Caution
Grafana Alloy is the new name for our distribution of the OTel collector. Grafana Agent has been deprecated and is in Long-Term Support (LTS) through October 31, 2025. Grafana Agent will reach an End-of-Life (EOL) on November 1, 2025. Read more about why we recommend migrating to Grafana Alloy.
Important: This documentation is about an older version. It's relevant only to the release noted, many of the features and functions have been updated or replaced. Please view the current version.
Debugging
Follow these steps to debug issues with Grafana Agent Flow:
- Use the Grafana Agent Flow UI to debug issues.
- If the UI doesn’t help with debugging an issue, logs can be examined instead.
Grafana Agent Flow UI
Grafana Agent Flow includes an embedded UI viewable from Grafana Agent’s HTTP
server, which defaults to listening at http://localhost:12345.
NOTE: For security reasons, installations of Grafana Agent Flow on non-containerized platforms default to listening on
localhost. default prevents other machines on the network from being able to view the UI.To expose the UI to other machines on the network on non-containerized platforms, refer to the documentation for how you installed Grafana Agent Flow.
If you are running a custom installation of Grafana Agent Flow, refer to the documentation for the
grafana-agent runcommand to learn how to change the HTTP listen address, and pass the appropriate flag when running Grafana Agent Flow.
Home page
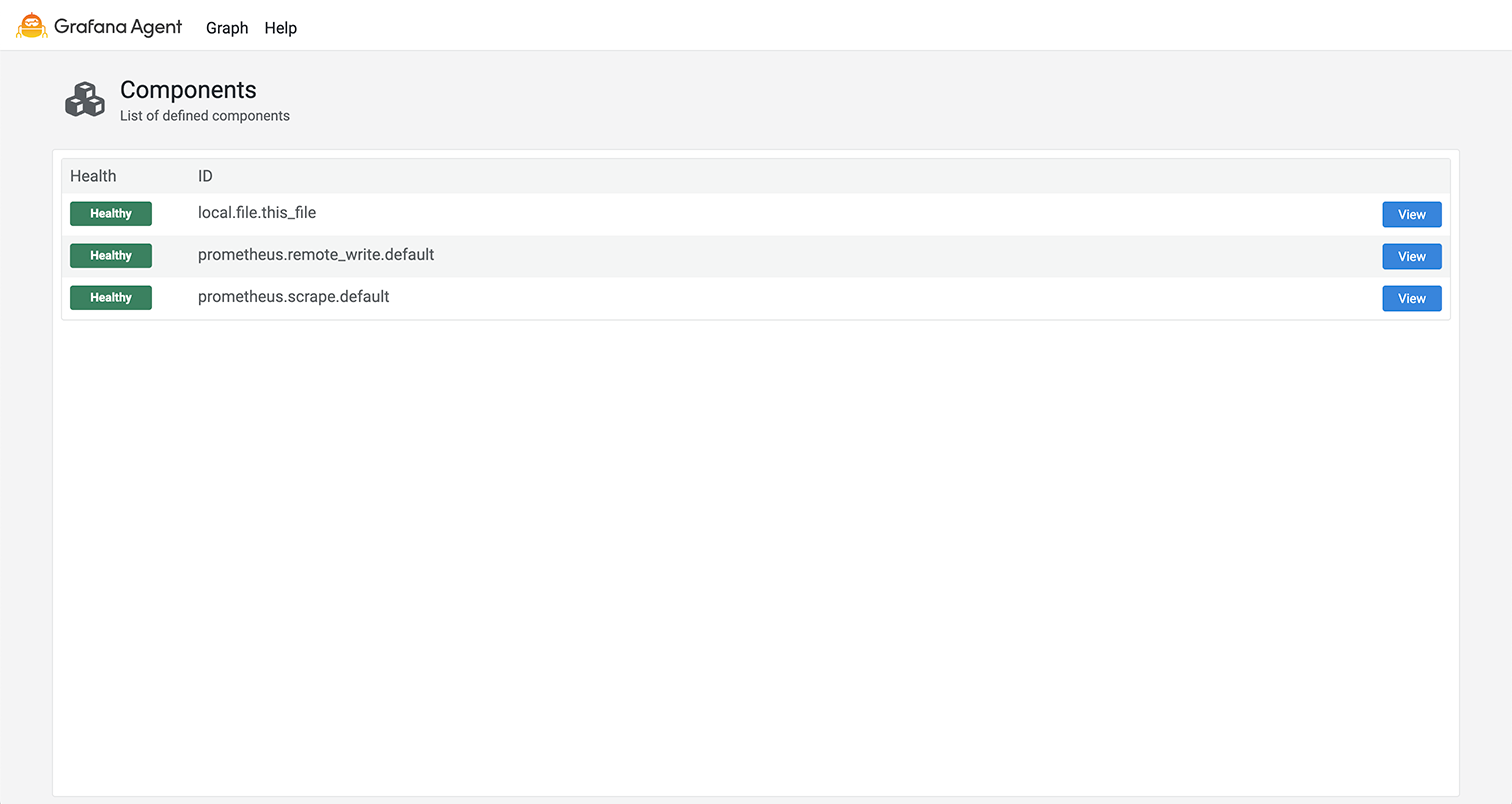
The home page shows a table of components defined in the config file along with their health.
Click View on a row in the table to navigate to the Component detail page for that component.
Click the Grafana Agent logo to navigate back to the home page.
Graph page
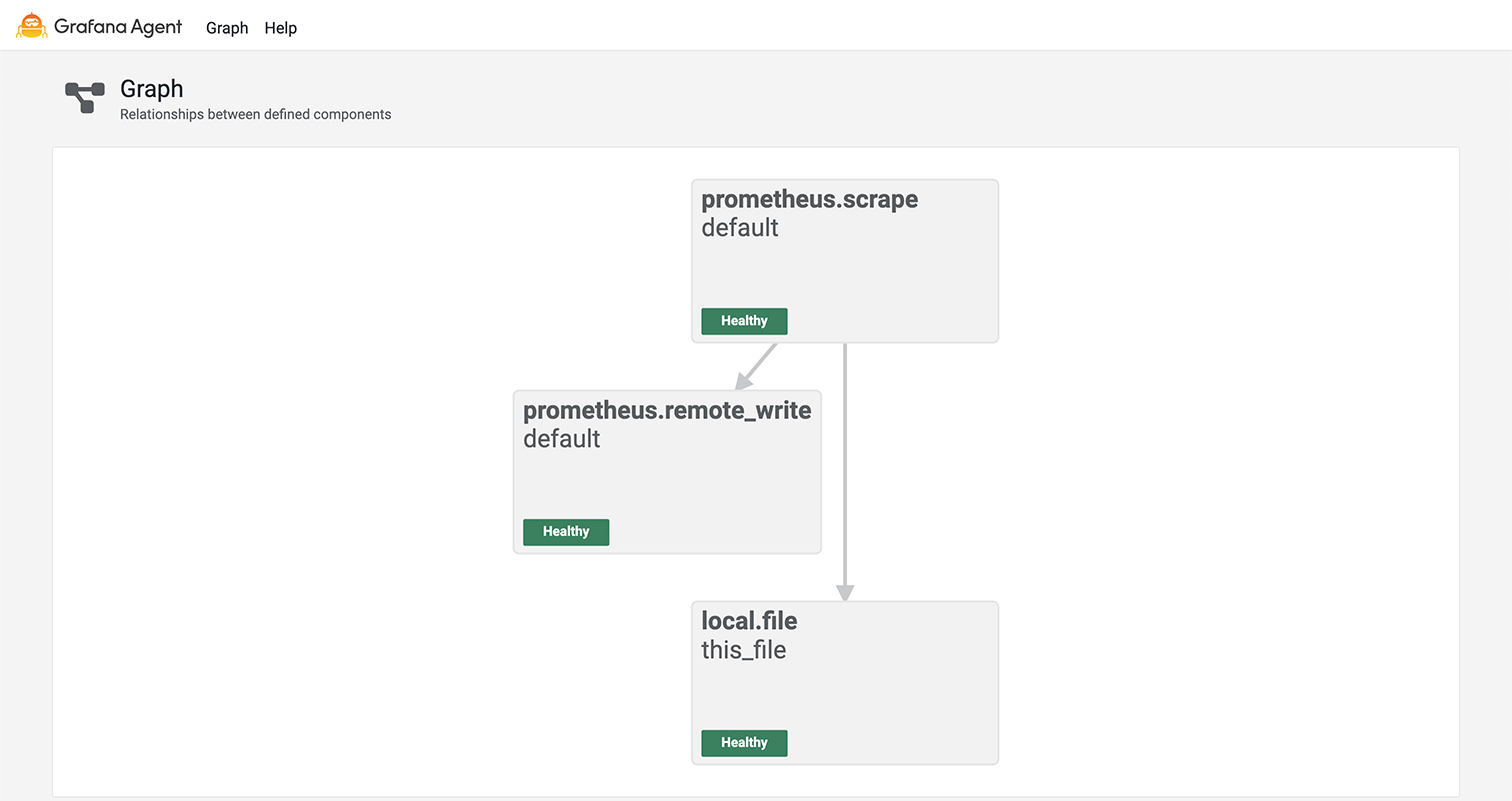
The Graph page shows a graph view of components defined in the config file along with their health. Clicking a component in the graph navigates to the Component detail page for that component.
Component detail page
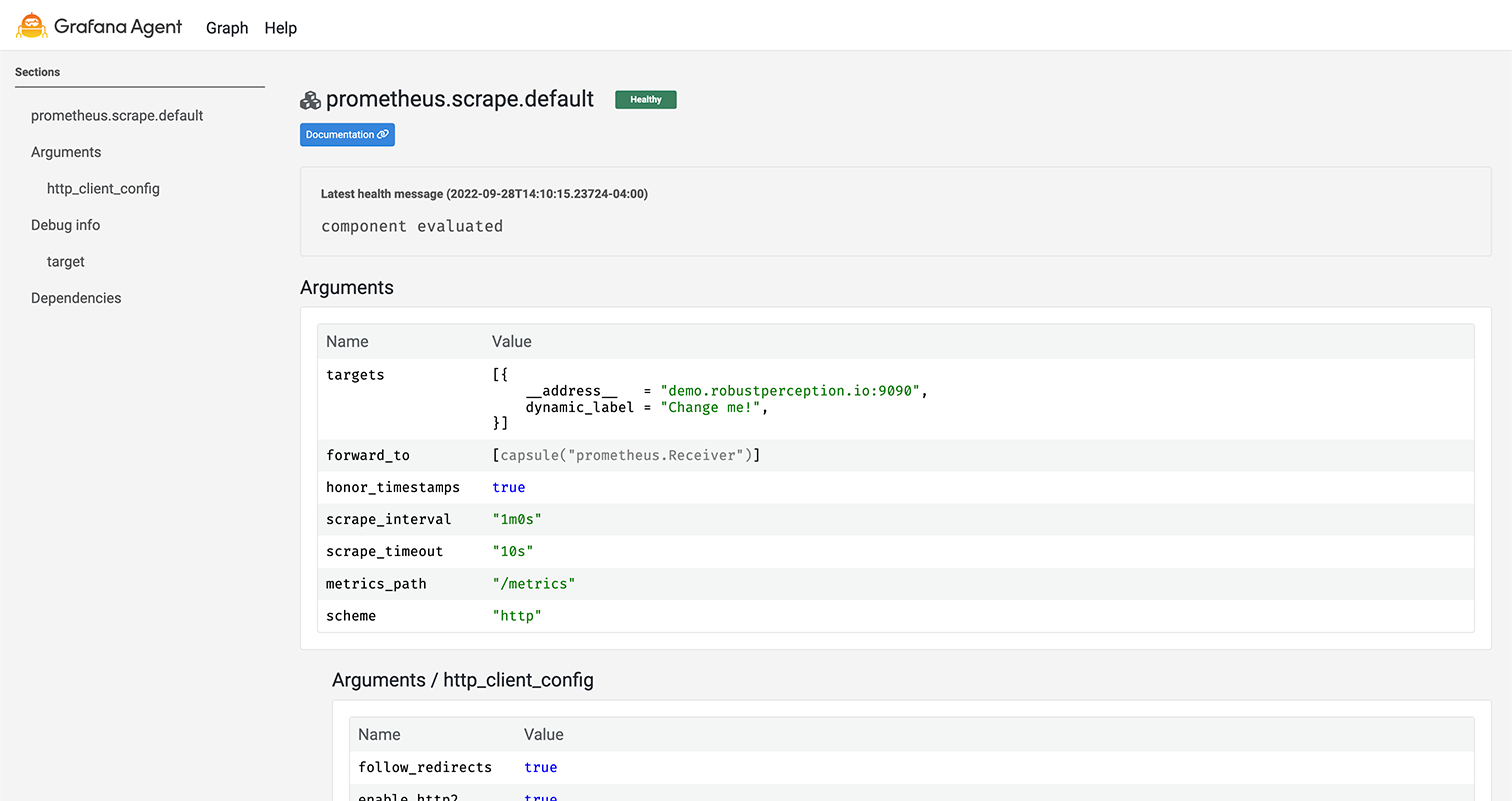
The component detail page shows the following information for each component:
- The health of the component with a message explaining the health.
- The current evaluated arguments for the component.
- The current exports for the component.
- The current debug info for the component (if the component has debug info).
Values marked as a secret are obfuscated and will display as the text
(secret).
Clustering page
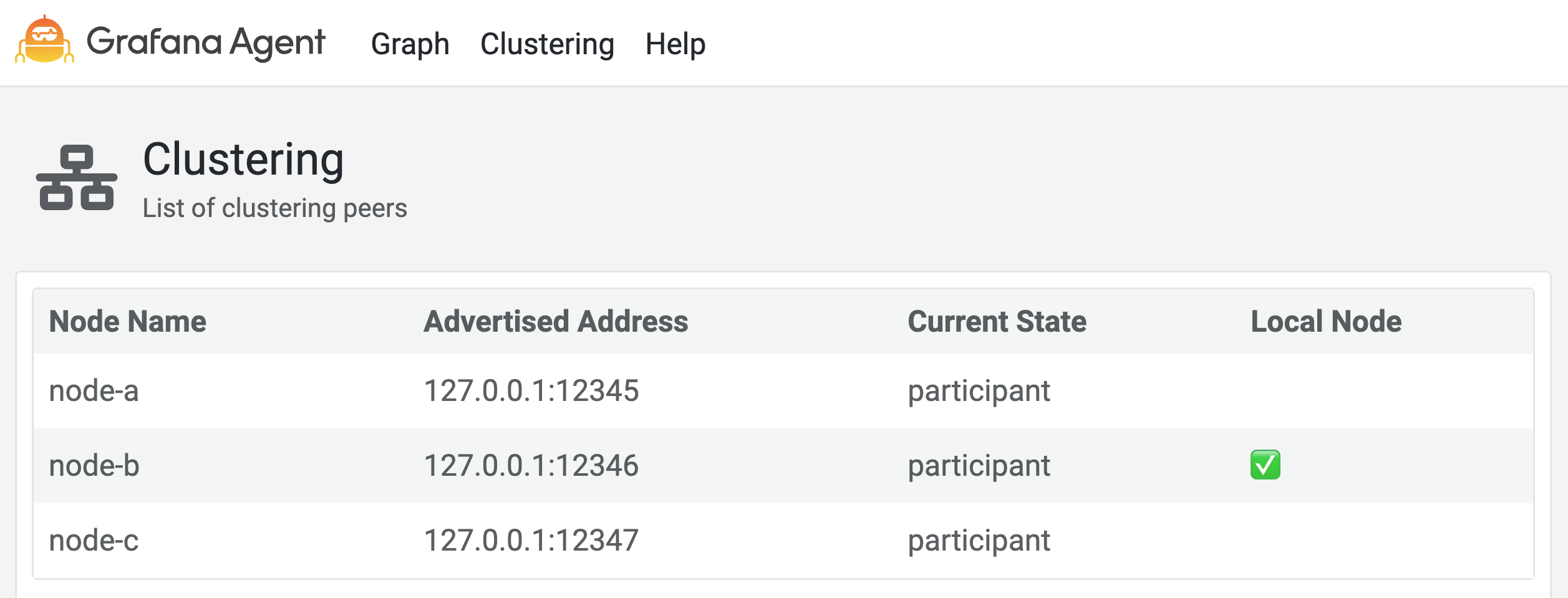
The clustering page shows the following information for each cluster node:
- The node’s name.
- The node’s advertised address.
- The node’s current state (Viewer/Participant/Terminating).
- The local node that serves the UI.
Debugging using the UI
To debug using the UI:
- Ensure that no component is reported as unhealthy.
- Ensure that the arguments and exports for misbehaving components appear correct.
Examining logs
Logs may also help debug issues with Grafana Agent Flow.
To reduce logging noise, many components hide debugging info behind debug-level
log lines. It is recommended that you configure the logging block
to show debug-level log lines when debugging issues with Grafana Agent Flow.
The location of Grafana Agent’s logs is different based on how it is deployed.
Refer to the logging block page to see how to find logs for your
system.
Debugging clustering issues
To debug issues when using clustering, check for the following symptoms.
- Cluster not converging: The cluster peers are not converging on the same view of their peers’ status. This is most likely due to network connectivity issues between the cluster nodes. Use the Flow UI of each running peer to understand which nodes are not being picked up correctly.
- Cluster split brain: The cluster peers are not aware of one another, thinking they’re the only node present. Again, check for network connectivity issues. Check that the addresses or DNS names given to the node to join are correctly formatted and reachable.
- Configuration drift: Clustering assumes that all nodes are running with the same configuration file at roughly the same time. Check the logs for issues with the reloaded configuration file as well as the graph page to verify changes have been applied.
- Node name conflicts: Clustering assumes all nodes have unique names; nodes with conflicting names are rejected and will not join the cluster. Look at the clustering UI page for the list of current peers with their names, and check the logs for any reported name conflict events.
- Node stuck in terminating state: The node attempted to gracefully shut down and set its state to Terminating, but it has not completely gone away. Check the clustering page to view the state of the peers and verify that the terminating Agent has been shut down.