Application Observability Go quickstart
Follow these steps to get started quickly with Grafana Application Observability:
- Install the instrumentation library
- Configure an application
- Run the application
- Observe the service in Application Observability
This guide is intended for local development or evaluation setups and sends data directly to Grafana Cloud without a data collector.
Note
For a production setup with a data collector and troubleshooting information, consult the production documentation.
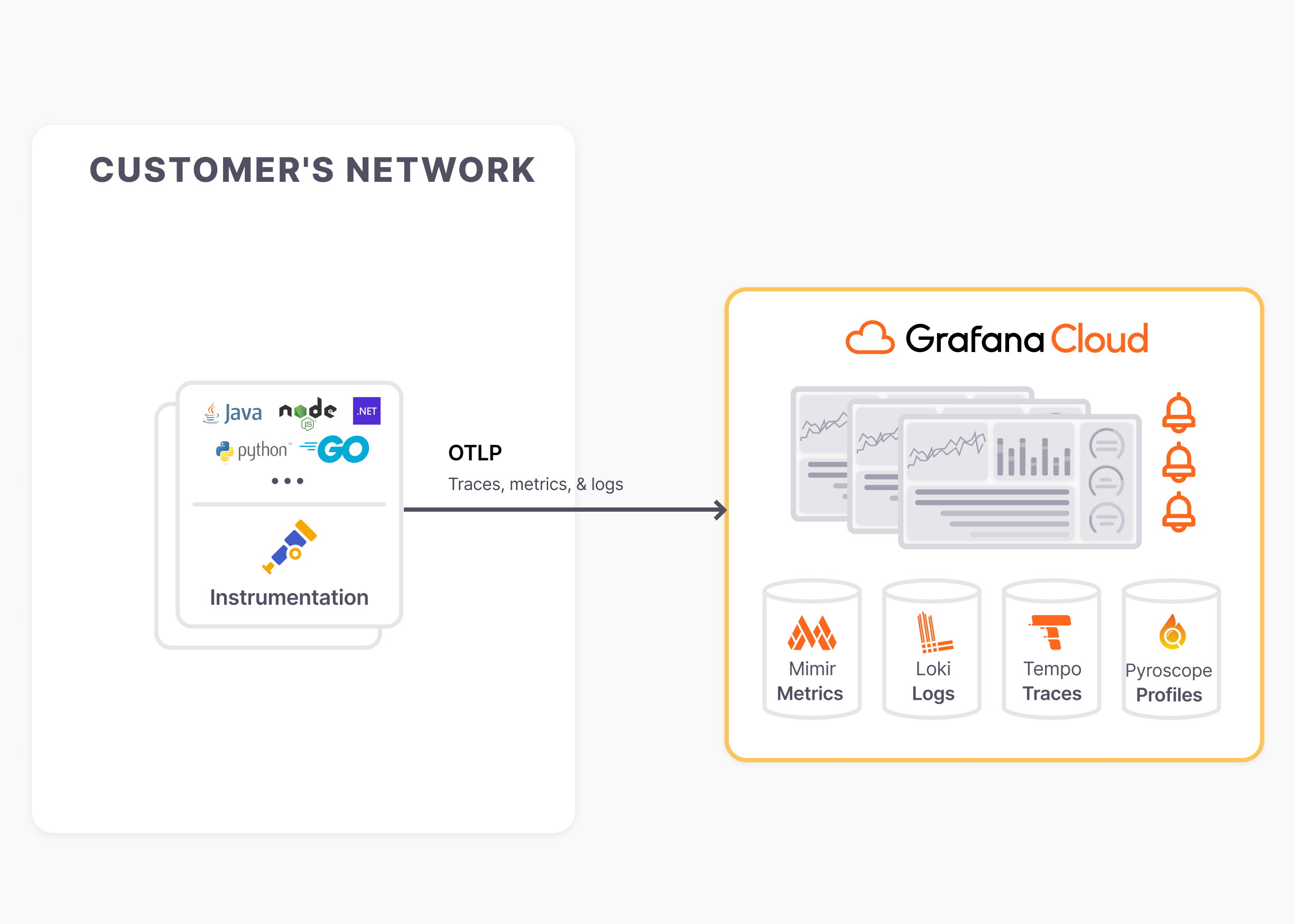
Install the instrumentation library
Add Dependencies
First, install OpenTelemetry SDK components and the net/http instrumentation.
go get "go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/net/http/otelhttp" \
"go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/runtime" \
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel" \
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/exporters/otlp/otlpmetric/otlpmetrichttp" \
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/exporters/otlp/otlptrace" \
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/exporters/otlp/otlptrace/otlptracehttp" \
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/sdk" \
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/sdk/metric"If you’re instrumenting a different library for network requests, you’ll need to install the appropriate instrumentation library. See libraries for more info.
Initialize the OpenTelemetry SDK
First, we’ll initialize the OpenTelemetry SDK. This is required for any application that exports telemetry.
Create otel.go with OpenTelemetry SDK bootstrapping code:
package main
import (
"context"
"errors"
"go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/runtime"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/exporters/otlp/otlpmetric/otlpmetrichttp"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/exporters/otlp/otlptrace"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/exporters/otlp/otlptrace/otlptracehttp"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/propagation"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/sdk/metric"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/sdk/trace"
"log"
"time"
)
// setupOTelSDK bootstraps the OpenTelemetry pipeline.
// If it does not return an error, make sure to call shutdown for proper cleanup.
func setupOTelSDK(ctx context.Context) (shutdown func(context.Context) error, err error) {
var shutdownFuncs []func(context.Context) error
// shutdown calls cleanup functions registered via shutdownFuncs.
// The errors from the calls are joined.
// Each registered cleanup will be invoked once.
shutdown = func(ctx context.Context) error {
var err error
for _, fn := range shutdownFuncs {
err = errors.Join(err, fn(ctx))
}
shutdownFuncs = nil
return err
}
// handleErr calls shutdown for cleanup and makes sure that all errors are returned.
handleErr := func(inErr error) {
err = errors.Join(inErr, shutdown(ctx))
}
prop := propagation.NewCompositeTextMapPropagator(
propagation.TraceContext{},
propagation.Baggage{},
)
otel.SetTextMapPropagator(prop)
traceExporter, err := otlptrace.New(ctx, otlptracehttp.NewClient())
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
tracerProvider := trace.NewTracerProvider(trace.WithBatcher(traceExporter))
if err != nil {
handleErr(err)
return
}
shutdownFuncs = append(shutdownFuncs, tracerProvider.Shutdown)
otel.SetTracerProvider(tracerProvider)
metricExporter, err := otlpmetrichttp.New(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
meterProvider := metric.NewMeterProvider(metric.WithReader(metric.NewPeriodicReader(metricExporter)))
if err != nil {
handleErr(err)
return
}
shutdownFuncs = append(shutdownFuncs, meterProvider.Shutdown)
otel.SetMeterProvider(meterProvider)
err = runtime.Start(runtime.WithMinimumReadMemStatsInterval(time.Second))
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
return
}Instrument the HTTP server
Now that we have the OpenTelemetry SDK initialized, we can instrument the HTTP server.
Let’s suppose the initial main.go looks like this:
package main
import (
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/rolldice", rolldice) // signature: func rolldice(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { .. }
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil))
}Modify main.go to include code that sets up OpenTelemetry SDK and instruments the HTTP server
using the go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/net/http/otelhttp instrumentation library:
package main
import (
"context"
"errors"
"log"
"net"
"net/http"
"os"
"os/signal"
"time"
"go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/net/http/otelhttp"
)
func main() {
if err := run(); err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
}
func run() (err error) {
// Handle SIGINT (CTRL+C) gracefully.
ctx, stop := signal.NotifyContext(context.Background(), os.Interrupt)
defer stop()
// Set up OpenTelemetry.
otelShutdown, err := setupOTelSDK(ctx)
if err != nil {
return
}
// Handle shutdown properly so nothing leaks.
defer func() {
err = errors.Join(err, otelShutdown(context.Background()))
}()
// Start HTTP server.
srv := &http.Server{
Addr: ":8080",
BaseContext: func(_ net.Listener) context.Context { return ctx },
ReadTimeout: time.Second,
WriteTimeout: 10 * time.Second,
Handler: newHTTPHandler(),
}
srvErr := make(chan error, 1)
go func() {
srvErr <- srv.ListenAndServe()
}()
// Wait for interruption.
select {
case err = <-srvErr:
// Error when starting HTTP server.
return
case <-ctx.Done():
// Wait for first CTRL+C.
// Stop receiving signal notifications as soon as possible.
stop()
}
// When Shutdown is called, ListenAndServe immediately returns ErrServerClosed.
err = srv.Shutdown(context.Background())
return
}
func newHTTPHandler() http.Handler {
mux := http.NewServeMux()
// handleFunc is a replacement for mux.HandleFunc
// which enriches the handler's HTTP instrumentation with the pattern as the http.route.
handleFunc := func(pattern string, handlerFunc func(http.ResponseWriter, *http.Request)) {
// Configure the "http.route" for the HTTP instrumentation.
handler := otelhttp.WithRouteTag(pattern, http.HandlerFunc(handlerFunc))
mux.Handle(pattern, handler)
}
// Register handlers.
handleFunc("/rolldice", rolldice)
// Add HTTP instrumentation for the whole server.
handler := otelhttp.NewHandler(mux, "/")
return handler
}Configure an application
Next, customize the following shell script to configure an application:
<authentication environment variables from step 3>
export OTEL_SERVICE_NAME=<Service Name>
go run .Follow these steps to get necessary information for the shell script:
Sign in to Grafana Cloud, register for a Free Grafana Cloud account if required, the browser will navigate to the Grafana Cloud Portal page https://grafana.com/profile/org.
If the account has access to multiple Grafana Cloud Organizations, select an organization from the top left organization dropdown.
If the organization has access to multiple Grafana Cloud Stacks, navigate to a stack from the left side bar or the main Stacks list.
With a stack selected, or in the single stack scenario, below Manage your Grafana Cloud Stack, click Configure in the OpenTelemetry section:
![]()
In the Password / API Token section, click on Generate now to create a new API token:
- Give the API token a name, for example
cart-service - Click on Create token
- Click on Close without copying the token
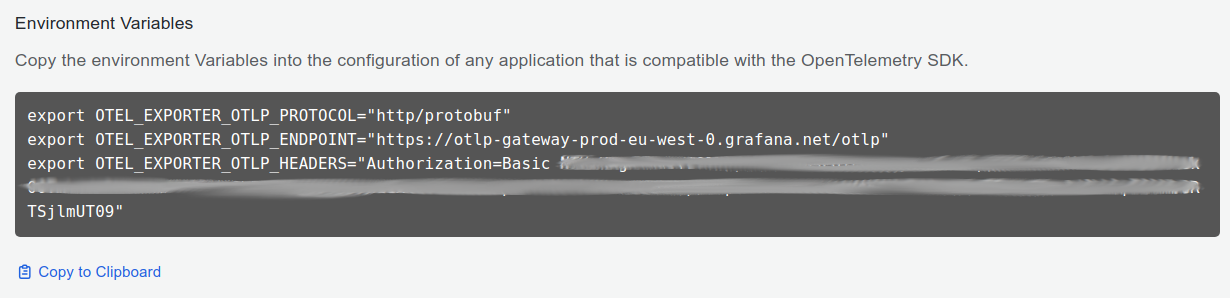
- Click on Copy to Clipboard to copy the environment variables to the clipboard
![]()
- Give the API token a name, for example
- Pick a Service Name to identify the service, for example
cart
Run the application
Finally, run the application with the shell script and make some requests to the service to send data to Grafana Cloud.
Observe the service in Application Observability
Open Application observability:
- Navigate to a stack
https://<your-stack-name.>grafana.net - Expand the top left menu below the Grafana logo
- Click on Application
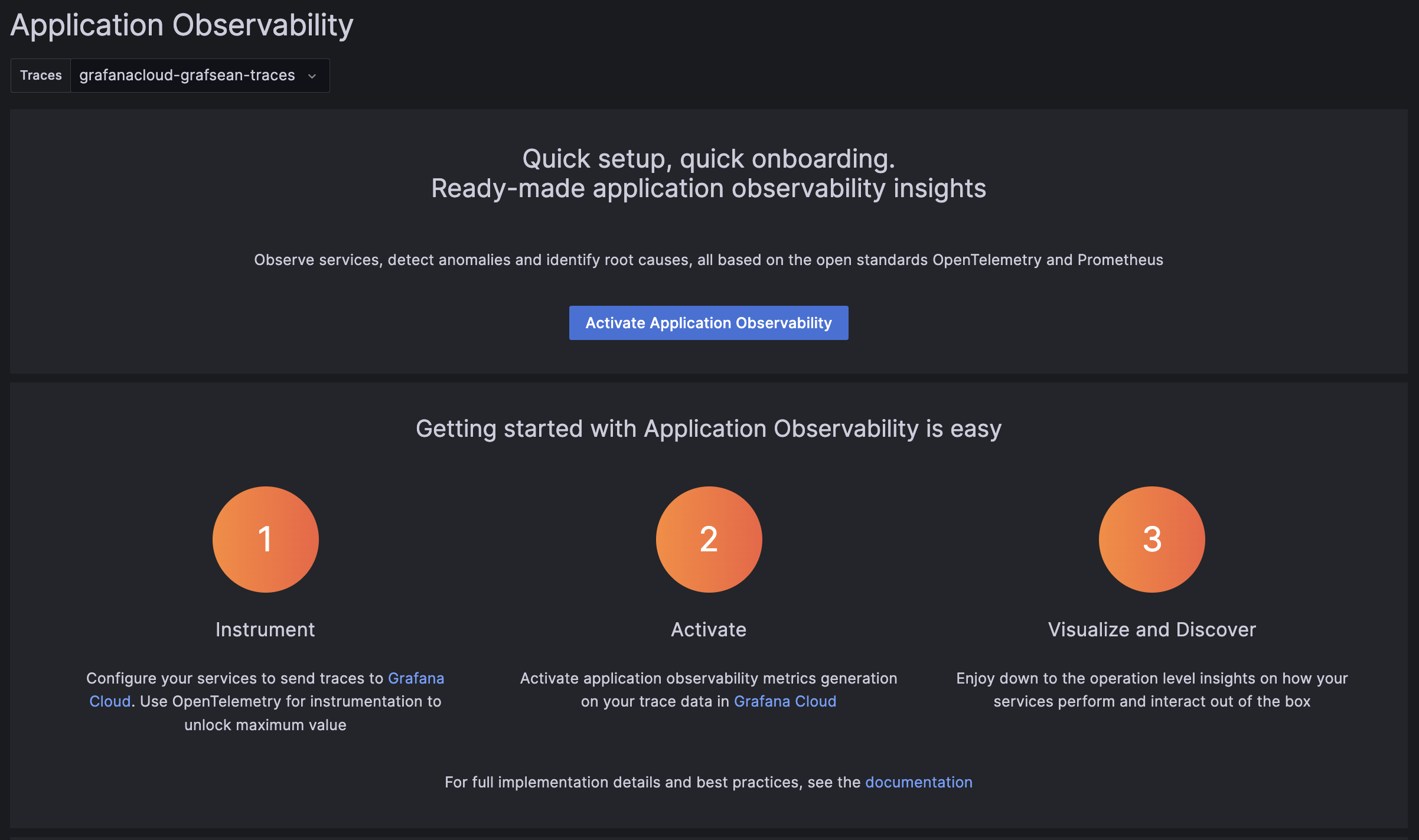
Activate metrics generation
Application Observability relies on metrics generated from traces already sent to Grafana Cloud Traces.
Metrics generation is self-serve, and can be enabled during onboarding and disabled from Application Observability configuration.
To complete the setup, click Activate Application Observability to enable metrics generation.
Note
After activating Application Observability and enabling metrics generation, it might take up to five minutes to generate metrics and show graphs.
Visualize and discover
Discover more about Application Observability in the documentation:
- Service Inventory: filter, and search services and view RED metrics.
- Service Overview: traces, logs, RED metrics, operations, and runtime information.
- Service Map: graph of connected services, service dependencies, and data flow.
Example application
See the Rolldice service for a complete example setup.