copied from Grafana Cloud at the beginning of the line.
- job_name: integrations/openldap
static_configs:
- targets: [localhost]
labels:
job: integrations/openldap
__path__: /var/log/slapd/*.log
instance: '<your-instance-name>'
pipeline_stages:
- multiline:
firstline: '^\[\d{2}-\d{2}-\d{4} \d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}\]'
- regex:
expression: '^\[\d{2}-\d{2}-\d{4} \d{2}:\d{2}:\d{2}\] (?P<component>\S+) (?P<level>\w+)'
- labels:
level:
component:
metrics:
configs:
- name: integrations
remote_write:
- basic_auth:
password: <your_prom_pass>
username: <your_prom_user>
url: <your_prom_url>
scrape_configs:
# Add here any snippet that belongs to the `metrics.configs.scrape_configs` section.
# For a correct indentation, paste snippets copied from Grafana Cloud at the beginning of the line.
- job_name: integrations/openldap
metrics_path: /metrics
static_configs:
- targets: ["<your-instance-name>:<your-instance-port>"]
global:
scrape_interval: 60s
wal_directory: /tmp/grafana-agent-walDashboards
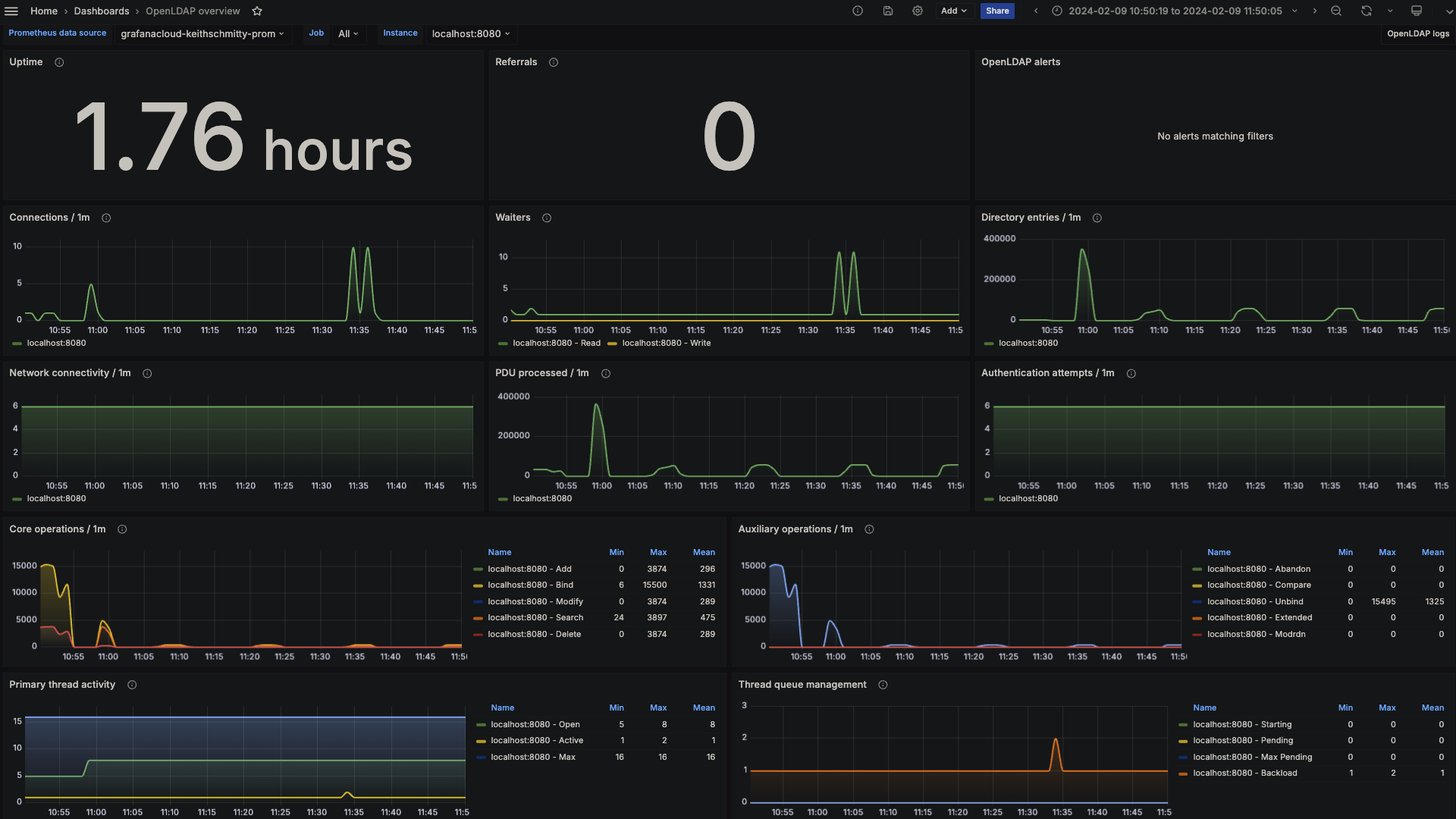
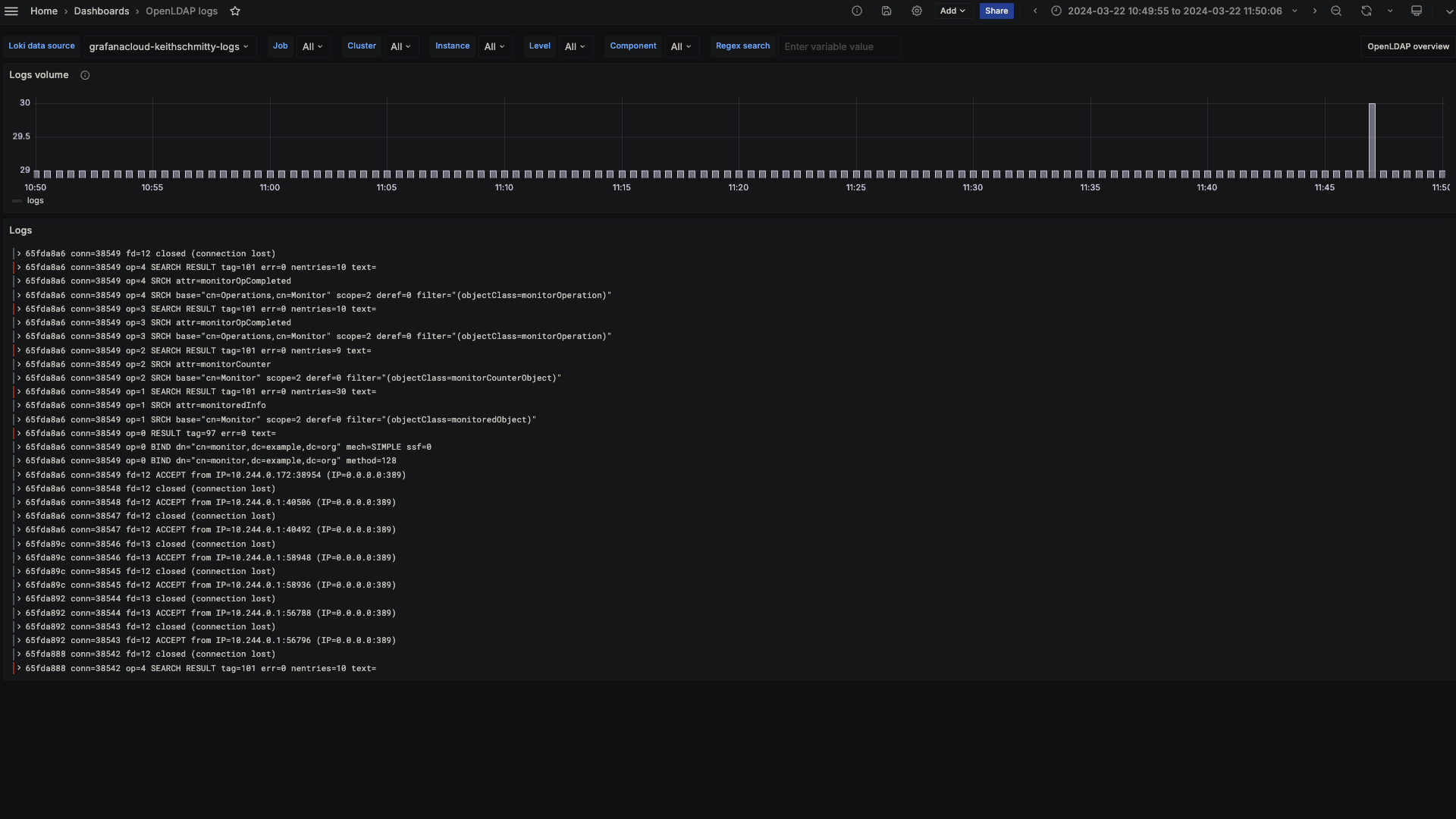
The OpenLDAP integration installs the following dashboards in your Grafana Cloud instance to help monitor your system.
- OpenLDAP logs
- OpenLDAP overview
OpenLDAP overview (LDAP stats)
OpenLDAP logs
Alerts
The OpenLDAP integration includes the following useful alerts:
| Alert | Description |
|---|---|
| OpenLDAPConnectionSpike | Warning: A sudden spike in OpenLDAP connections indicates potential high usage or security issues. |
| OpenLDAPHighSearchOperationRateSpike | Warning: A significant spike in OpenLDAP search operations indicates inefficient queries, potential abuse, or unintended heavy load. |
| OpenLDAPDialFailures | Warning: Significant increase in LDAP dial failures indicates network issues, problems with the LDAP service, or configuration errors that may lead to service unavailability. |
| OpenLDAPBindFailureRateIncrease | Warning: Significant increase in LDAP bind failures indicates authentication issues, potential security threats or problems with user directories. |
Metrics
The most important metrics provided by the OpenLDAP integration, which are used on the pre-built dashboards and Prometheus alerts, are as follows:
- openldap_bind
- openldap_dial
- openldap_monitor_counter_object
- openldap_monitor_operation
- openldap_monitored_object
- up
Changelog
# 1.0.1 - November 2024
- Update status panel check queries
# 1.0.0 - April 2024
- Initial releaseCost
By connecting your OpenLDAP instance to Grafana Cloud, you might incur charges. To view information on the number of active series that your Grafana Cloud account uses for metrics included in each Cloud tier, see Active series and dpm usage and Cloud tier pricing.



