Before you begin
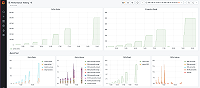
Follow the checklist to ensure that your application is generating metrics, traces, and exemplars.
- Verify that your application is using the official Prometheus client libraries.
- Ensure that the client library you choose is emitting metrics in OpenMetrics format by referencing its documentation. For the Prometheus Go client library, for example, this requires you to set
EnableOpenMetricstotrue. For the Java library, follow its instructions on setting the proper header format. - Obtain the trace ID for the current request and include the trace ID in calls to emit metrics.
- For histograms, use the
ObserveWithExemplarmethod to emit the trace ID along with a value for the histogram. These functions are from the Go library but you can find similar functions in the other libraries. - For counters, use the
AddWithExemplarmethod to emit the trace ID along with a counter increment.
- For histograms, use the
- Verify that metrics are being generated with exemplars by running the following command in a shell:
curl -H "Accept: application/openmetrics-text" http://<your application>/metrics | grep -i "traceid".
See also: